Causes of Shortness of Breath: Heart Problems and Blood Clots in the Lungs
Learn about the causes of shortness of breath, including heart problems and blood clots in the lungs, and why it is important not to ignore these symptoms. Understand the potential risks and seek medical attention if you experience difficulty breathing.
Shortness of breath, also known as dyspnea, is a common symptom that can be caused by various underlying conditions. In some cases, it may indicate a serious issue related to the heart or the lungs. Understanding the causes of shortness of breath is crucial in order to receive appropriate medical attention and treatment.
Heart problems can often lead to shortness of breath. When the heart is not functioning properly, it may struggle to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. This can result in fluid accumulation in the lungs, causing difficulty in breathing. Conditions such as heart failure, coronary artery disease, and arrhythmias can contribute to this symptom. If you experience sudden or worsening shortness of breath, it is important to seek medical help as it may be a sign of a heart problem that requires immediate attention.
Another potential cause of shortness of breath is blood clots in the lungs, also known as pulmonary embolism. Blood clots can form in the deep veins of the legs or pelvis and travel to the lungs, obstructing blood flow. This can lead to symptoms such as sudden onset of shortness of breath, chest pain, and coughing up blood. Pulmonary embolism is a medical emergency and should be treated as such. If you suspect a blood clot in your lungs, it is vital to seek immediate medical assistance to prevent further complications.
Shortness of breath should never be ignored, as it can be a sign of a serious underlying condition. Whether it is related to heart problems or blood clots in the lungs, seeking prompt medical attention is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Your doctor will evaluate your symptoms, perform relevant tests, and develop a plan to address the underlying cause of your shortness of breath.
Understanding Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath, also known as dyspnea, is a common symptom that can be caused by various underlying conditions. It is characterized by a feeling of difficulty or discomfort in breathing, often accompanied by a rapid or shallow breathing pattern. While shortness of breath can be a normal response to physical exertion or intense emotions, persistent or recurrent episodes may indicate an underlying health problem.
There are several potential causes of shortness of breath, including heart problems and blood clots in the lungs. Heart conditions such as congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, and arrhythmias can affect the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively, leading to fluid buildup in the lungs and subsequent breathlessness.
Blood clots in the lungs, known as pulmonary embolisms, can also cause shortness of breath. These clots typically originate from deep veins in the legs and travel to the lungs, where they can block blood flow and impair oxygen exchange. This can result in sudden onset of breathlessness, chest pain, and a rapid heart rate.
In addition to heart problems and blood clots, other potential causes of shortness of breath include lung diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, pneumonia, and lung cancer. Anemia, which is a deficiency in red blood cells or hemoglobin, can also lead to decreased oxygen-carrying capacity and subsequent breathlessness.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or worsening shortness of breath, as it can be a sign of a serious underlying condition. Your healthcare provider will perform a thorough evaluation to determine the cause of your symptoms and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
If you are experiencing sudden, severe shortness of breath accompanied by chest pain, dizziness, or fainting, call emergency services immediately.
In conclusion, shortness of breath is a symptom that should not be ignored. It can be a sign of various health problems, including heart issues and blood clots in the lungs. Understanding the potential causes of shortness of breath can help you recognize when to seek medical attention and receive appropriate treatment.
Heart Problems Causing Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath can be a symptom of various heart problems. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygen-rich blood to the body’s tissues, and if it is not functioning properly, it can lead to a lack of oxygen and shortness of breath.
One common heart problem that can cause shortness of breath is heart failure. In heart failure, the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. This can lead to fluid buildup in the lungs, which can make it difficult to breathe.
Another heart problem that can result in shortness of breath is coronary artery disease. This occurs when the arteries that supply blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked, reducing the amount of oxygen-rich blood that reaches the heart. This can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, and other symptoms.
Heart valve disease is yet another heart problem that can cause shortness of breath. When a heart valve doesn’t function properly, it can interfere with the flow of blood through the heart. This can lead to a buildup of fluid in the lungs and difficulty breathing.
Lastly, arrhythmias, or abnormal heart rhythms, can also cause shortness of breath. When the heart beats too fast or too slow, it may not be able to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs, resulting in shortness of breath.
| Heart Failure | Fluid buildup in the lungs, fatigue, swelling in the legs |
| Coronary Artery Disease | Chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue |
| Heart Valve Disease | Shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling in the legs, rapid weight gain |
| Arrhythmias | Fluttering in the chest, rapid heartbeat, lightheadedness |
If you are experiencing shortness of breath, it is important to see a healthcare professional for an evaluation. They can determine the underlying cause and provide appropriate treatment.
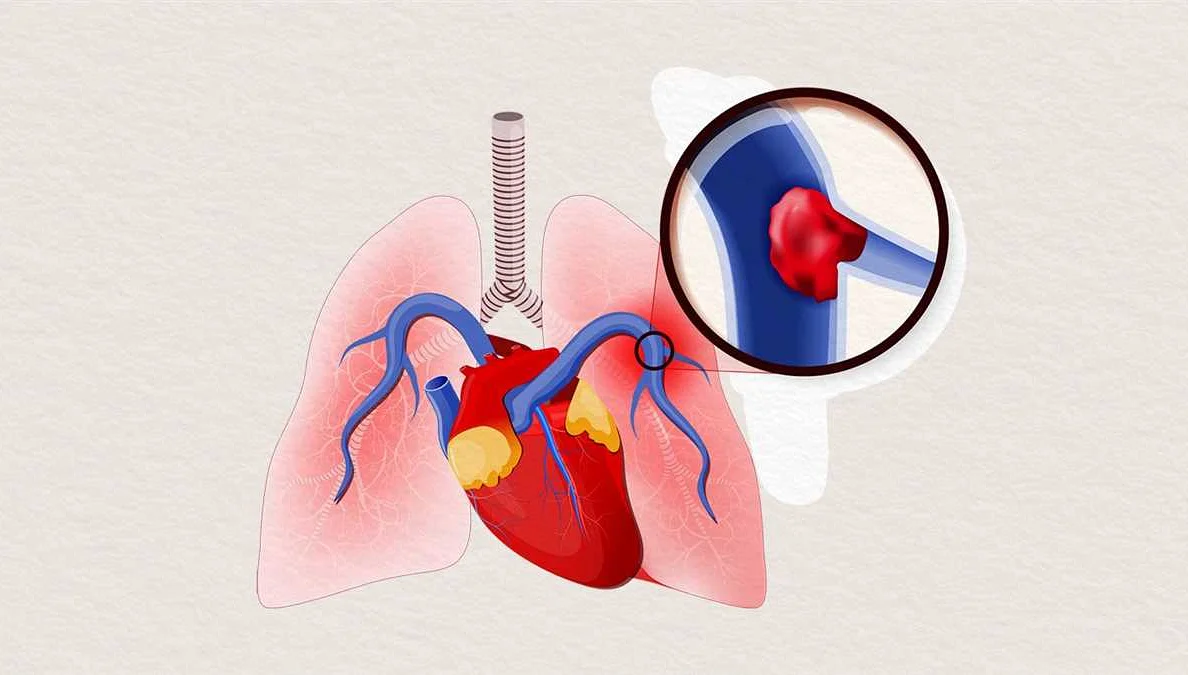
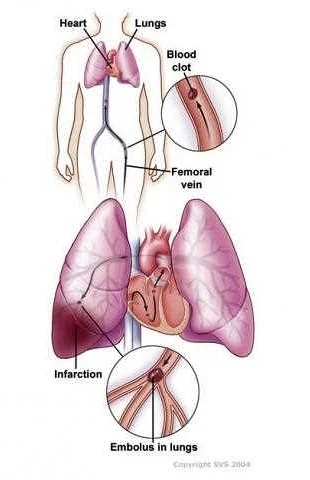
Blood Clots in the Lungs and Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath can be caused by various factors, one of which is blood clots in the lungs. A blood clot, also known as a pulmonary embolism, occurs when a clot forms in one of the blood vessels in the lungs. This can be a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
When a blood clot forms in the lungs, it can block the flow of blood and oxygen to the tissues, leading to difficulty in breathing. The most common symptoms of a blood clot in the lungs include sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, coughing up blood, and a rapid heart rate.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical help right away. A healthcare professional can perform tests, such as a CT scan or a pulmonary angiogram, to confirm the presence of a blood clot in the lungs.
Treatment for blood clots in the lungs usually involves the use of blood thinners to prevent further clot formation and to help dissolve the existing clot. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the clot.
Prevention of blood clots in the lungs can be achieved by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, quitting smoking, and managing any underlying medical conditions that increase the risk of blood clots.
In conclusion, blood clots in the lungs can cause shortness of breath and other symptoms that require immediate medical attention. It is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of a blood clot in the lungs and to seek medical help if they occur.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional if you have any concerns or questions about your health.
Common Symptoms of Shortness of Breath
Shortness of breath, also known as dyspnea, can present itself with various symptoms. These symptoms may vary depending on the underlying cause of the condition. However, there are some common signs to look out for:
Rapid or shallow breathing: People experiencing shortness of breath may breathe faster than usual or take shallow breaths.
Tightness in the chest: Shortness of breath can be accompanied by a feeling of tightness or discomfort in the chest.
Wheezing: Some individuals may experience a high-pitched whistling sound when breathing.
Coughing: Shortness of breath can be associated with coughing, especially if it is persistent or accompanied by mucus.
Lightheadedness or dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or dizzy can be a result of inadequate oxygen supply to the brain due to shortness of breath.
Fatigue: Shortness of breath can cause fatigue and a general feeling of weakness.
Anxiety: Feeling anxious or panicky is a common symptom of shortness of breath.
Bluish lips or fingertips: In severe cases, a bluish discoloration of the lips or fingertips may occur, indicating a lack of oxygen.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
When experiencing shortness of breath, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. The healthcare provider will begin by taking a detailed medical history and conducting a physical examination. They may also recommend the following diagnostic tests:
- Chest X-ray: This test provides an image of the heart and lungs and can help identify any issues, such as an enlarged heart or fluid in the lungs.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This non-invasive test records the electrical activity of the heart and can detect any abnormalities, such as irregular heart rhythms.
- Echocardiogram: This test uses ultrasound waves to create images of the heart, allowing healthcare providers to assess its structure and function.
- Pulmonary function tests: These tests evaluate lung function and can help determine if shortness of breath is due to a lung-related problem.
- Cardiac stress tests: These tests measure the heart’s response to physical activity and can help diagnose heart-related causes of shortness of breath.
- Blood tests: Certain blood tests can provide information about heart and lung function, as well as rule out other potential causes for shortness of breath.
Once a diagnosis is made, the healthcare provider will recommend appropriate treatment options. The specific treatment will depend on the underlying cause of shortness of breath, but common options include:
- Medications: In cases where heart problems or blood clots are causing shortness of breath, medications to manage these conditions may be prescribed.
- Oxygen therapy: If shortness of breath is severe, supplemental oxygen may be administered to help improve oxygen levels in the blood.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation: This program includes breathing exercises, physical activity, and education to improve lung function and manage shortness of breath.
- Lifestyle changes: Making changes to diet, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight can help improve heart and lung health, reducing the severity of shortness of breath.
- Surgery or procedures: In some cases, surgical interventions or procedures may be necessary to treat underlying heart or lung conditions causing shortness of breath.
It is important to follow the healthcare provider’s recommendations and attend regular follow-up appointments to ensure optimal management of shortness of breath and prevention of complications.