Preventing Patient Pain: National Medical Research Center for Oncology Freezes Patients to Ensure Comfort
At the National Medical Research Center for Oncology, patients are frozen to prevent pain and discomfort.
When it comes to cancer treatment, managing pain is one of the top priorities. Patients undergoing various procedures often experience intense pain, which can significantly impact their quality of life. To address this issue, the National Medical Research Center for Oncology has developed a groundbreaking technique – freezing patients.
Freezing, or cryotherapy, has long been used in medicine for various purposes. However, the National Medical Research Center for Oncology has taken it to a new level by utilizing it as a pain management strategy. By freezing specific areas of the body, doctors are able to numb the nerves and block pain signals.
The procedure involves applying a cold probe to the targeted area, which rapidly freezes the surrounding tissues. This freezing effect causes the nerves to become temporarily inactive, resulting in a significant reduction in pain sensation. The procedure is performed under the supervision of highly trained medical professionals, ensuring the safety and well-being of the patients.
Unlike traditional pain management techniques, such as medication or invasive procedures, cryotherapy offers a non-invasive and drug-free alternative. It has been proven to be highly effective in managing pain for a variety of conditions, including cancer-related pain. The National Medical Research Center for Oncology is at the forefront of utilizing this innovative approach, providing patients with much-needed relief and improved quality of life.
Cryotherapy: Innovative Approach to Pain Management

Cryotherapy, also known as cold therapy, is an innovative approach to pain management that has gained popularity in recent years. This technique involves the use of extreme cold temperatures to relieve pain and inflammation in various parts of the body. It is particularly effective in treating musculoskeletal injuries, such as sprains, strains, and arthritis.
During cryotherapy treatment, patients are exposed to freezing temperatures for a short period of time. This can be done through the use of ice packs, cold towels, or specialized cryotherapy machines. The extreme cold helps to numb the affected area, reducing pain and swelling.
One of the main advantages of cryotherapy is its ability to provide quick and temporary pain relief without the need for medication. This makes it a particularly attractive option for patients who are looking for alternative pain management techniques or who are unable to tolerate traditional pain medications.
In addition to pain relief, cryotherapy has been found to have other health benefits. It can improve blood circulation, boost the immune system, and even enhance athletic performance. Some athletes use cryotherapy as a way to speed up recovery after intense training or competition.
While cryotherapy is generally considered safe, it is important to note that it is not suitable for everyone. People with certain medical conditions, such as Raynaud’s disease or cold intolerance, may need to avoid cryotherapy. It is always best to consult with a healthcare professional before undergoing any new treatment.
In conclusion, cryotherapy is an innovative approach to pain management that offers quick and temporary relief without the need for medication. It has gained popularity for its effectiveness in treating musculoskeletal injuries and its potential health benefits. However, it is important to use caution and consult with a healthcare professional before trying cryotherapy.
The Role of Cryoablation in Cancer Treatment
Cryoablation is an innovative technique that has shown promising results in the field of cancer treatment. It involves freezing cancer cells to destroy them and prevent their further growth. This minimally invasive procedure is often used when surgery is not a viable option or when a patient prefers a less invasive treatment approach.
During cryoablation, a probe is inserted into the tumor, and extremely cold temperatures are applied to freeze the cancer cells. This freezing process causes the cells to undergo cell death, resulting in the destruction of the tumor. Cryoablation can be used to treat various types of cancer, including liver, kidney, lung, and prostate cancer.
One of the major advantages of cryoablation is its ability to target and destroy cancer cells without affecting the surrounding healthy tissues. Unlike traditional surgery or radiation therapy, cryoablation offers a precise and targeted approach, minimizing the risk of complications and side effects.
Additionally, cryoablation can be repeated if necessary, allowing for ongoing treatment and monitoring of the tumor. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for patients with recurrent or metastatic cancer, as it provides an alternative treatment option when other methods have failed.
Furthermore, cryoablation is a relatively quick procedure that can be performed on an outpatient basis. This means that patients can return home on the same day, reducing the need for hospitalization and recovery time. The recovery period after cryoablation is typically shorter compared to other cancer treatments, enabling patients to resume their normal activities sooner.
Although cryoablation has shown great promise in cancer treatment, it is not suitable for all types and stages of cancer. The eligibility for cryoablation depends on various factors, including the size and location of the tumor, as well as the patient’s overall health and specific cancer characteristics.
In conclusion, cryoablation plays a significant role in cancer treatment by offering a minimally invasive and targeted approach to destroy cancer cells. It provides a viable alternative when surgery is not feasible and allows for ongoing treatment and monitoring. With its precise nature and shorter recovery period, cryoablation is a valuable tool in the fight against cancer.
Benefits of Cryotherapy for Cancer Patients
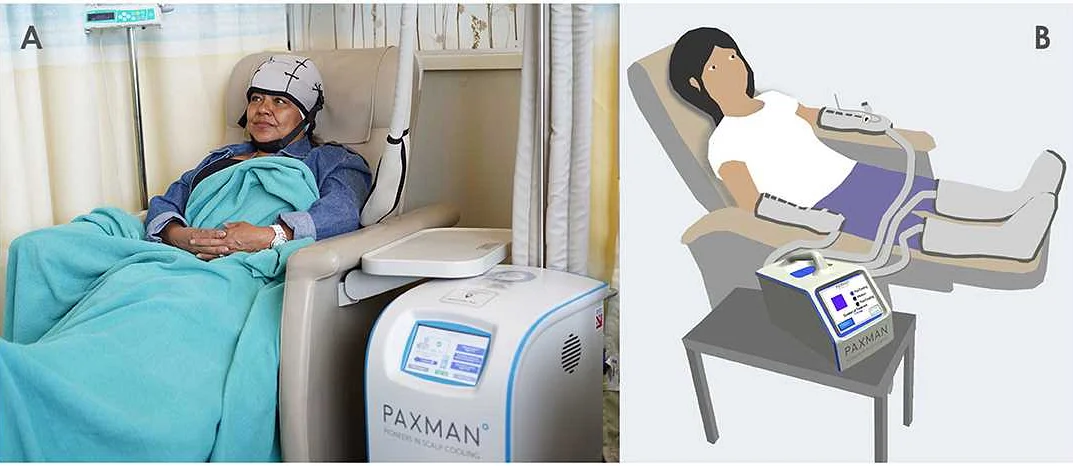
Cryotherapy, also known as cold therapy, has been found to provide several benefits for cancer patients. This innovative treatment involves freezing affected areas or tumors to alleviate symptoms and improve overall quality of life. Here are some of the key advantages of cryotherapy for cancer patients:
- Pain relief: Cryotherapy can effectively numb nerve endings and reduce pain associated with cancer. By freezing the affected area, it can provide immediate relief and improve the patient’s comfort level.
- Tumor destruction: Cryotherapy can directly target tumors and freeze them, causing cell death and tumor shrinkage. This can be a valuable treatment option for patients with localized tumors or for those who are not eligible for surgery.
- Minimally invasive: Unlike surgery or radiation therapy, cryotherapy is a minimally invasive procedure that does not require any incisions. This means that patients experience less pain, have reduced recovery time, and minimal scarring.
- Fewer side effects: Cryotherapy has fewer side effects compared to other cancer treatments. Patients may experience temporary swelling, redness, or blistering, but these are usually mild and can be managed with medications.
- Improved quality of life: By reducing pain, destroying tumors, and minimizing side effects, cryotherapy can greatly improve the overall quality of life for cancer patients. This allows them to engage in daily activities and enjoy a better physical and emotional well-being.
It is important to note that cryotherapy may not be suitable for all cancer patients and should be discussed with a healthcare professional. However, for many individuals, it can offer significant benefits and serve as a valuable addition to their treatment plan.
Procedure and Techniques Used in Cryoablation
Cryoablation is a medical procedure used to freeze certain tissues in order to treat various conditions, including cancer. It is a minimally invasive technique that involves the use of extreme cold temperatures to destroy abnormal cells.
The procedure begins with the insertion of a small, needle-like probe called a cryoprobe into the target area. The cryoprobe is connected to a console that controls the flow of liquid nitrogen or argon gas, which is used to create freezing temperatures. This freezing process is known as cryoablation.
Once the cryoprobe is properly positioned, the freezing temperatures are applied, causing the cells to freeze and form ice crystals. These ice crystals disrupt the cell membranes and structures, leading to cell death. The freezing temperatures also activate the body’s immune response, which helps in the removal of the dead cells and promotes healing.
During the procedure, the physician carefully monitors the temperature and duration of the freezing to ensure its effectiveness and minimize damage to surrounding healthy tissue. The use of imaging techniques, such as ultrasound or MRI, may also be employed to guide the placement of the cryoprobe and monitor the freezing process in real-time.
After the desired freezing is achieved, the cryoprobe is removed, and the treated area is left to thaw naturally. Over time, the frozen tissue is reabsorbed by the body or may be removed through a subsequent surgical procedure, depending on the specific situation.
Cryoablation has several advantages over traditional surgical procedures:
- It is minimally invasive, resulting in less trauma to the patient.
- It can be performed under local anesthesia, reducing the risks associated with general anesthesia.
- It has a shorter recovery time, allowing patients to return to their normal activities more quickly.
- It can be repeated if necessary, without significant complications.
Overall, cryoablation is a valuable technique in the field of medical research and treatment, offering a less invasive option for patients with certain conditions, including cancer.