Acute adenoiditis: causes, diagnosis, symptoms and treatment
Learn about acute adenoiditis, a condition characterized by inflammation of the adenoids. Discover the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for this condition.
Acute adenoiditis is a condition characterized by the inflammation of the adenoid glands, which are located at the back of the throat. These glands play a crucial role in the immune system, helping to filter and trap bacteria and viruses that enter through the nose and mouth. When the adenoid glands become infected, they can become swollen and cause a variety of symptoms.
There are several potential causes of acute adenoiditis. The most common cause is a bacterial or viral infection, often resulting from a cold or flu. Other possible causes include allergies, sinus infections, and exposure to irritants such as cigarette smoke. It is more common in children than adults, as their adenoid glands are larger and more active in the immune response.
Diagnosing acute adenoiditis typically involves a physical examination of the throat and nose, as well as a review of the patient’s medical history and symptoms. The doctor may also order additional tests, such as a throat culture or imaging studies, to confirm the diagnosis and determine the underlying cause. Prompt diagnosis is important to ensure appropriate treatment and prevent complications.
The symptoms of acute adenoiditis can vary depending on the severity of the infection, but may include sore throat, difficulty breathing through the nose, snoring, and ear pain or infections. In some cases, it may also cause enlarged adenoids to block the Eustachian tubes, leading to fluid buildup in the middle ear and hearing problems.
Treatment for acute adenoiditis often involves a combination of medication and home care. Antibiotics may be prescribed if the infection is bacterial, while over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage symptoms. Nasal sprays or saline rinses may also be recommended to relieve congestion. In severe cases or when conservative treatments are ineffective, surgery to remove the adenoids may be necessary.
In conclusion, acute adenoiditis is a common condition characterized by inflammation of the adenoid glands. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are essential to relieve symptoms and prevent complications. If you or your child is experiencing symptoms of acute adenoiditis, consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Understanding Acute Adenoiditis: Causes, Diagnosis, Symptoms, and Treatment
Acute adenoiditis is a condition characterized by the inflammation of the adenoids, which are small glands located at the back of the nasal cavity. This condition is most commonly seen in children, but it can also affect adults.
The exact cause of acute adenoiditis is often a viral or bacterial infection. The infection can spread from the nose or throat to the adenoids, causing them to become swollen and painful. Common viruses that can cause acute adenoiditis include the rhinovirus, adenovirus, and influenza virus. Bacterial infections caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Staphylococcus aureus can also lead to acute adenoiditis.
Diagnosing acute adenoiditis involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and sometimes additional tests. The doctor will ask about symptoms such as nasal congestion, difficulty breathing through the nose, snoring, and a sore throat. They will also inspect the throat and nasal passages using a lighted instrument called an otoscope or nasal endoscope.
In some cases, further tests may be needed to confirm the diagnosis. These can include imaging tests like X-rays or computed tomography (CT) scans, which can provide detailed images of the adenoids and surrounding structures. A throat swab may also be taken to check for bacterial infection.
The symptoms of acute adenoiditis can vary depending on the severity of the inflammation. Common symptoms include nasal congestion, difficulty breathing through the nose, snoring, a sore throat, ear pain or pressure, and a persistent cough. In severe cases, the inflammation can lead to complications such as obstructive sleep apnea, middle ear infections, or sinusitis.
Treatment for acute adenoiditis may involve both medical and surgical interventions. Mild cases can often be managed with rest, fluids, and over-the-counter pain relievers. Antibiotics may be prescribed if a bacterial infection is present.
In more severe cases or in recurrent episodes of acute adenoiditis, surgical removal of the adenoids may be recommended. This procedure, known as an adenoidectomy, is typically performed under general anesthesia and involves the complete removal of the adenoids. Adenoidectomy is a safe and effective treatment option that can relieve symptoms and prevent future infections.
In conclusion, acute adenoiditis is a common condition characterized by inflammation of the adenoids. It can cause symptoms such as nasal congestion, difficulty breathing, and sore throat. Diagnosis involves medical history, physical examination, and sometimes additional tests. Treatment may include rest, fluids, pain relievers, and antibiotics. In severe cases, surgical removal of the adenoids may be necessary. If you or your child is experiencing symptoms of acute adenoiditis, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What Causes Acute Adenoiditis?
Acute adenoiditis is primarily caused by a bacterial or viral infection. The adenoids, which are small glands located in the back of the throat, can become infected when bacteria or viruses enter the body through the nose or mouth. Common culprits include the streptococcus bacteria, as well as various strains of the flu and common cold viruses.
Children are more commonly affected by acute adenoiditis due to the fact that their immune systems are still developing. Additionally, the adenoids are larger in children and can therefore become infected more easily. Close proximity in daycare or school settings can also increase the risk of infection spreading among children.
Other factors that can contribute to acute adenoiditis include allergies, sinus infections, and exposure to secondhand smoke. Allergies can cause the adenoids to become inflamed and more susceptible to infection. Sinus infections can also lead to the spread of infection to the adenoids. Exposure to secondhand smoke irritates the respiratory system and weakens the immune response, making individuals more prone to infections such as acute adenoiditis.
In rare cases, acute adenoiditis may be caused by a foreign object becoming lodged in the nasal cavity. This can lead to irritation and infection of the adenoids. It is important to seek medical attention if a foreign object is suspected.
Overall, acute adenoiditis is primarily caused by bacterial or viral infections, with additional risk factors including allergies, sinus infections, exposure to secondhand smoke, and foreign objects in the nasal cavity.
Diagnosing Acute Adenoiditis: Key Indicators and Tests
The diagnosis of acute adenoiditis involves a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and sometimes diagnostic tests. The healthcare provider will look for key indicators and perform specific tests to confirm the diagnosis.
Key Indicators:
- Recurrent or persistent nasal congestion
- Nasal speech or voice changes
- Mouth breathing
- Snoring during sleep
- Frequent ear infections
- Difficulty swallowing
- Poor weight gain in children
Physical Examination:
During the physical examination, the healthcare provider will examine the nasal passages and throat using a lighted instrument called an otoscope. They will also check for enlarged adenoids by gently pressing on the back of the throat.
Diagnostic Tests:
In some cases, diagnostic tests may be performed to further evaluate the adenoids and confirm the diagnosis. These may include:
- X-ray: A lateral neck X-ray can provide a clear image of the adenoids, showing their size and shape.
- Nasal endoscopy: A flexible tube with a light and camera on the end is inserted into the nostrils to visualize the adenoids and surrounding structures.
- Adenoid biopsy: Rarely, a small tissue sample may be taken for laboratory analysis if there are concerns about a more serious condition.
It is important to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment of acute adenoiditis. They will consider the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and the results of any tests to develop an individualized treatment plan.
Identifying Symptoms of Acute Adenoiditis: What to Look Out For
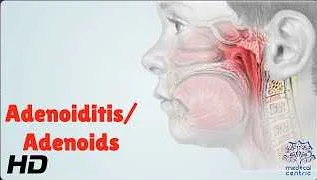
Acute adenoiditis is a condition that affects the adenoids, which are small glands located at the back of the throat. When these glands become infected or inflamed, it can lead to a variety of symptoms that can be both uncomfortable and disruptive.
One of the most common symptoms of acute adenoiditis is a sore throat. This can make it difficult to swallow and can cause discomfort throughout the day. In addition to a sore throat, individuals with acute adenoiditis may also experience difficulty breathing through the nose. This is because the infected adenoids can block the nasal passages, making it harder to breathe.
Another symptom to look out for is a persistent runny nose. This can be accompanied by frequent sneezing and a feeling of congestion in the nasal passages. Additionally, individuals with acute adenoiditis may experience voice changes. Their voice may sound muffled or nasal, and they may have difficulty speaking clearly.
In some cases, acute adenoiditis can also cause ear pain or hearing problems. This is because the adenoids are located close to the Eustachian tubes, which are responsible for equalizing the pressure in the ears. When the adenoids become infected, it can affect the function of the Eustachian tubes, leading to symptoms such as ear pain or temporary hearing loss.
It is important to note that not all individuals will experience the same symptoms, and the severity of symptoms can vary. Additionally, some individuals may not experience any symptoms at all. If you or your child are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.