Factors that Increase the Risk of Prostate Cancer in Men
Содержимое
Learn about the risk factors for prostate cancer and find out which men are more prone to developing this disease. Understand the importance of age, family history, race, and certain lifestyle factors in determining the likelihood of prostate cancer.
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in men, with millions of cases diagnosed each year worldwide. While the exact cause of prostate cancer is still unknown, there are several factors that can increase a man’s risk of developing the disease.
Age is one of the most significant risk factors for prostate cancer. The risk of developing the disease increases with age, with the majority of cases occurring in men over the age of 65. This may be due to the fact that as men age, their prostate cells undergo natural changes that can lead to the development of cancer.
Another important factor is family history. Men with a close relative, such as a father or brother, who has had prostate cancer are at a higher risk of developing the disease themselves. This suggests that there may be a genetic component to prostate cancer risk.
Additionally, race and ethnicity can also play a role in prostate cancer risk. African-American men have the highest incidence rate of prostate cancer, followed by Caucasian men. Asian and Hispanic men have a lower risk, although the reasons for these differences are not yet fully understood.
Other factors that may influence prostate cancer risk include diet, lifestyle choices, and exposure to certain chemicals or toxins. Some studies have suggested that a diet high in red meat and dairy products, as well as a sedentary lifestyle, may increase the risk of developing prostate cancer. On the other hand, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, as well as regular physical activity, may help reduce the risk.
While these factors can increase the risk of prostate cancer, it’s important to note that having one or more risk factors doesn’t necessarily mean a man will develop the disease. Likewise, men without any risk factors can still develop prostate cancer. Regular screening and early detection are crucial for improving outcomes and increasing the chances of successful treatment.
Prostate Cancer Risk Factors
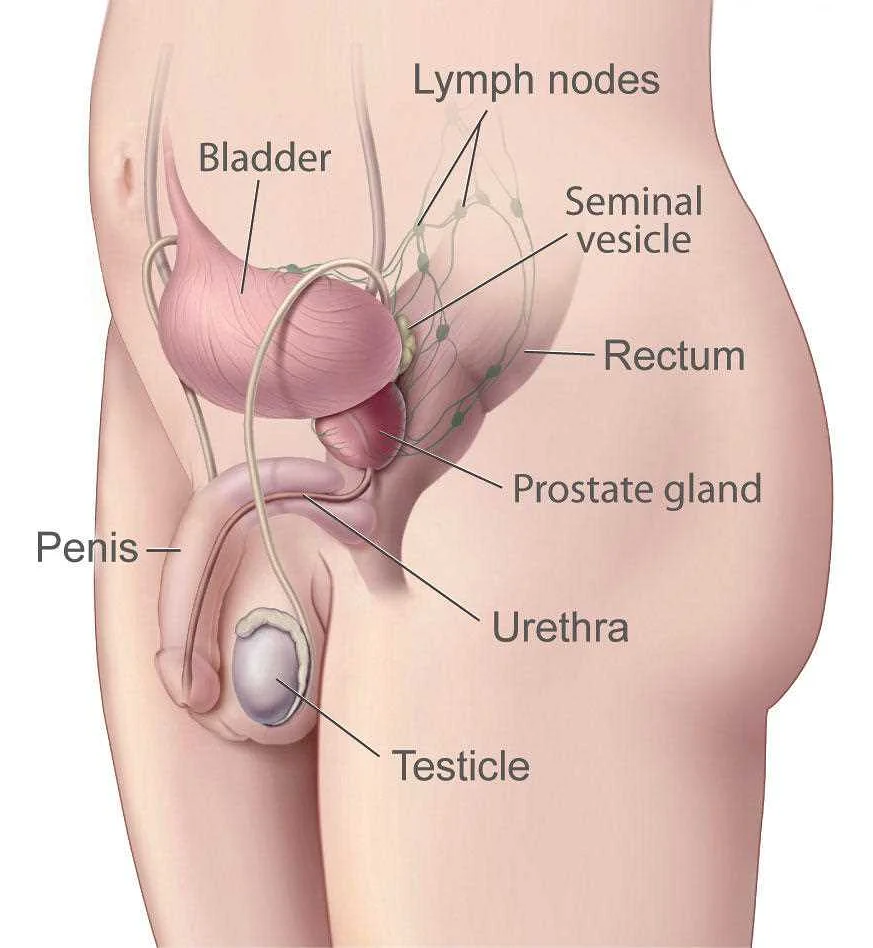
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in men, and there are several factors that can increase a man’s risk of developing this disease.
Age is one of the biggest risk factors for prostate cancer. The likelihood of developing prostate cancer increases with age, with the majority of cases occurring in men over the age of 50. Family history also plays a role, as men who have a close relative, such as a father or brother, with prostate cancer are more likely to develop the disease themselves.
Ethnicity is another factor that can influence prostate cancer risk. African American men have the highest rate of prostate cancer, followed by Caucasian men. Asian men have the lowest rate of prostate cancer. It is not yet fully understood why these differences exist, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Diet and lifestyle choices can also impact a man’s risk of prostate cancer. A diet high in red meat and processed foods, as well as a lack of physical activity, has been associated with an increased risk of developing prostate cancer. On the other hand, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, as well as regular exercise, may help reduce the risk.
Other factors that may contribute to prostate cancer risk include obesity, smoking, exposure to certain chemicals, and inflammation in the prostate gland. It is important for men to be aware of these risk factors and to take steps to maintain a healthy lifestyle to reduce their risk of developing prostate cancer.
Age and Prostate Cancer
Age is a significant factor in the development of prostate cancer. The risk of developing prostate cancer increases significantly with age. In fact, prostate cancer is most commonly diagnosed in men over the age of 65. According to the American Cancer Society, about six in ten cases of prostate cancer are diagnosed in men aged 65 or older.
As men age, changes in the prostate gland can occur that may lead to the development of prostate cancer. These changes can include an increase in the size of the prostate gland, as well as changes in hormone levels. The risk of developing prostate cancer also increases with the length of time a man has been exposed to various risk factors, such as certain chemicals or hormones.
It is important for men, especially those over the age of 50, to be proactive in monitoring their prostate health. Regular screenings, such as a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test, can help detect potential issues early on and improve the chances of successful treatment. It’s worth noting that while age is a significant risk factor for prostate cancer, it is not the only factor. Other factors, such as family history and race, can also play a role in a man’s risk for developing prostate cancer.
In conclusion, age is an important factor to consider when assessing an individual’s risk for developing prostate cancer. As men age, the risk of developing prostate cancer increases, making regular screenings and early detection crucial for maintaining prostate health.
Ethnicity and Prostate Cancer
Ethnicity has been found to play a significant role in determining the risk of prostate cancer in men. Studies have consistently shown that certain ethnic groups have a higher incidence of prostate cancer compared to others.
One of the highest risk groups for prostate cancer is African American men. They have been found to have the highest incidence and mortality rates of prostate cancer worldwide. Researchers are still trying to understand the reasons behind this disparity, but it is believed that genetic factors, access to healthcare, and socioeconomic factors may contribute to this increased risk.
Asian men, on the other hand, have been found to have a lower risk of prostate cancer compared to other ethnic groups. Studies have shown that Asian men living in Asia have lower incidence rates of prostate cancer than Asian men living in Western countries. The exact reasons for this lower risk are still being investigated, but it is believed that dietary factors and lifestyle choices may play a role.
Hispanic and Latino men have a lower incidence of prostate cancer compared to African American men but a higher incidence compared to Asian men. The reasons for these differences are not well understood and further research is needed to uncover the underlying factors.
It is important to note that these statistics are generalizations and do not apply to every individual within a specific ethnic group. It is still crucial for all men, regardless of their ethnicity, to be aware of their risk factors and to undergo regular prostate cancer screenings.
In conclusion, ethnicity is a significant factor in determining the risk of prostate cancer in men. African American men have the highest risk, while Asian men have a lower risk compared to other ethnic groups. This knowledge can help healthcare professionals tailor prevention and screening strategies to specific populations, ultimately leading to better outcomes for individuals at risk.
Family History and Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is known to have a familial component, with men who have a family history of the disease being at a higher risk of developing it themselves. Having a first-degree relative, such as a father or brother, with prostate cancer can increase a man’s risk by two to three times.
Researchers believe that family history plays a role in prostate cancer risk due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It is believed that certain genes may be associated with an increased risk of prostate cancer, and having a family history of the disease can increase the likelihood of inheriting these genes.
In addition to genetic factors, family history may also influence prostate cancer risk through shared environmental exposures. For example, if a family has a history of smoking or exposure to certain chemicals, this may increase the risk of developing prostate cancer.
It is important for men with a family history of prostate cancer to be proactive in their health. Regular screenings, such as prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests and digital rectal exams, can help detect prostate cancer early when it is most treatable. Men with a family history of the disease may also benefit from lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and eating a balanced diet.
In summary, family history is an important factor in prostate cancer risk. Men with a family history of the disease should be aware of their increased risk and take steps to monitor their health and reduce their risk. By staying proactive, men can improve their chances of detecting and treating prostate cancer at an early stage.
Diet and Prostate Cancer
Evidence suggests that diet plays a significant role in the development and progression of prostate cancer. Certain dietary factors have been identified as potential risk factors for the disease, while others have been associated with a reduced risk. Here are some key findings related to diet and prostate cancer:
- Fatty foods: Diets high in saturated and trans fats have been linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer. These fats are commonly found in red meat, processed meats, fried foods, and high-fat dairy products. It is recommended to limit the consumption of these foods.
- Fruits and vegetables: Numerous studies have shown that a diet rich in fruits and vegetables can help lower the risk of prostate cancer. The antioxidants and phytochemicals found in these foods may play a protective role against the development of cancer.
- Soy products: Some research suggests that consuming soy products, such as tofu and soy milk, may decrease the risk of prostate cancer. Soy contains isoflavones, which have been shown to have anti-cancer properties.
- Tomatoes: Tomatoes and tomato-based products, like tomato sauce and tomato paste, contain a powerful antioxidant called lycopene. Several studies have found that lycopene-rich foods may reduce the risk of prostate cancer.
- Fish: Fish, particularly fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and trout, are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. These healthy fats have been associated with a decreased risk of prostate cancer. It is recommended to include fish in the diet on a regular basis.
While the link between diet and prostate cancer is still being investigated, adopting a healthy diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins may help reduce the risk of developing this disease. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized dietary recommendations.