Importance of Blood Pressure Monitoring after 35 Years of Age
Содержимое
Find out why it is important to monitor your blood pressure after the age of 35 to prevent potential health risks and maintain overall well-being. Regular monitoring can help detect and manage hypertension, reduce the risk of heart disease, and improve long-term health outcomes.
Blood pressure is a vital sign that measures the force of blood against the walls of your arteries. It is an important indicator of your cardiovascular health and can help detect potential issues before they become more serious. After the age of 35, the risk of developing high blood pressure increases, making regular monitoring crucial.
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is often called the “silent killer” because it often has no symptoms. If left untreated, it can lead to serious health problems such as heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease. Monitoring your blood pressure regularly can help you identify any changes or abnormalities early on and take appropriate steps to manage it.
Regular blood pressure monitoring is especially important after the age of 35 because the risk of developing hypertension increases with age. Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and high stress levels can also contribute to high blood pressure. By monitoring your blood pressure, you can make necessary lifestyle changes and seek medical attention if needed.
In addition to monitoring your blood pressure, it is important to understand what constitutes a healthy blood pressure range. A reading of 120/80 mmHg is considered normal, while readings above 130/80 mmHg indicate prehypertension or hypertension. By knowing your numbers, you can work with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan to manage your blood pressure and reduce your risk of complications.
Overall, blood pressure monitoring after the age of 35 is a crucial step in maintaining your cardiovascular health. By staying proactive and taking preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of developing hypertension and its associated complications. Remember to prioritize regular blood pressure checks and consult with your healthcare provider for guidance on managing your blood pressure effectively.
The Significance of Blood Pressure Monitoring
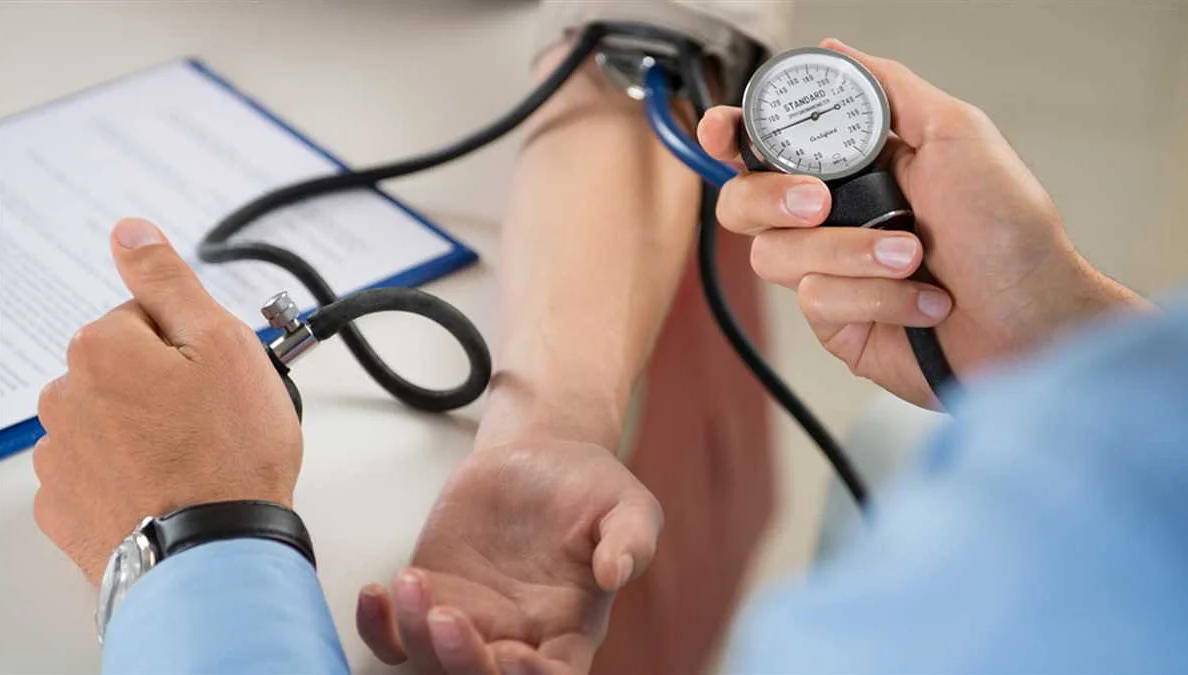
Monitoring blood pressure is crucial for maintaining good health, especially after the age of 35. High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common condition that can lead to serious health problems if left untreated. By regularly monitoring your blood pressure, you can detect any abnormalities early on and take necessary measures to prevent complications.
One of the main reasons why blood pressure monitoring is important is because high blood pressure usually has no noticeable symptoms. Without regular monitoring, you may not be aware that your blood pressure is elevated, putting you at risk for heart disease, stroke, and other health issues.
Regular monitoring also allows you to track any changes in your blood pressure over time. This is especially important for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or a family history of high blood pressure. By keeping a record of your blood pressure readings, you can provide valuable information to your healthcare provider, who can then make informed decisions about your treatment plan.
Blood pressure monitoring can be done in the comfort of your own home using a home blood pressure monitor. These devices are simple to use and provide accurate readings. By monitoring your blood pressure at different times of the day, you can also identify any patterns or triggers that may be contributing to elevated blood pressure.
In addition to home monitoring, regular blood pressure checks during routine doctor visits are essential. Your healthcare provider can use these readings to assess your overall health and determine if any intervention is necessary.
Overall, blood pressure monitoring is a vital tool in maintaining good health, especially as you get older. By being proactive and regularly monitoring your blood pressure, you can take control of your health and minimize the risk of developing serious complications associated with high blood pressure.
Why Blood Pressure Matters
Monitoring your blood pressure is essential for maintaining good health, especially after the age of 35. Blood pressure refers to the force exerted by the blood against the walls of your arteries as it is pumped around your body. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and recorded as two numbers, systolic pressure over diastolic pressure.
High blood pressure, or hypertension, occurs when the force of blood against the artery walls is consistently too high. This condition puts extra strain on your heart and blood vessels, increasing your risk of serious health problems, including heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. It is often called the “silent killer” because it typically has no symptoms until it causes a significant health issue.
By monitoring your blood pressure regularly, you can detect any abnormalities early on and take necessary steps to manage it. This may include lifestyle changes such as adopting a healthy diet, regular exercise, weight loss, and reducing stress. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help control high blood pressure.
Additionally, knowing your blood pressure numbers is important for understanding your overall cardiovascular health. It serves as an indicator of your risk for developing heart disease and other related conditions. By keeping your blood pressure within a healthy range, you can lower your risk and live a longer, healthier life.
Remember, prevention is key when it comes to maintaining good health. Monitoring your blood pressure after the age of 35 is an important step in preventing future health complications and ensuring your well-being.
Understanding Blood Pressure Levels
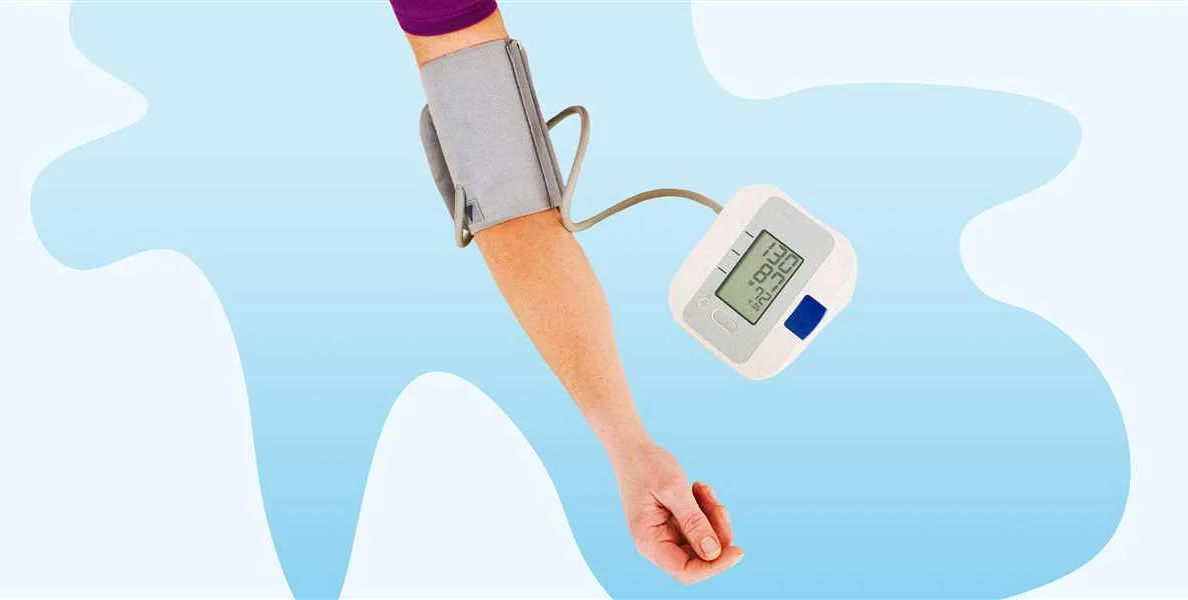
Blood pressure is a measure of the force exerted by the blood against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps it around the body. It is recorded as two numbers: systolic pressure over diastolic pressure. Systolic pressure is the higher number and represents the pressure when the heart contracts and pushes blood out into the arteries. Diastolic pressure is the lower number and represents the pressure when the heart is at rest between beats.
Normal blood pressure is typically defined as a reading below 120/80 mmHg. This means that the systolic pressure is below 120 mmHg and the diastolic pressure is below 80 mmHg. Elevated blood pressure falls between 120-129 mmHg for systolic pressure and below 80 mmHg for diastolic pressure.
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a condition in which blood pressure levels are consistently elevated. It is classified into two stages: stage 1 hypertension and stage 2 hypertension. Stage 1 hypertension is defined as systolic pressure between 130-139 mmHg or diastolic pressure between 80-89 mmHg. Stage 2 hypertension is defined as systolic pressure of 140 mmHg or higher or diastolic pressure of 90 mmHg or higher.
Monitoring blood pressure levels is important as it can help detect and manage hypertension, which is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as heart attack and stroke. Regular blood pressure checks can provide valuable information about the health of your cardiovascular system and help guide lifestyle changes or medical interventions if necessary.
If your blood pressure levels are consistently elevated, it is important to work with your healthcare provider to develop a plan to lower your blood pressure. This may involve lifestyle modifications such as adopting a healthier diet, increasing physical activity, managing stress, and quitting smoking. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help control blood pressure.
Understanding blood pressure levels and the importance of monitoring them can empower individuals to take control of their cardiovascular health and make informed decisions about their well-being.
Health Risks Associated with High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a serious medical condition that can lead to various health risks if left untreated. Here are some of the potential risks associated with high blood pressure:
| 1. Cardiovascular diseases: | High blood pressure can strain the heart and blood vessels, increasing the risk of heart diseases such as coronary artery disease, heart attack, and heart failure. |
| 2. Stroke: | When the blood pressure is consistently high, it can damage the blood vessels in the brain, leading to a stroke. |
| 3. Kidney problems: | Elevated blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, which can result in kidney disease or kidney failure. |
| 4. Vision loss: | High blood pressure can affect the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision problems and even blindness. |
| 5. Sexual dysfunction: | Uncontrolled hypertension can contribute to erectile dysfunction in men and reduced libido in both men and women. |
| 6. Metabolic syndrome: | High blood pressure is often associated with other risk factors such as obesity, high cholesterol, and insulin resistance, which together can increase the risk of metabolic syndrome. |
| 7. Dementia: | Research suggests a link between high blood pressure and an increased risk of cognitive decline and dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease. |
It is essential to monitor blood pressure regularly and take necessary measures to maintain it within a healthy range to reduce the risk of these health complications.
The Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups are crucial for maintaining good health, especially as we age. They provide an opportunity to monitor our overall well-being, identify any potential health issues, and take necessary preventive measures. When it comes to blood pressure monitoring, regular check-ups are essential for individuals over the age of 35.
During a regular check-up, your healthcare provider will measure your blood pressure using a sphygmomanometer. This important screening tool helps detect any deviations from the normal range and allows for early intervention if necessary. High blood pressure, or hypertension, is often referred to as the “silent killer” because it usually does not have obvious symptoms. Regular blood pressure monitoring can help identify this condition before it leads to serious health complications such as heart disease, stroke, or kidney damage.
In addition to blood pressure monitoring, regular check-ups also include other important health assessments. These may include cholesterol level testing, blood sugar testing, and body mass index (BMI) calculation. By regularly monitoring these health markers, your healthcare provider can detect any abnormalities and provide appropriate interventions or lifestyle recommendations.
Regular check-ups are also an opportunity to discuss any concerns or questions you may have with your healthcare provider. They can provide guidance on healthy lifestyle choices, such as diet and exercise, as well as address any specific health concerns you may have. The doctor-patient relationship is a partnership, and regular check-ups help build trust and ensure that you receive the best possible care.
In conclusion, regular check-ups are crucial for maintaining good health, and blood pressure monitoring is an important component of these check-ups, especially after the age of 35. By monitoring your blood pressure and other key health markers, you can take proactive steps to prevent serious health issues and ensure a longer and healthier life.