Ectoparasites: Understanding and Removing Parasites on the Body
Содержимое
Learn about ectoparasites, which are parasites that live on the surface of the body of humans and animals. Discover effective methods to get rid of these parasites and protect yourself and your pets from infestations.
Ectoparasites are organisms that live on the outer surface of their hosts, feeding on blood or tissue. They can be found on both humans and animals and can cause a range of health problems. Understanding the different types of ectoparasites, as well as how to prevent and treat infestations, is crucial for maintaining the well-being of both ourselves and our beloved pets.
There are several types of ectoparasites that commonly affect humans and animals. Fleas, ticks, lice, and mites are among the most common. Fleas, for example, are small insects that feed on the blood of their hosts and can cause severe itching and skin irritation. Ticks, on the other hand, are arachnids that can transmit diseases such as Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
Preventing ectoparasite infestations is key to protecting ourselves and our pets. Regular grooming, such as brushing and bathing, can help remove and prevent the buildup of ectoparasites. Additionally, using preventive medications and products specifically designed to repel or kill ectoparasites can greatly reduce the risk of infestation. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or veterinarian to determine the most suitable preventive measures for you and your pets.
If an infestation does occur, prompt treatment is essential to minimize the discomfort and health risks associated with ectoparasites. Treatment options vary depending on the type of ectoparasite and the severity of the infestation. Medications, shampoos, and topical treatments are commonly used to kill and remove ectoparasites. It is crucial to follow the instructions provided by healthcare professionals or veterinarians to ensure effective treatment and prevent re-infestation.
Conclusion
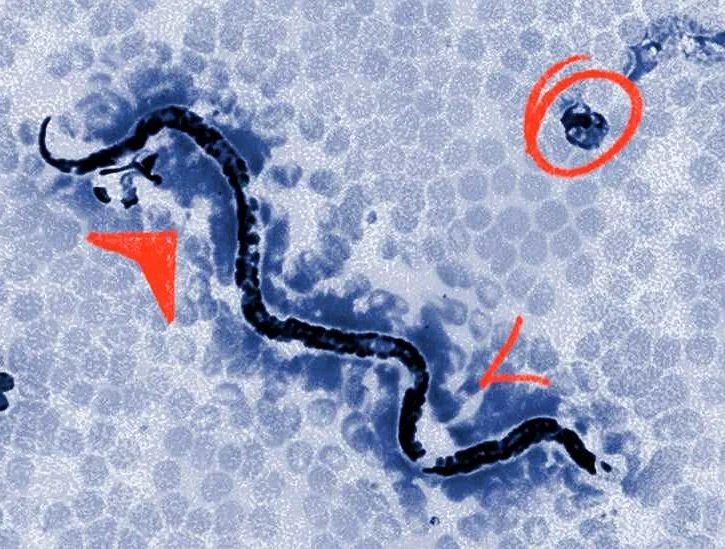
Ectoparasites can pose a significant threat to the health and well-being of humans and animals. Understanding the different types of ectoparasites, implementing preventive measures, and seeking prompt treatment can help protect ourselves and our beloved pets from the discomfort and potential health risks associated with infestations. Remember to consult with healthcare professionals or veterinarians for personalized advice and guidance on preventing and treating ectoparasites.
What are Ectoparasites?
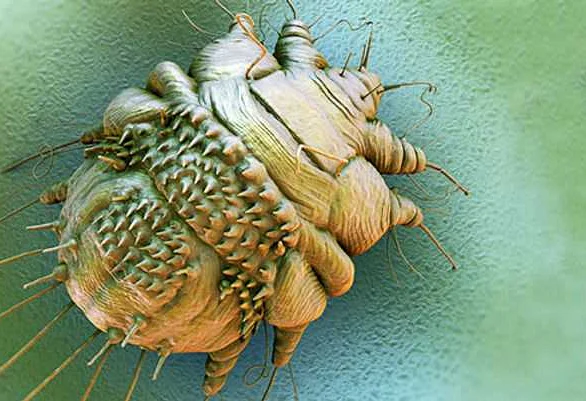
Ectoparasites are organisms that live on the external surfaces of other organisms, known as hosts, and derive their nutrients by feeding on the host’s blood or tissue. These parasites can infest both humans and animals, causing a range of health problems including skin irritation, allergic reactions, and the transmission of diseases.
There are various types of ectoparasites, including fleas, ticks, lice, and mites. Each type of ectoparasite has its own unique characteristics and methods of infestation. For example, fleas are small wingless insects that can jump long distances and infest both pets and humans. Ticks, on the other hand, are arachnids that attach themselves to the host’s skin and feed on blood.
Ectoparasites can be found in different environments, such as in the home, outdoors, or in natural habitats. They can be introduced into an environment through contact with infested animals or through exposure to infested areas. Once introduced, ectoparasites can quickly multiply and spread, making it important to take preventative measures to avoid infestations.
Preventing ectoparasites involves a combination of personal hygiene practices and environmental management. Regular bathing, grooming, and cleaning of pets can help prevent infestations, as well as keeping the living areas clean and free of clutter. In addition, using appropriate insect repellents and wearing protective clothing when venturing into infested areas can help reduce the risk of ectoparasite bites.
Treatment for ectoparasite infestations typically involves a combination of topical medications, oral medications, and environmental control measures. Medications may need to be administered to both the affected individuals and their living areas to ensure effective eradication of the parasites. It is important to follow the instructions provided by healthcare professionals or veterinarians when treating ectoparasite infestations.
| Fleas | Pets, humans | Jumping |
| Ticks | Pets, humans, wildlife | Attaching and biting |
| Lice | Humans, animals | Direct contact |
| Mites | Humans, animals | Direct contact |
Common Types of Ectoparasites
Ectoparasites are organisms that live on the outer surface of a host organism. They can cause various diseases and discomfort in both humans and animals. Here are some common types of ectoparasites:
| Fleas | Humans, cats, dogs, rodents | Flea allergy dermatitis, flea-borne diseases (e.g., tularemia) |
| Ticks | Humans, dogs, cats, livestock, wildlife | Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, tick-borne encephalitis |
| Lice | Humans, primates, livestock, birds | Pediculosis, typhus, trench fever |
| Mites | Humans, dogs, cats, livestock | Scabies, mange, ear mites |
| Bedbugs | Humans, bats, birds | Bedbug bites, allergic reactions |
| Mosquitoes | Humans, animals | Malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus |
These ectoparasites can be prevented and treated through various methods, including regular grooming, use of flea and tick preventatives, and practicing good hygiene.
How to Prevent Ectoparasite Infestation
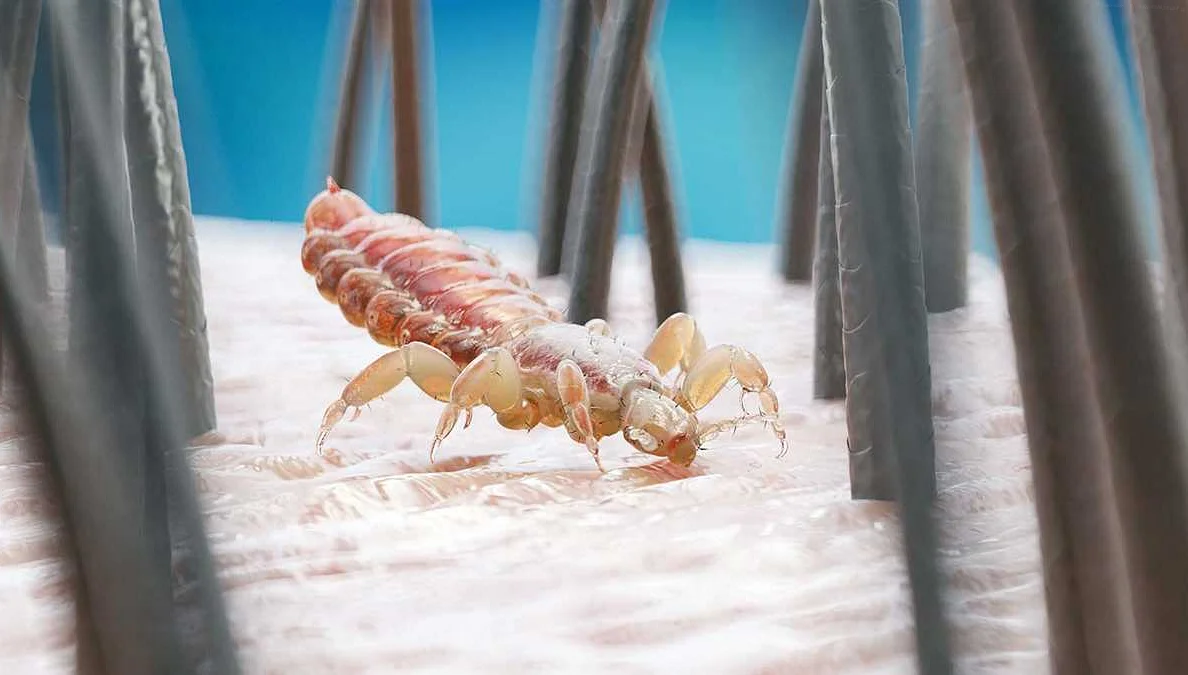

Preventing ectoparasite infestation is crucial for the well-being of both humans and animals. Here are some effective measures that can help prevent ectoparasite infestations:
1. Regular Cleaning: Keeping your living space clean and tidy is essential in preventing ectoparasite infestations. Vacuuming regularly, washing bedding and curtains, and cleaning pets’ resting areas can help eliminate potential habitats for ectoparasites.
2. Personal Hygiene: Maintaining good personal hygiene is vital to prevent ectoparasite infestation. Regularly showering, washing clothes, and avoiding sharing personal items with others can reduce the risk of ectoparasite transmission.
3. Pet Care: Taking proper care of your pets is essential in preventing ectoparasite infestation. Regular bathing, grooming, and using vet-approved ectoparasite prevention products such as flea collars or topical treatments can help protect your pets from infestation.
4. Avoiding Contact with Infested Animals: Avoiding direct contact with animals known to be infested with ectoparasites can help prevent transmission. Be cautious while visiting animal shelters, parks, or areas with a high prevalence of ectoparasites.
5. Pest Control Measures: Implementing effective pest control measures in and around your home can reduce the risk of ectoparasite infestation. Regularly inspecting and treating outdoor areas, such as gardens and yards, can help eliminate potential habitats for ectoparasites.
6. Protective Clothing: When venturing into areas with a high risk of ectoparasite infestation, such as forests or grasslands, wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and closed-toe shoes can provide a physical barrier against ectoparasites.
7. Regular Check-ups: Regularly checking yourself, your family members, and your pets for signs of ectoparasite infestation is crucial in detecting and treating the problem early on. Prompt action can prevent the infestation from spreading and causing further harm.
By following these preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of ectoparasite infestation and protect yourself, your loved ones, and your pets from the harmful effects of ectoparasites.
Signs and Symptoms of Ectoparasite Infestation
Ectoparasites are tiny organisms that live on the surface of their hosts, including humans and animals. While some ectoparasites may not cause any noticeable symptoms, others can lead to discomfort and health issues. It is important to be able to recognize the signs of ectoparasite infestation in order to seek appropriate treatment.
1. Itching and irritation: One of the most common signs of ectoparasite infestation is itching and irritation in the affected areas. This can be caused by the ectoparasite’s bites, secretions, or presence on the skin. The itching may intensify at night or after exposure to heat.
2. Skin rashes: Ectoparasites such as fleas, ticks, and mites can cause red, bumpy, or scaly skin rashes. These rashes may be localized to the area where the ectoparasite is present or may spread to other parts of the body.
3. Visible parasites: In some cases, ectoparasites may be visible to the naked eye. This can include ticks, lice, or fleas crawling on the skin or in the hair. It is important to carefully examine the skin and hair for any signs of ectoparasites.
4. Hair loss: Ectoparasites can cause hair loss in both humans and animals. This can occur as a result of constant scratching and biting, as well as the ectoparasite’s feeding habits. Hair loss may be patchy or generalized, depending on the type and severity of infestation.
5. Allergic reactions: Some individuals may develop allergic reactions to ectoparasites or their bites. This can manifest as hives, swelling, or intense itching. In severe cases, anaphylaxis can occur, which requires immediate medical attention.
6. Secondary infections: Scratching and biting at ectoparasite-infested areas can break the skin and lead to secondary bacterial or fungal infections. These infections may present as redness, swelling, pain, or pus-filled lesions.
If you notice any of these signs and symptoms of ectoparasite infestation, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional or veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment. Prompt intervention can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications.