If the xiphoid process hurts
Содержимое
If the xiphoid process hurts, it could be a sign of various conditions such as inflammation, injury, or a gastrointestinal issue. This article explores the possible causes and treatment options for xiphoid process pain.
The xiphoid process is a small, cartilaginous structure at the lower part of the sternum, or breastbone. It serves as an attachment point for several abdominal and chest muscles. While it is usually not a cause for concern, pain or discomfort in the xiphoid process can be a source of distress and worry for individuals experiencing it.
There are several potential causes for xiphoid process pain. One common cause is physical strain or injury, such as a direct blow to the chest or overexertion during exercise. Additionally, certain medical conditions, including costochondritis (inflammation of the cartilage connecting the ribs to the sternum) and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), can also lead to xiphoid process pain.
The symptoms of xiphoid process pain can vary from person to person, but often include localized tenderness or soreness in the area of the xiphoid process. Some individuals may also experience pain that radiates to the surrounding chest or abdominal areas. In severe cases, pain may be accompanied by difficulty breathing or swallowing.
Treatment for xiphoid process pain depends on the underlying cause. In cases of physical strain or injury, rest and pain relief medications may be sufficient. However, if the pain is caused by a medical condition such as costochondritis or GERD, additional treatment may be necessary. This can include anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, or lifestyle changes to manage symptoms and prevent future episodes of pain.
If you are experiencing xiphoid process pain, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. They can help identify the underlying cause of your symptoms and provide guidance on how to alleviate pain and prevent further discomfort. Remember, self-diagnosis and self-medication are not recommended, as they may lead to potentially harmful consequences.
Causes of xiphoid process pain
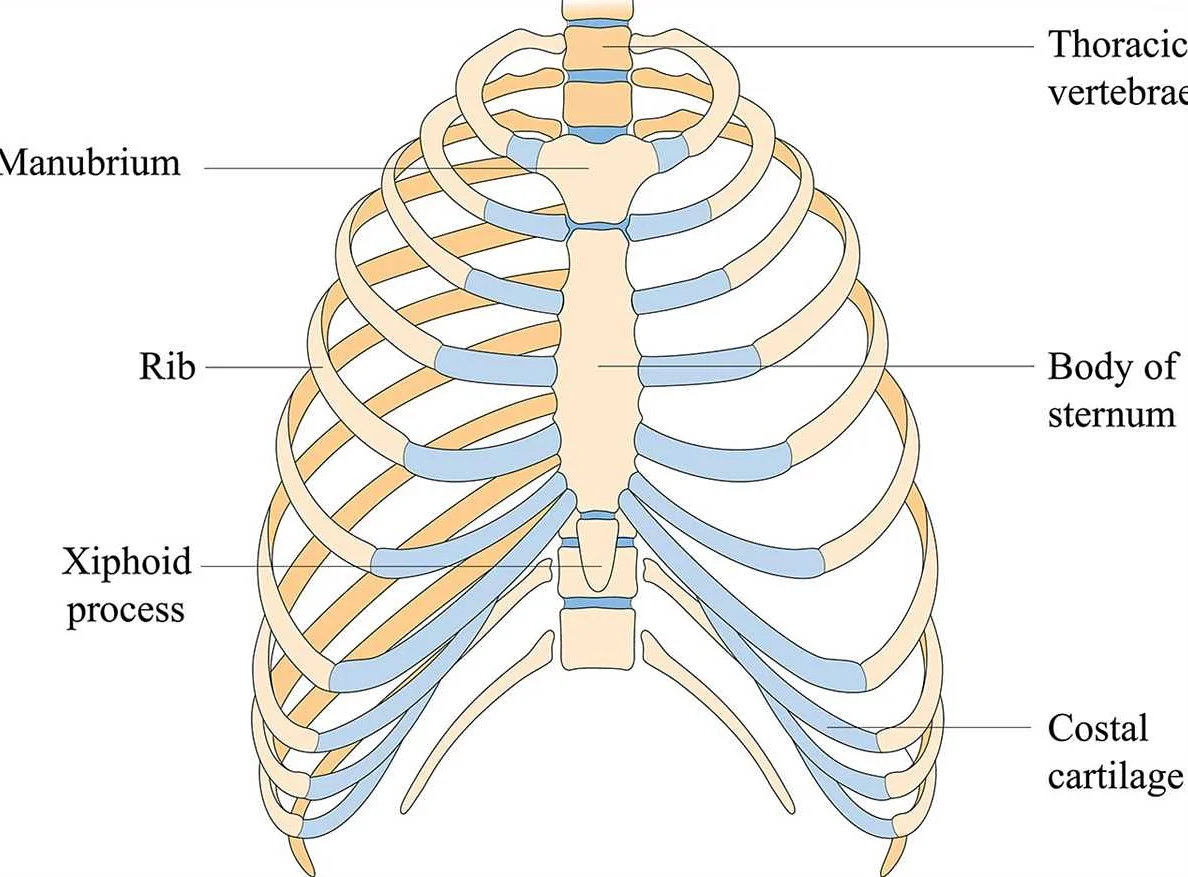
The xiphoid process is a small cartilaginous extension located at the lower end of the sternum. When this area becomes painful, it can be a result of various factors. Here are some common causes of xiphoid process pain:
1. Trauma: Direct trauma to the chest, such as from a fall, car accident, or sports injury, can cause the xiphoid process to become inflamed and painful.
2. Costochondritis: Costochondritis is an inflammation of the cartilage that connects the ribs to the sternum. If the inflammation extends to the xiphoid process, it can cause pain in this area.
3. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): GERD is a condition in which stomach acid flows back up into the esophagus. This can cause inflammation and pain in the xiphoid process area.
4. Hiatal hernia: A hiatal hernia occurs when part of the stomach pushes up through the diaphragm into the chest. This can put pressure on the xiphoid process and cause discomfort.
5. Costosternal syndrome: Also known as Tietze syndrome, costosternal syndrome is a condition characterized by inflammation of the costosternal joints, which connect the ribs to the sternum. This inflammation can extend to the xiphoid process and cause pain.
6. Infection: In rare cases, an infection in the xiphoid process area, such as a localized abscess or osteomyelitis, can cause pain and discomfort.
If you are experiencing pain in the xiphoid process, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. They will be able to identify the underlying cause of your pain and provide you with the necessary care.
Symptoms of xiphoid process pain
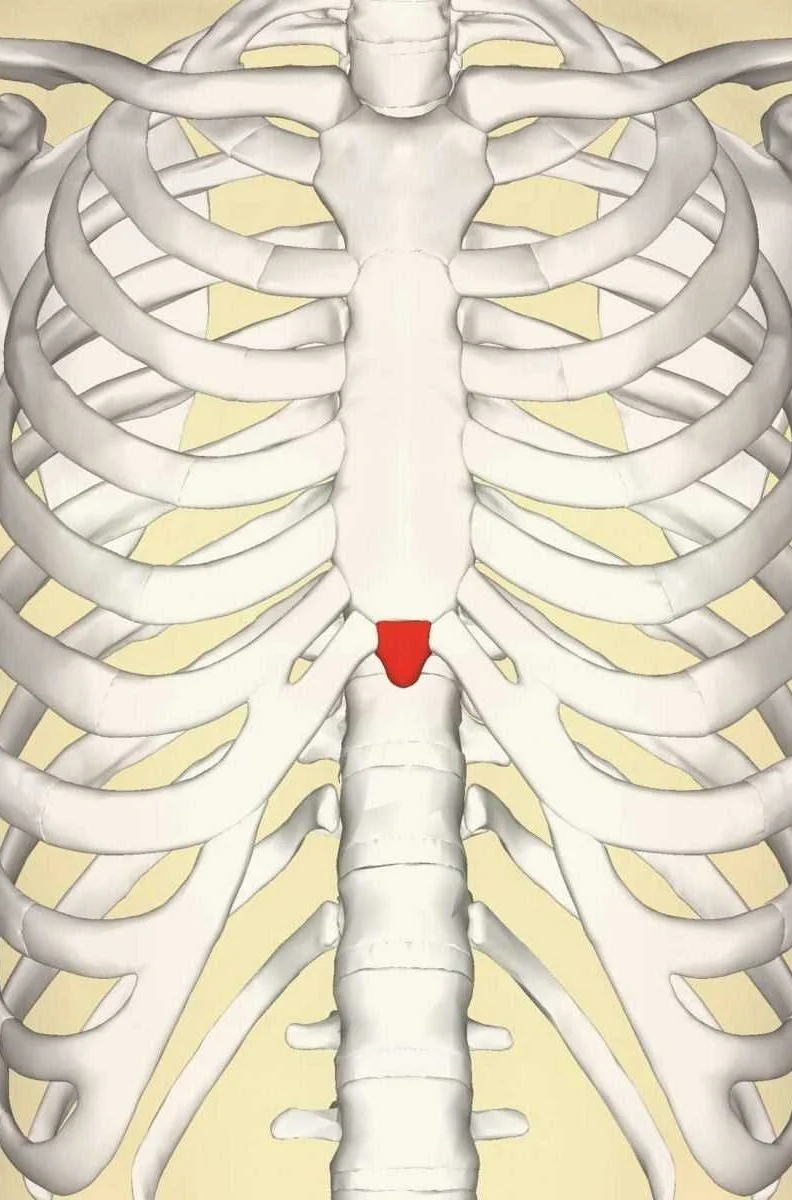
The xiphoid process, a small bone located at the bottom of the sternum, can sometimes cause pain or discomfort. Understanding the symptoms associated with xiphoid process pain can help individuals seek appropriate treatment and relief.
Some common symptoms of xiphoid process pain include:
| 1. Pain and tenderness: | Individuals with xiphoid process pain often experience localized pain and tenderness at the site of the xiphoid process, which is usually located just below the sternum. |
| 2. Sharp or stabbing pain: | The pain may be sharp, stabbing, or aching in nature, and it may worsen with certain movements or activities, such as bending, coughing, or sneezing. |
| 3. Radiating pain: | In some cases, the pain from the xiphoid process may radiate to other areas of the chest, abdomen, or back. |
| 4. Difficulty breathing: | Severe or persistent xiphoid process pain may make it difficult to take deep breaths or breathe comfortably. |
| 5. Swelling or inflammation: | Inflammation or swelling around the xiphoid process may be present in some cases, leading to additional discomfort. |
It’s important to note that the symptoms of xiphoid process pain can vary from person to person. Some individuals may only experience mild discomfort, while others may have more severe pain. If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s recommended to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Diagnosing xiphoid process pain
Diagnosing xiphoid process pain can be challenging due to the wide range of potential causes and overlapping symptoms. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
During the diagnostic process, the healthcare provider will typically start by taking a detailed medical history and performing a physical examination. They will ask about the specific location and nature of the pain, as well as any other accompanying symptoms.
The healthcare provider may also use diagnostic imaging tests, such as X-rays or CT scans, to get a clearer view of the xiphoid process and surrounding structures. These tests can help identify any abnormalities or potential sources of pain.
In some cases, additional tests may be ordered to rule out other conditions that can cause similar symptoms, such as gastrointestinal disorders or heart problems. Blood tests, electrocardiograms (ECGs), or endoscopic procedures may be used to gather more information.
Once a diagnosis has been made, the healthcare provider will discuss the treatment options with the patient. Treatment for xiphoid process pain will depend on the underlying cause and may involve a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and physical therapy.
If the pain persists or worsens despite treatment, it is important to follow up with the healthcare provider for further evaluation and management. It is also important to seek immediate medical attention if there are signs of a serious underlying condition, such as severe chest pain, difficulty breathing, or dizziness.
Treatment for xiphoid process pain
When experiencing pain or discomfort in the xiphoid process, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. The underlying cause of the pain will determine the appropriate course of action. Here are some potential treatment options:
1. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or naproxen sodium can help reduce inflammation and alleviate xiphoid process pain.
2. Rest and limited physical activity: Resting the affected area and avoiding activities that aggravate the pain can be beneficial for healing. It is important to give the xiphoid process time to recover.
3. Ice or heat therapy: Applying ice packs or warm compresses to the area can help reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief. Alternating between the two can also be beneficial.
4. Physical therapy: In some cases, a healthcare professional may recommend physical therapy exercises to strengthen the muscles around the xiphoid process and improve posture. These exercises can help alleviate pain and prevent future discomfort.
5. Avoiding triggers: If certain activities or movements consistently trigger xiphoid process pain, it is important to avoid or modify them. This may involve changes to daily activities or work ergonomics.
6. Stress reduction techniques: Stress and tension can contribute to muscle tightness and pain. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga may help manage xiphoid process pain.
7. Surgical intervention: In rare cases where conservative treatments have failed and the pain is severe or persistent, surgical intervention may be considered. This may involve removing the xiphoid process, although this is usually a last resort.
It is important to follow the advice of a healthcare professional and avoid self-diagnosis or self-treatment. Properly addressing the underlying cause of xiphoid process pain is crucial for effective treatment and long-term relief.
Preventing xiphoid process pain
To prevent xiphoid process pain, it is important to take steps to maintain good posture and avoid activities that put excessive strain on the chest area. Here are some tips to help prevent xiphoid process pain:
1. Maintain good posture: Practice proper posture while sitting, standing, and walking. This can help relieve pressure on the xiphoid process and prevent pain.
2. Avoid heavy lifting: Avoid lifting heavy objects or putting excessive strain on the chest area, as this can cause injury to the xiphoid process and lead to pain.
3. Use proper lifting techniques: When lifting objects, use your legs to lift the weight, rather than straining your chest and upper body. This can help prevent injuries to the xiphoid process.
4. Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can put additional strain on the xiphoid process and increase the risk of pain. Maintain a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet.
5. Avoid repetitive movements: Avoid repetitive movements that put strain on the chest area, such as excessive twisting or bending. This can help prevent injuries to the xiphoid process.
6. Stretch and strengthen the chest muscles: Regular stretching and strengthening exercises for the chest muscles can help prevent strain and injuries to the xiphoid process.
7. Practice stress management techniques: Stress can exacerbate xiphoid process pain. Practice stress management techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga, to help relieve stress and prevent pain.
By following these preventive measures, individuals can reduce the risk of xiphoid process pain and maintain a healthy and pain-free chest area.