Alternative Methods to Treat Intervertebral Hernia Without Surgery
Содержимое
Learn natural methods to treat intervertebral hernia without the need for surgery. Discover exercises, stretches, and lifestyle changes that can help alleviate pain and promote healing.
An intervertebral hernia, also known as a herniated disc, can cause debilitating pain and limited mobility. Traditionally, surgery has been seen as the primary treatment option for this condition. However, advancements in non-surgical treatments have shown promising results in reducing pain and improving overall function.
Non-surgical methods for treating intervertebral hernia focus on relieving pressure on the affected disc and promoting the body’s natural healing processes. One effective non-surgical treatment option is physical therapy. Physical therapists can develop individualized exercise programs that target specific muscle groups to help stabilize the spine and relieve pressure on the herniated disc. These exercises can also improve flexibility and strengthen the back, providing long-term benefits.
In addition to physical therapy, non-surgical treatments for intervertebral hernia can also include medication and injection therapy. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Epidural steroid injections can also be effective in reducing pain and inflammation around the herniated disc. These injections deliver a powerful anti-inflammatory medication directly to the affected area, providing targeted relief.
Another non-surgical treatment option for intervertebral hernia is spinal decompression therapy. This technique uses a traction device to gently stretch the spine, creating negative pressure that can help pull the herniated disc back into place. This therapy can also promote the influx of oxygen and nutrients to the affected area, aiding in the healing process.
When it comes to treating intervertebral hernia, surgery is not always the only option. Non-surgical methods such as physical therapy, medication, injection therapy, and spinal decompression therapy can provide effective relief and improve overall quality of life. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment plan for your specific condition.
Why is non-surgical treatment important?
Non-surgical treatment is important for intervertebral hernia because it offers several advantages over surgical options. Firstly, non-surgical methods are less invasive, meaning they do not require any incisions or cutting of the body. This reduces the risk of complications and reduces the recovery time for the patient.
Non-surgical treatment also allows patients to preserve their natural anatomy and avoid the potential risks associated with surgery, such as infections or adverse reactions to anesthesia. By opting for non-surgical methods, patients can maintain their quality of life and minimize the disruption caused by the herniated disc.
Furthermore, non-surgical treatment options are often more cost-effective compared to surgery. They can involve therapies like physical therapy, chiropractic adjustments, and pain management techniques, which are typically more affordable and accessible to patients. This accessibility makes non-surgical treatment an attractive option for those who may not have the financial means to undergo surgery.
Another important aspect of non-surgical treatment is its ability to address the root causes of intervertebral hernia. While surgery may provide immediate relief by removing or repairing the herniated disc, it does not necessarily address the underlying factors that contributed to the condition. Non-surgical methods, on the other hand, focus on strengthening the muscles, improving posture, and promoting overall spinal health to prevent future hernias.
In conclusion, non-surgical treatment is important for intervertebral hernia due to its less invasive nature, preservation of natural anatomy, cost-effectiveness, and ability to address underlying causes. It offers patients a viable alternative that can alleviate pain, promote healing, and improve long-term outcomes without the risks associated with surgery.
Physical therapy for intervertebral hernia
Physical therapy is a crucial component in the effective non-surgical treatment of intervertebral hernia. It focuses on improving flexibility, strength, and overall function of the affected area, helping individuals manage pain and regain mobility.
Stretching exercises: Stretching helps to alleviate muscle tension and tightness in the back, which can contribute to the compression of discs. Regular stretching exercises can enhance flexibility and relieve pressure on the intervertebral discs.
Strengthening exercises: Strengthening the surrounding muscles can provide support to the spine and reduce the stress on the intervertebral discs. Exercises such as core strengthening and targeted muscle group workouts can help improve stability and prevent future injuries.
Posture correction: Maintaining proper posture is vital for individuals with intervertebral hernia. Physical therapy can teach patients correct body mechanics, helping them avoid excessive strain on the affected area and reducing the risk of hernia recurrence.
Manual therapy: Physical therapists may use hands-on techniques such as massage, joint mobilization, and spinal manipulation to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. These techniques can also improve blood flow and enhance the healing process.
Pain management techniques: Physical therapy can incorporate various pain management techniques, including heat and cold therapy, electrical stimulation, and ultrasound. These modalities can provide temporary relief from pain and promote faster healing.
Education and lifestyle modification: Physical therapists also play a crucial role in educating patients about proper body mechanics, ergonomics, and lifestyle modifications. They provide guidance on activities to avoid or modify to prevent further exacerbation of the condition.
Overall, physical therapy is an essential component of non-surgical treatment for intervertebral hernia. It aims to reduce pain, improve function, and promote long-term recovery. By incorporating physical therapy into their treatment plan, individuals with intervertebral hernia can experience improved quality of life and a reduced risk of future complications.
Injections as a non-surgical option
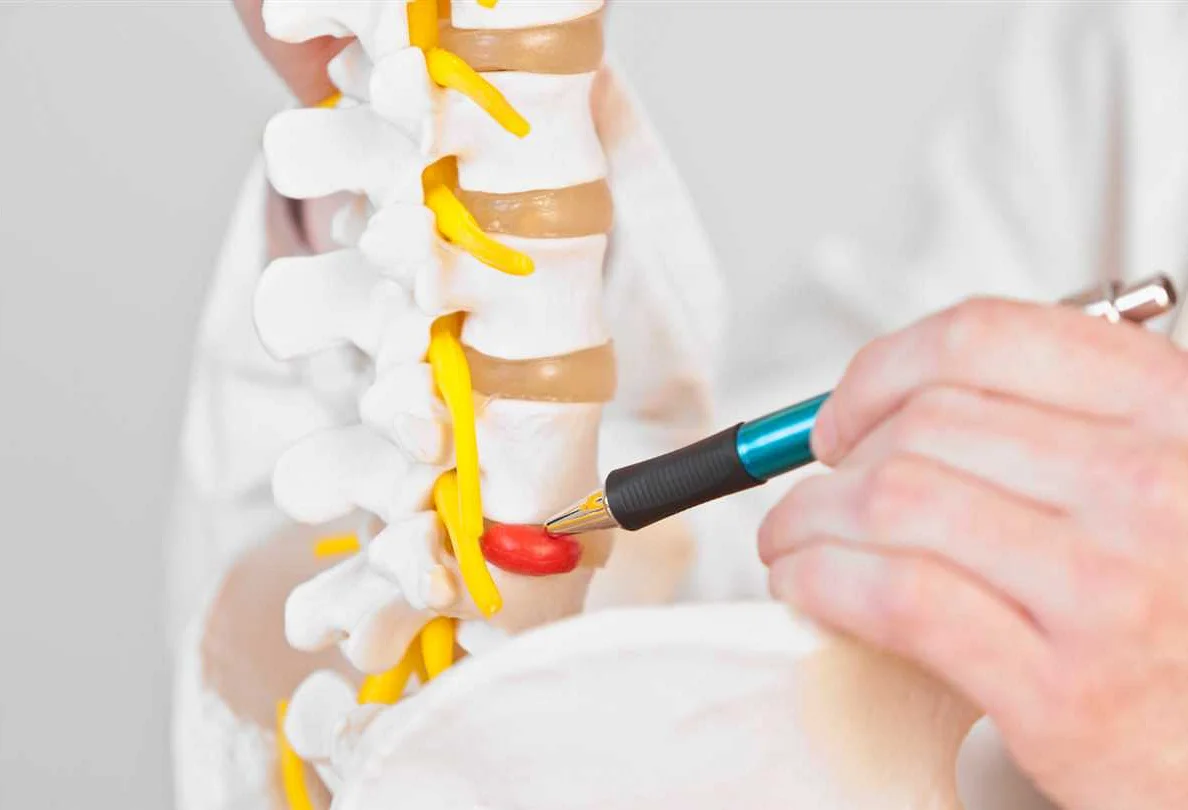
When it comes to treating intervertebral hernias, injections can be an effective non-surgical option. These injections, also known as epidural steroid injections, work by delivering targeted medication directly to the site of the herniation. The medication typically includes a corticosteroid to reduce inflammation and a local anesthetic to alleviate pain.
One of the main benefits of injections as a non-surgical option is their ability to provide immediate relief. While other treatments may take time to show results, injections can quickly reduce pain and discomfort. They offer a targeted approach, which is especially important in treating specific areas affected by the herniation.
Injections are also considered a minimally invasive option, as they do not require any surgical incisions. Instead, a needle is inserted into the affected area, guided by imaging techniques such as fluoroscopy or computed tomography. This minimizes the risk of complications and reduces the recovery time compared to surgical interventions.
Furthermore, injections as a non-surgical option have shown to be effective in both short-term and long-term pain relief. The corticosteroid helps reduce inflammation, which in turn alleviates symptoms. Additionally, the local anesthetic provides immediate pain relief, allowing patients to resume their daily activities with less discomfort.
It is important to note that injections are not a cure for intervertebral hernias, but rather a way to manage symptoms. However, they can provide significant relief and help patients avoid more invasive surgical interventions. Each patient’s condition is unique, and the suitability of injections as a treatment option should be determined on an individual basis in consultation with a healthcare professional.
Alternative medicine for intervertebral hernia
While traditional medical treatments such as surgery or pain medication can be effective for treating intervertebral hernia, some individuals may prefer to explore alternative medicine options. These alternative approaches often aim to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and improve overall well-being. While there is limited scientific evidence supporting these alternative treatments, many people have reported positive results.
1. Acupuncture: Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to promote healing and pain relief. It is believed to work by stimulating the release of endorphins, which are the body’s natural painkillers. Acupuncture may help reduce pain and inflammation associated with intervertebral hernia.
2. Herbal remedies: Some herbs, such as devil’s claw, turmeric, and ginger, have anti-inflammatory properties and can help relieve pain associated with intervertebral hernia. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before using any herbal remedies, as they may interact with other medications or have adverse side effects.
3. Chiropractic care: Chiropractic care involves manual adjustments to the spine, aiming to improve alignment and reduce pressure on the affected discs. This can help alleviate pain and discomfort associated with intervertebral hernia. It is important to seek treatment from a qualified and experienced chiropractor.
4. Yoga and stretching exercises: Gentle yoga poses and stretching exercises can help improve flexibility, strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, and alleviate pain. However, it is important to practice under the guidance of a trained instructor to ensure proper alignment and technique.
5. Massage therapy: Massage therapy can help relax tense muscles, improve circulation, and reduce pain. It can be especially beneficial for individuals experiencing muscle spasms or tightness as a result of intervertebral hernia.
Although alternative medicine approaches may provide relief for some individuals with intervertebral hernia, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before trying any new treatments. They can help determine appropriate options and ensure they do not interfere with other medical interventions.