Understanding Sprains and Other Soft-Tissue Injuries: An Overview
Learn about the different types of sprains and other soft-tissue injuries, including their causes, symptoms, and treatment options. This article provides an overview of these common injuries and offers tips for prevention and recovery.
Sprains and soft-tissue injuries are common occurrences that can happen to anyone, regardless of age or level of physical activity. Whether you’re an athlete or a couch potato, it’s important to know how to properly understand and treat these types of injuries to ensure a quick and successful recovery.
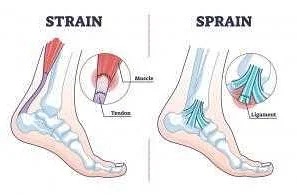
A sprain occurs when the ligaments, which are the tough bands of tissue that connect bones together, are stretched or torn. Soft-tissue injuries, on the other hand, refer to damage that occurs to the muscles, tendons, or other soft tissues in the body. Both of these types of injuries can cause immense pain, swelling, and limited range of motion, making daily activities challenging.
Understanding the severity of a sprain or soft-tissue injury is crucial in determining the best course of treatment. Mild injuries can often be treated at home using the R.I.C.E. method – Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. This involves resting the injured area, applying ice to reduce swelling, using compression to support the injured area, and elevating the affected limb to reduce inflammation.
However, more severe sprains and soft-tissue injuries may require medical intervention. In such cases, it’s important to seek the expertise of a healthcare professional who can properly diagnose the injury and provide a tailored treatment plan. This may include physical therapy, pain management techniques, and in some cases, surgery.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for sprains and soft-tissue injuries, you can take proactive measures to prevent them from occurring or worsening. Additionally, knowing how to properly care for these injuries can speed up the recovery process and help you get back to your normal activities as quickly as possible.
The Basics of Sprains and Soft-Tissue Injuries
Sprains and soft-tissue injuries are common types of injuries that affect the ligaments, tendons, and muscles in the body. These injuries can occur as a result of physical activity, sports injuries, or accidents, and they can range in severity from mild to severe.
When it comes to sprains, they typically occur when a ligament is stretched or torn. Ligaments are tough bands of tissue that connect bones to each other and provide stability to joints. Common areas for sprains include the ankles, knees, and wrists.
Soft-tissue injuries, on the other hand, refer to damage to muscles, tendons, or both. Muscles are responsible for generating force and movement in the body, while tendons connect muscles to bones. Soft-tissue injuries can result from overuse, trauma, or repetitive motion.
Symptoms of sprains and soft-tissue injuries can vary depending on the severity of the injury, but common signs include pain, swelling, bruising, and limited mobility. In severe cases, there may be a loss of function or an inability to bear weight.
Diagnosis of sprains and soft-tissue injuries typically involves a physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans. Treatment options can vary based on the type and severity of the injury, but may include rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), physical therapy, medications, or in some cases, surgery.
Prevention is key when it comes to sprains and soft-tissue injuries. It’s important to warm up before physical activity, wear appropriate protective gear, use proper techniques, and avoid overexertion. Regular exercise, strength training, and maintaining a healthy weight can also help reduce the risk of these injuries.
If you experience a sprain or soft-tissue injury, it’s important to seek medical attention to ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Early intervention and proper management can help promote healing, reduce pain, and restore function.
In conclusion, sprains and soft-tissue injuries are common and can range from mild to severe. Understanding the basics of these injuries, including their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention, is essential for taking appropriate measures to protect and heal the body.
Common Causes of Sprains and Soft-Tissue Injuries
Sprains and soft-tissue injuries are commonly caused by accidents or activities that put stress on the muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Understanding the common causes of these injuries can help you take measures to prevent them. Here are some of the most frequent causes:
- Twisting or turning abruptly: Sudden movements that involve twisting or turning of the body can lead to sprains or soft-tissue injuries. This can occur while playing sports, dancing, or even during everyday activities like walking or climbing stairs.
- Overexertion: Pushing your body beyond its limits can result in sprains and soft-tissue injuries. This can happen when lifting heavy objects, performing repetitive motions, or participating in strenuous physical activities without proper warm-up and conditioning.
- Falling: Falls are a common cause of sprains and soft-tissue injuries, especially when landing awkwardly or on an outstretched hand. This can happen while walking on uneven surfaces, tripping over objects, or during sports and recreational activities.
- Sports injuries: Participating in sports activities, especially high-impact or contact sports, increases the risk of sprains and soft-tissue injuries. This can result from collisions with other players, incorrect form or technique, or sudden movements during gameplay.
- Improper footwear: Wearing ill-fitting or inappropriate footwear can contribute to sprains and soft-tissue injuries. Shoes that lack support or have worn-out soles can increase the risk of accidents and strain on the muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
- Repetitive stress: Engaging in repetitive activities or motions, such as typing, running, or playing musical instruments, can cause sprains and soft-tissue injuries over time. The constant strain on specific muscles, tendons, or ligaments can lead to inflammation and damage.
By being aware of these common causes, you can make informed choices to reduce your risk of sprains and soft-tissue injuries. Always practice proper techniques, use appropriate protective gear, and listen to your body’s signals to prevent such injuries from occurring.
Diagnosis and Assessment of Sprains and Soft-Tissue Injuries
Accurate diagnosis and assessment of sprains and soft-tissue injuries are crucial in determining the appropriate treatment plan and ensuring a successful recovery. Healthcare professionals employ various techniques and tools to identify the extent and severity of these injuries.
One commonly used method is a physical examination, wherein the healthcare provider assesses the affected area for signs of swelling, bruising, tenderness, and limited range of motion. They may also palpate the area to detect any abnormalities or deformities. The patient’s medical history, including previous injuries and underlying conditions, is also taken into consideration during this process.
Imaging tests, such as X-rays, are often utilized to rule out fractures and assess the integrity of the bones in the affected area. X-rays are effective in identifying bone-related injuries but may not provide detailed information about soft tissues. In cases where soft-tissue injuries are suspected, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans may be recommended. MRI scans offer a comprehensive view of the soft tissues, including ligaments, tendons, and muscles, allowing healthcare professionals to accurately diagnose and assess the extent of the injury.
In some instances, diagnostic injections may be used to confirm the source of pain and inflammation. These injections involve injecting a local anesthetic or contrast material into the affected area, providing temporary relief and helping healthcare professionals pinpoint the exact location of the injury.
Another useful tool for diagnosing and assessing sprains and soft-tissue injuries is ultrasound imaging. Ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the muscles, ligaments, tendons, and other soft tissues. This non-invasive technique allows healthcare professionals to visualize the injury and assess the damage in real-time, aiding in the development of an appropriate treatment plan.
Overall, accurate diagnosis and assessment of sprains and soft-tissue injuries are crucial for providing effective and targeted treatment. By carefully evaluating the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and utilizing various diagnostic tools, healthcare professionals can develop personalized treatment plans that promote optimal recovery and help patients regain their functionality.
Effective Treatment Options for Sprains and Soft-Tissue Injuries
When it comes to sprains and soft-tissue injuries, there are various treatment options available that can help relieve pain and promote healing. The specific treatment plan will depend on the severity and location of the injury, as well as the individual’s overall health and medical history. Here are some effective treatment options to consider:
| Rest | One of the most important aspects of healing a sprain or soft-tissue injury is rest. It allows the body to begin the healing process and prevents further damage to the affected area. Resting the injured area may involve avoiding certain activities or using crutches or a brace for support. |
| Ice | Applying ice to the injured area can help reduce swelling and inflammation. Ice should be applied for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day, for the first few days after the injury. It is important to wrap the ice pack in a thin towel to protect the skin. |
| Compression | Compression is an effective way to control swelling and provide support to the injured area. This can be done by using an elastic bandage or compression wrap. It is important not to wrap too tightly, as it can restrict blood flow. |
| Elevation | Raising the injured limb above heart level can help reduce swelling by allowing fluids to drain away from the injured area. This can be done by propping up the limb with pillows or using a sling or cradle. |
| Physical Therapy | In many cases, physical therapy is recommended to help improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected area. A physical therapist can provide specific exercises and techniques to aid in the recovery process. |
| Medications | In some cases, over-the-counter or prescription medications may be used to manage pain and reduce inflammation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often recommended for pain relief. |
| Bracing or Splinting | In more severe cases or when there is instability in the affected area, bracing or splinting may be necessary. This provides added support and protection during the healing process. |
| Surgery | In rare cases, surgery may be required to repair severe sprains or soft-tissue injuries. This is typically reserved for cases where conservative treatment options have been unsuccessful or for injuries that involve significant damage to surrounding structures. |
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan for sprains and soft-tissue injuries. Following the recommended treatment options can help speed up the healing process and prevent long-term complications.