Exacerbation of Gastritis: Symptoms and Treatment
Содержимое
Learn about the symptoms of gastritis exacerbation and find out how to treat it. Get important information about the causes, prevention, and management of gastritis flare-ups.
Gastritis is a common gastrointestinal disorder characterized by inflammation of the stomach lining. It can be caused by various factors, including bacteria, certain medications, excessive alcohol consumption, or prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). While the condition can often be managed with lifestyle changes and medication, it can sometimes worsen, leading to an exacerbation of symptoms.
An exacerbation of gastritis can be a distressing and uncomfortable experience for those affected. It is typically characterized by a sudden onset of symptoms, such as severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and a feeling of fullness or bloating. In some cases, individuals may also experience a loss of appetite, weight loss, and black, tarry stools, indicating the presence of bleeding in the stomach.
If you suspect that you are experiencing an exacerbation of gastritis, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare professional can evaluate your symptoms, perform diagnostic tests, such as an endoscopy or blood tests, and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Depending on the severity of the exacerbation, treatment may involve medications to reduce inflammation, antibiotics to address bacterial infections, or acid-suppressing drugs to alleviate symptoms.
What is Gastritis?
Gastritis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the lining of the stomach. The stomach lining becomes swollen and irritated, which can lead to symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
There are two main types of gastritis: acute and chronic. Acute gastritis is usually caused by a sudden infection or injury, such as alcohol abuse or the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Chronic gastritis, on the other hand, develops gradually over time and is often caused by long-term irritation of the stomach lining, such as regular use of NSAIDs, infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, or autoimmune disorders.
Common symptoms of gastritis include a burning or gnawing pain in the upper abdomen, nausea, vomiting, bloating, loss of appetite, and a feeling of fullness after eating. In some cases, gastritis can also cause blood in the vomit or stools.
Treatment for gastritis depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In many cases, lifestyle changes and medications can help manage symptoms and promote healing of the stomach lining. This may include avoiding foods that irritate the stomach, such as spicy or acidic foods, limiting alcohol consumption, quitting smoking, and taking medications to reduce stomach acid or treat H. pylori infection.
If left untreated, gastritis can lead to complications such as stomach ulcers, bleeding, and an increased risk of stomach cancer. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or severe symptoms of gastritis.
Understanding Gastritis and Its Causes
Gastritis is a common condition that refers to the inflammation of the stomach lining. It is a condition that can be acute, meaning it occurs suddenly and lasts for a short period of time, or chronic, meaning it persists for a long time. Understanding the causes of gastritis is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
The stomach lining is protected by a layer of mucus, which helps to prevent the stomach acid from damaging the stomach lining. Gastritis occurs when there is a breakdown in this protective layer, leading to inflammation and damage to the stomach lining. There are several factors that can contribute to the development of gastritis.
| Infection | Bacterial and viral infections can cause gastritis. The most common bacterial infection is caused by Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) bacteria. Viral infections, such as those caused by the herpes simplex virus, can also lead to gastritis. |
| Medications | Certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids, can irritate the stomach lining and lead to gastritis. Prolonged use of these medications can increase the risk of developing gastritis. |
| Alcohol and Substance Abuse | Excessive alcohol consumption and substance abuse can irritate the stomach lining and cause gastritis. Alcohol and certain substances, such as cocaine, can directly damage the stomach lining. |
| Autoimmune Disorders | Autoimmune disorders, such as autoimmune gastritis and pernicious anemia, can cause the immune system to mistakenly attack the stomach lining, leading to inflammation. |
| Stress | Chronic stress can increase the production of stomach acid and weaken the protective mucus layer, making the stomach lining more susceptible to inflammation. |
It is important to note that gastritis can also develop as a result of certain medical conditions, such as Crohn’s disease, HIV/AIDS, and kidney failure. Additionally, certain dietary factors, such as consuming spicy or acidic foods, can worsen symptoms of gastritis.
If you are experiencing symptoms of gastritis or have concerns about your digestive health, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Common Symptoms of Gastritis
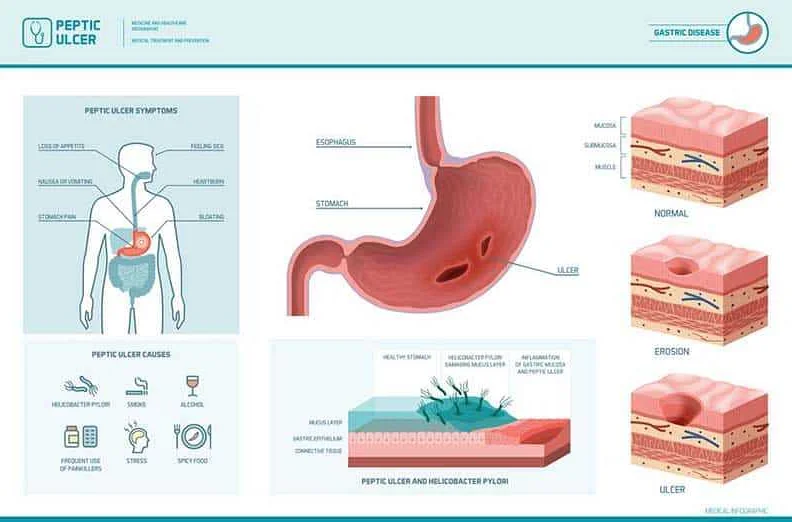
Gastritis is a condition that occurs when the lining of the stomach becomes inflamed or irritated. This inflammation can cause a variety of symptoms, which can vary in severity from person to person. If you are experiencing any of the following symptoms, it is possible that you have gastritis:
- Abdominal pain: This is one of the most common symptoms of gastritis. The pain can be dull or sharp and may be located in the upper abdomen.
- Nausea and vomiting: Many individuals with gastritis experience feelings of nausea and may also vomit. This can be particularly common after eating a meal.
- Indigestion: Gastritis can cause indigestion, which may manifest as a feeling of fullness or discomfort in the upper abdomen.
- Loss of appetite: Some individuals with gastritis may experience a loss of appetite, which can lead to unintended weight loss.
- Bloating and belching: Gastritis can cause excess gas to build up in the stomach, leading to bloating and frequent belching.
- Heartburn: Many individuals with gastritis experience a burning sensation in the chest, commonly known as heartburn.
- Black, tarry stools: In some cases of gastritis, there may be bleeding in the stomach, which can cause the stool to appear black and tarry.
- Weakness and fatigue: Chronic gastritis can lead to a decrease in the absorption of important nutrients, leading to weakness and fatigue.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Types of Gastritis
Gastritis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the stomach lining. There are several different types of gastritis, each with its own causes and symptoms. Understanding the different types can help in diagnosing and treating the condition effectively.
Here are the most common types of gastritis:
| Acute Gastritis | Infection (such as Helicobacter pylori), excessive alcohol consumption, prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) | Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, bloating, indigestion |
| Chronic Gastritis | Long-term inflammation of the stomach lining, infection with Helicobacter pylori, autoimmune disorders, pernicious anemia | Upper abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, indigestion, loss of appetite, weight loss |
| Erosive Gastritis | Long-term use of NSAIDs, alcohol abuse, severe stress, bile reflux | Abdominal pain, bleeding, nausea, vomiting, black, tarry stools |
| Atrophic Gastritis | Chronic inflammation of the stomach lining, long-term infection with Helicobacter pylori, autoimmune disorders | Loss of appetite, weight loss, stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, anemia |
| Reactive Gastritis | Infection, injury, or irritation of the stomach lining | Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, indigestion, loss of appetite |
It’s important to note that the symptoms of gastritis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition. If you experience persistent or severe symptoms, it’s recommended to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Acute Gastritis: Causes and Symptoms
Gastritis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the stomach lining. Acute gastritis refers to the sudden onset of these symptoms and can be caused by various factors. Understanding the causes and symptoms of acute gastritis can help in its management and treatment.
The following table outlines some common causes and symptoms of acute gastritis:
| 1. Infection | 1. Abdominal pain |
| 2. Medications | 2. Nausea and vomiting |
| 3. Alcohol consumption | 3. Loss of appetite |
| 4. Stress | 4. Bloating and gas |
| 5. Autoimmune diseases | 5. Indigestion |
| 6. Bacterial toxins | 6. Blood in vomit or stool |
These are just a few examples of the many possible causes and symptoms of acute gastritis. It’s important to note that the symptoms may vary depending on the underlying cause and individual factors. If you are experiencing persistent or severe symptoms, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment for acute gastritis often involves addressing the underlying cause, managing symptoms, and promoting healing of the stomach lining. This may include lifestyle changes, such as avoiding triggers like certain medications or foods, as well as medications to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms.
In conclusion, understanding the causes and symptoms of acute gastritis is crucial for its proper management and treatment. By identifying and addressing the underlying causes, individuals can find relief from the discomfort and promote healing of the stomach lining.