Chief Pediatrician of the North-West: Childhood Diseases from Improper Food and Water
Содержимое
Learn from the chief pediatrician of the North-West about the link between improper food and water and childhood diseases. Discover how to keep your child healthy with proper nutrition and hydration.
As the Chief Pediatrician of the North-West region, I have seen firsthand the detrimental impact that improper food and water can have on the health of our children. It is a growing concern that needs to be addressed urgently. In this article, we will explore the various childhood diseases that are caused by consuming contaminated or unhealthy food and water.
Food and water play a crucial role in the growth and development of children. However, when they are contaminated with harmful bacteria, viruses, or toxins, they can lead to serious health problems. One of the most common diseases caused by improper food and water is food poisoning. This occurs when children consume food that is contaminated with bacteria such as Salmonella or E. coli. The symptoms of food poisoning include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach cramps.
In addition to food poisoning, contaminated water can also cause diseases such as dysentery and cholera. These diseases are characterized by severe diarrhea, dehydration, and can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. It is important for parents to ensure that the water their children consume is clean and safe, especially in areas where the water supply might be compromised.
Furthermore, improper food and water can also lead to malnutrition in children. When children do not receive the necessary nutrients from their food, their growth and development can be stunted. Malnutrition weakens the immune system, making children more susceptible to infections and diseases. It is crucial for parents to provide a balanced and nutritious diet for their children to prevent malnutrition.
In conclusion, the impact of improper food and water on childhood health cannot be underestimated. It is essential for parents, caregivers, and authorities to take the necessary steps to ensure that children have access to clean and healthy food and water. By doing so, we can protect our children from the various diseases that are caused by consuming contaminated or unhealthy food and water.
Food Poisoning and Gastrointestinal Infections
Food poisoning and gastrointestinal infections are common childhood diseases caused by improper food and water consumption. These conditions occur when harmful bacteria, viruses, or parasites enter the body through contaminated food or water.
Food poisoning can range from mild discomfort to severe illness. Symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. In some cases, dehydration and other complications can occur.
Gastrointestinal infections, also known as gastroenteritis, are characterized by inflammation of the stomach and intestines. This can result in symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and fever. Gastrointestinal infections can be caused by various pathogens, including norovirus, rotavirus, salmonella, and E. coli.
Preventing food poisoning and gastrointestinal infections requires proper food handling and hygiene practices. This includes washing hands before and after preparing food, cooking food thoroughly, and storing perishable items at proper temperatures.
If a child shows symptoms of food poisoning or a gastrointestinal infection, it is important to seek medical attention. Treatment may involve fluid replacement to prevent dehydration, medication to alleviate symptoms, and rest to allow the body to recover.
By following proper food safety guidelines and maintaining good hygiene practices, parents can help protect their children from food poisoning and gastrointestinal infections.
Allergies and Intolerances
Allergies and intolerances to certain foods can cause a range of symptoms in children. An allergy occurs when the immune system reacts negatively to a specific food, resulting in symptoms such as hives, swelling, vomiting, or difficulty breathing. On the other hand, intolerances occur when the body has difficulty digesting a particular food, leading to symptoms like bloating, diarrhea, or stomach pain.
Common food allergies in children include peanuts, milk, eggs, soy, and wheat. These allergies can be diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and allergy testing. Once diagnosed, it is important to strictly avoid the allergenic food to prevent severe allergic reactions.
Food intolerances, such as lactose intolerance, can also cause discomfort in children. Lactose intolerance occurs when the body lacks the enzyme lactase, which is needed to digest lactose, the sugar found in milk and dairy products. Symptoms of lactose intolerance may include bloating, diarrhea, and gas.
If your child is experiencing symptoms of a food allergy or intolerance, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and management. They can provide guidance on how to avoid the specific allergenic or intolerant food and may recommend alternative dietary choices or supplements.
Additionally, it is crucial to educate children, parents, and caregivers about food allergies and intolerances to ensure their safety. This includes teaching them how to read food labels, recognize common allergens, and understand the importance of informing others about their condition.
Remember, early diagnosis and management of allergies and intolerances can significantly improve a child’s quality of life and help prevent potentially life-threatening reactions. Proper monitoring and education are essential in keeping our children safe and healthy.
Vitamin and Mineral Deficiencies
Proper nutrition is essential for the healthy growth and development of children, and vitamin and mineral deficiencies can have serious consequences. These deficiencies occur when a child’s diet lacks the necessary vitamins and minerals that are required for their optimal health.
Some common deficiencies in children include:
- Vitamin D deficiency: Lack of exposure to sunlight and inadequate intake of vitamin D-rich foods can lead to weakened bones and an increased risk of conditions like rickets.
- Vitamin C deficiency: Insufficient intake of fruits and vegetables can result in weakened immune system function and an increased susceptibility to infections.
- Iron deficiency: Iron is crucial for the production of red blood cells and overall growth. A deficiency can lead to anemia, fatigue, and impaired cognitive development.
- Vitamin A deficiency: Lack of vitamin A can cause poor vision, increased susceptibility to infections, and growth stunting.
- Iodine deficiency: Inadequate intake of iodine can result in impaired brain development and growth, leading to intellectual disabilities.
Preventing and addressing vitamin and mineral deficiencies in children requires a well-balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods. Healthcare providers may also recommend vitamin and mineral supplements in certain cases.
Parents and caregivers play a crucial role in ensuring that children receive adequate nutrition. Regular check-ups with a pediatrician can help monitor a child’s growth and development and identify any potential deficiencies early on.

Dehydration occurs when the body loses more water than it takes in. It can happen when a child does not drink enough fluids or when they lose a large amount of fluid through sweating. This can be especially common during hot weather or when a child is physically active.
Dehydration can lead to various heat-related illnesses, including heat cramps, heat exhaustion, and heatstroke. Heat cramps are muscle cramps that are often caused by heavy sweating and dehydration. They usually occur in the legs, arms, or abdomen and can be very painful.
Heat exhaustion is a more severe form of dehydration and can occur when the body is unable to cool itself down. Symptoms of heat exhaustion may include heavy sweating, dizziness, weakness, nausea, and headache.
Heatstroke is the most serious heat-related illness and can be life-threatening. It occurs when the body’s temperature regulation system fails, and the body temperature rises to a dangerous level. Symptoms of heatstroke may include a high body temperature, rapid heartbeat, confusion, and loss of consciousness.
Preventing dehydration and heat-related illnesses is essential, especially in children. It is important for children to drink plenty of fluids, especially water, to stay hydrated. Encouraging children to rest in a cool and shaded area, wearing light and loose-fitting clothing, and using sunscreen can also help prevent heat-related illnesses.
If a child shows symptoms of dehydration or any of the heat-related illnesses, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately. Prompt treatment can prevent complications and ensure a faster recovery.
Remember: Prevention is key when it comes to dehydration and heat-related illnesses. Stay hydrated, stay cool, and stay safe!
Obesity and Malnutrition
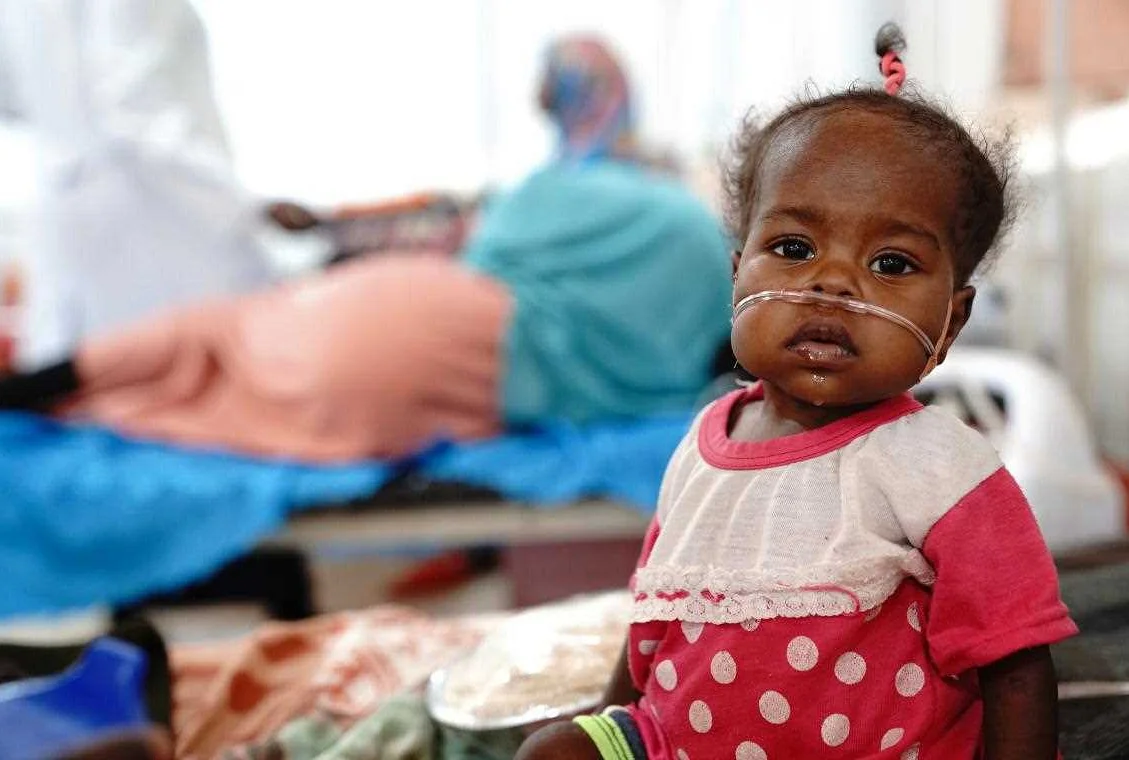
Obesity and malnutrition are two major problems that affect children’s health around the world. While they may seem like opposite ends of the spectrum, both conditions are linked to improper food intake.
Obesity occurs when a child consumes more calories than they burn, leading to an excess accumulation of fat in the body. This can be the result of consuming high-calorie, low-nutrient foods such as fast food, sugary drinks, and processed snacks. Lack of physical activity also plays a significant role in the development of obesity.
On the other hand, malnutrition occurs when a child does not receive adequate nutrients from their diet. This can be due to a lack of access to healthy and nutritious foods or an unbalanced diet. Malnutrition can lead to stunted growth, weakened immune system, and cognitive development issues.
Both obesity and malnutrition have serious long-term consequences for children’s health. Obesity increases the risk of developing chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and certain types of cancer. Malnutrition can impair a child’s physical and mental development, making them more susceptible to infections and diseases.
It is crucial for parents and caregivers to provide their children with a balanced and nutritious diet. This means including a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in their meals. Limiting the consumption of sugary beverages and processed foods is also important.
Preventing childhood obesity and malnutrition requires a multi-faceted approach. Education about healthy eating habits and the importance of physical activity should be promoted in schools and communities. Access to affordable and nutritious food should be improved, especially in underserved areas.
In conclusion, obesity and malnutrition are interconnected problems that stem from improper food intake. By addressing these issues and promoting healthy eating habits, we can ensure the well-being of our children and future generations.