Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Symptoms, Treatment
Содержимое
Learn about the symptoms and treatment options for carpal tunnel syndrome, a condition that causes pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and arm. Find out how to manage the symptoms and prevent further damage.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common condition that affects the hand and wrist. It occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm to the hand through a narrow space called the carpal tunnel, becomes compressed or squeezed. CTS can cause pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and fingers. It can also affect grip strength and dexterity, making everyday tasks difficult.
The symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome usually develop gradually and can vary from person to person. Some common signs include pain and numbness in the thumb, index, middle, and ring fingers. This discomfort can radiate up the forearm and may be more noticeable at night. People with CTS may also experience weakness in the hand and a tendency to drop objects.
Treatment options for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome depend on the severity of the symptoms. In mild cases, simple lifestyle modifications can provide relief. These include taking regular breaks from activities that require repetitive hand movements, avoiding positions that bend the wrist for prolonged periods, and wearing wrist splints to keep the wrist in a neutral position.
For more severe cases, medical intervention may be necessary. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation. Physical therapy exercises can strengthen the hand and wrist, improving function and reducing symptoms. In some cases, corticosteroid injections or surgery may be recommended to relieve pressure on the median nerve.
Prevention is key when it comes to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Maintaining good posture, taking regular breaks, and practicing hand and wrist stretches can help reduce the risk of developing CTS. It’s also important to use proper ergonomics when working or performing repetitive tasks. By being mindful of hand and wrist health, individuals can minimize their chances of experiencing the discomfort and limitations associated with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: What You Need to Know
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a condition that affects the hand and wrist. It occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm to the hand through a narrow passage called the carpal tunnel, becomes compressed or irritated.
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome include numbness, tingling, and pain in the hand and fingers. These symptoms can be felt in the thumb, index finger, middle finger, and part of the ring finger. Some people may also experience weakness in the hand and a dropping sensation of objects.
Treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome usually begins with conservative methods, such as resting the hand and wrist, wearing a splint, and taking over-the-counter pain medications. If these methods do not provide relief, a doctor may recommend corticosteroid injections or surgery to relieve pressure on the median nerve.
Prevention is key when it comes to carpal tunnel syndrome. It is important to maintain a good ergonomic posture while working, take frequent breaks to rest the hands and wrists, and perform stretching exercises to keep the muscles and tendons flexible. Using proper techniques and tools, such as ergonomic keyboards and mouse pads, can also help prevent carpal tunnel syndrome.
In conclusion, carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition that affects the hand and wrist. It is important to be aware of the symptoms, seek treatment if necessary, and take preventive measures to avoid the development or worsening of carpal tunnel syndrome. By taking care of our hands and wrists, we can maintain their health and functionality for years to come.
Understanding Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
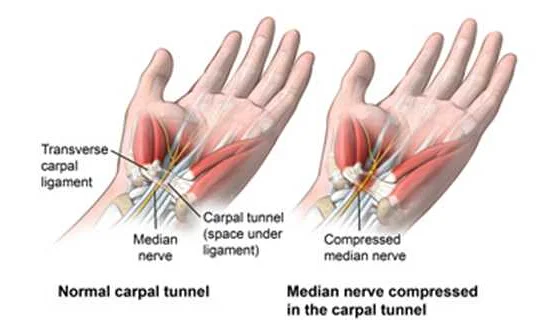
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a common condition that affects the hand and wrist. It occurs when the median nerve, which runs through the carpal tunnel in the wrist, becomes compressed or squeezed. This compression can cause a variety of symptoms, including pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand and fingers.
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. These can include repetitive hand movements, such as typing or using a mouse, as well as certain medical conditions like diabetes, arthritis, and thyroid disorders. Additionally, hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy, can also increase the risk of developing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
The symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome can vary from person to person, but some common signs to look out for include pain or discomfort in the hand or wrist, tingling or numbness in the fingers (especially the thumb, index, and middle fingers), and weakness in the hand or a tendency to drop things. These symptoms may start gradually and worsen over time.
If you suspect you may have Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, it is important to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can diagnose the condition through a physical examination, as well as by conducting nerve tests or imaging studies. Treatment for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome may include lifestyle changes, such as taking breaks from activities that may aggravate the condition, using ergonomic tools and equipment, and wearing a wrist splint at night.
In more severe cases, medication or corticosteroid injections may be recommended to reduce inflammation and relieve symptoms. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the median nerve and improve symptoms. However, surgery is typically considered a last resort and is only recommended if other treatment options have not been effective.
To prevent Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, it is important to take breaks from repetitive hand movements, maintain good posture, and use ergonomic equipment whenever possible. Stretching and strengthening exercises for the hands and wrists can also help to prevent the condition. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing underlying medical conditions, and avoiding excessive weight gain can reduce the risk of developing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
In conclusion, Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a common condition that can cause pain, numbness, and weakness in the hand and wrist. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options can help individuals manage the condition and prevent further complications.
Recognizing the Symptoms
If you have been experiencing any of the following symptoms, you may be suffering from carpal tunnel syndrome:
- Numbness or tingling in the thumb, index finger, middle finger, or ring finger
- Weakness in the hand or difficulty gripping objects
- Pain or aching in the wrist or forearm
- Burning sensation or swelling in the hand or fingers
- Difficulty with fine motor skills, such as buttoning a shirt or gripping a pen
It is important to recognize these symptoms early on to seek proper treatment and prevent further damage. If you suspect you may have carpal tunnel syndrome, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
When it comes to treating carpal tunnel syndrome, there are several options available. The best treatment approach will depend on the severity of the symptoms and the individual’s specific needs. Here are some common treatment options:
1. Rest and immobilization: In mild cases of carpal tunnel syndrome, resting the affected hand and avoiding activities that worsen the symptoms may be enough to relieve the pain and discomfort. Immobilizing the hand with a splint or brace can also help to reduce pressure on the median nerve.
2. Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be used to reduce inflammation and relieve pain associated with carpal tunnel syndrome. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be recommended to provide temporary relief from symptoms.
3. Physical therapy: A physical therapist can help to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the wrist and hand. They may also recommend specific exercises and stretches to relieve symptoms and prevent further damage.
4. Splinting: Wearing a splint or brace at night can help to keep the wrist in a neutral position, reducing pressure on the median nerve and relieving symptoms. Splinting may also be recommended for certain activities or during periods of rest.
5. Ergonomic modifications: Making changes to the workspace and equipment can help to reduce strain on the wrists and hands. This may include using an ergonomic keyboard and mouse, adjusting the height and position of the desk and chair, and taking regular breaks to stretch and rest the hands.
6. Surgery: In severe cases of carpal tunnel syndrome where other treatments have failed to provide relief, surgery may be recommended. The procedure involves releasing the pressure on the median nerve by cutting the ligament that forms the roof of the carpal tunnel.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment approach for your specific case of carpal tunnel syndrome. They will be able to assess your symptoms, recommend appropriate treatment options, and provide guidance on managing and preventing the condition in the long term.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome can be prevented or minimized through certain lifestyle changes. By incorporating these changes into your daily routine, you can reduce the risk of developing this condition.
Here are some lifestyle changes that can help prevent Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
- Ergonomics: Maintain proper ergonomics at your workplace and home. Use ergonomic keyboards, chairs, and desks that promote a neutral wrist position. Adjust your chair height and monitor height to maintain proper posture.
- Take Breaks: Take regular breaks from repetitive hand movements. Stretch your hands and fingers during these breaks to relieve tension and promote blood circulation.
- Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to strengthen your muscles and improve overall flexibility. Focus on exercises that target the wrists, hands, and fingers.
- Avoid Repetitive Movements: Try to avoid or minimize repetitive hand movements, especially those that involve force or vibration. If your job requires repetitive actions, consider using assistive devices or tools to reduce strain.
- Practice Good Posture: Maintain good posture while sitting or standing. Avoid slouching or hunching over, as this can put unnecessary pressure on your wrists and hands.
- Manage Weight: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce the pressure on your wrists and hands. Excess weight can increase the risk of developing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
- Avoid Tight Gripping: Avoid gripping objects too tightly, as this can put strain on the muscles and tendons in your hands and wrists. Use tools or equipment with padded handles or ergonomic grips.
- Warm-up and Stretch: Before engaging in any activities that involve repetitive hand movements, warm up your hands and stretch your fingers and wrists. This can help prevent muscle strain and promote flexibility.
- Use Proper Technique: When performing tasks that require manual dexterity, use proper technique to minimize strain on your wrists and hands. Avoid bending or twisting your wrists excessively.
By implementing these lifestyle changes, you can reduce the risk of developing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and improve overall hand and wrist health.