Inguinal dermatophytosis: symptoms, causes and treatment features
Inguinal dermatophytosis, also known as jock itch, is a common fungal infection that affects the groin area. This article explores the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for inguinal dermatophytosis, providing valuable information for those seeking to understand and manage this condition.
Inguinal dermatophytosis, also known as jock itch, is a common fungal infection that affects the skin of the groin area. It is caused by a group of fungi called dermatophytes, which thrive in warm and moist environments. This condition typically affects men, although women can also develop it.
One of the main symptoms of inguinal dermatophytosis is a red, itchy rash in the groin area. The rash may spread to the inner thighs and buttocks, and it can be very uncomfortable and irritating. Other symptoms may include a burning sensation, pain, and inflammation. It is important to note that jock itch is not a sexually transmitted infection and is not related to poor hygiene.
The causes of inguinal dermatophytosis can vary, but it is most commonly spread through direct contact with the fungus. This can occur through sharing towels, clothing, or sports equipment, or by coming into contact with contaminated surfaces, such as gym floors or locker room benches. People who sweat excessively or have a weakened immune system are more prone to developing the infection.
Treatment for inguinal dermatophytosis usually involves antifungal medications, such as creams or ointments, which can be applied directly to the affected area. In some cases, oral antifungal medications may be necessary. Additionally, keeping the affected area clean and dry can help prevent the infection from spreading or recurring. It is also important to avoid sharing personal items and to practice good hygiene to reduce the risk of reinfection.
In conclusion, inguinal dermatophytosis, or jock itch, is a common fungal infection that affects the groin area. It can cause discomfort and irritation, but it is treatable with antifungal medications and proper hygiene practices. If you suspect you have jock itch, it is important to seek medical attention for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of Inguinal Dermatophytosis
Inguinal dermatophytosis, also known as jock itch, is a fungal infection that affects the groin area. It is characterized by a variety of symptoms that can vary in severity and duration. Common symptoms of inguinal dermatophytosis include:
- Itching and irritation in the groin area
- Red, scaly rash that may spread to the inner thighs, buttocks, and genitals
- Burning sensation or discomfort in the affected area
- Persistent itching that worsens with sweat or friction
- Cracking or peeling of the skin
- Pain and tenderness in the affected area
- Blisters or ulcers in severe cases
The symptoms of inguinal dermatophytosis can be bothersome and can interfere with daily activities. They can also be embarrassing, leading to self-consciousness and decreased quality of life. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience these symptoms to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Causes of Inguinal Dermatophytosis
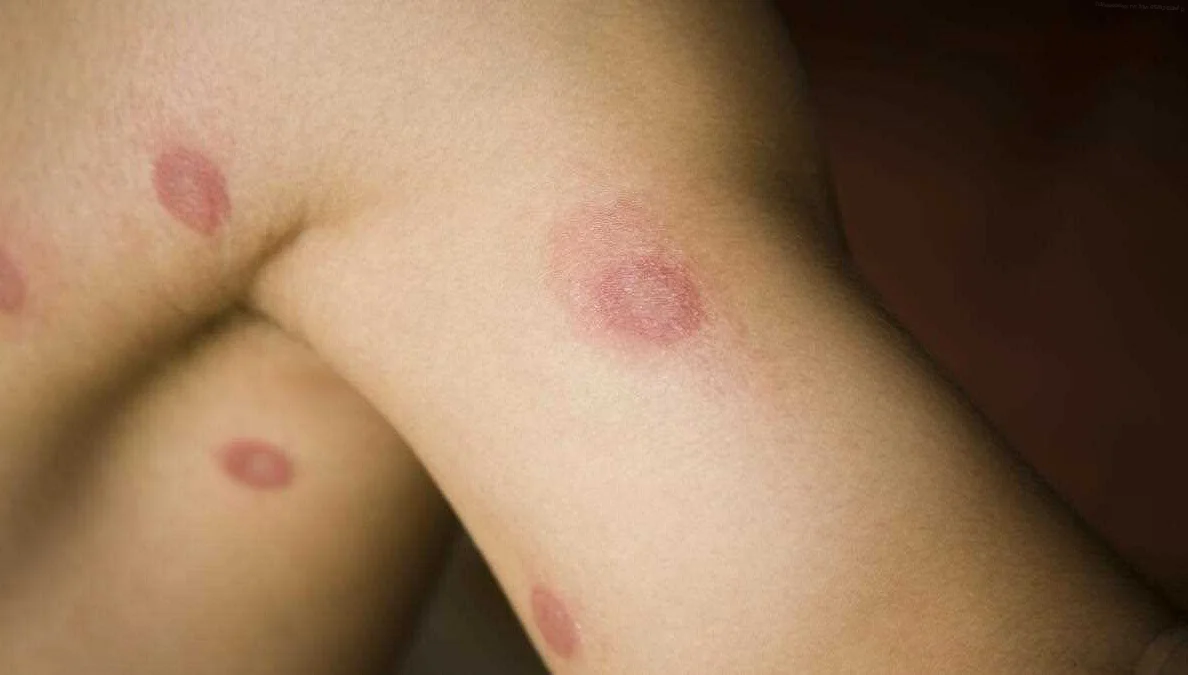
Inguinal dermatophytosis, also known as jock itch, is a fungal infection that affects the groin area. It is caused by a group of fungi called dermatophytes, which thrive in warm and moist environments.
The main causes of inguinal dermatophytosis include:
| 1. | Poor hygiene: | Not maintaining proper hygiene in the groin area can create an environment favorable for the growth of dermatophytes. Failing to keep the area clean and dry can increase the risk of infection. |
| 2. | Tight clothing: | Wearing tight underwear or pants can create friction and trap moisture in the groin area, providing an ideal breeding ground for fungi to thrive. |
| 3. | Sweating: | Excessive sweating can exacerbate the risk of developing inguinal dermatophytosis. Sweat provides a moist environment that encourages fungal growth. |
| 4. | Direct contact: | Coming into direct contact with an infected person or contaminated surfaces can transmit the fungi responsible for jock itch. |
| 5. | Weakened immune system: | Individuals with a weakened immune system, such as those with diabetes or HIV/AIDS, are more susceptible to fungal infections, including inguinal dermatophytosis. |
| 6. | Warm and humid climate: | Living in a hot and humid climate can increase the likelihood of developing inguinal dermatophytosis due to the favorable conditions it provides for fungal growth. |
These factors contribute to the development and spread of inguinal dermatophytosis, emphasizing the importance of maintaining good hygiene practices and avoiding prolonged exposure to warm and moist environments.
Treatment Options for Inguinal Dermatophytosis
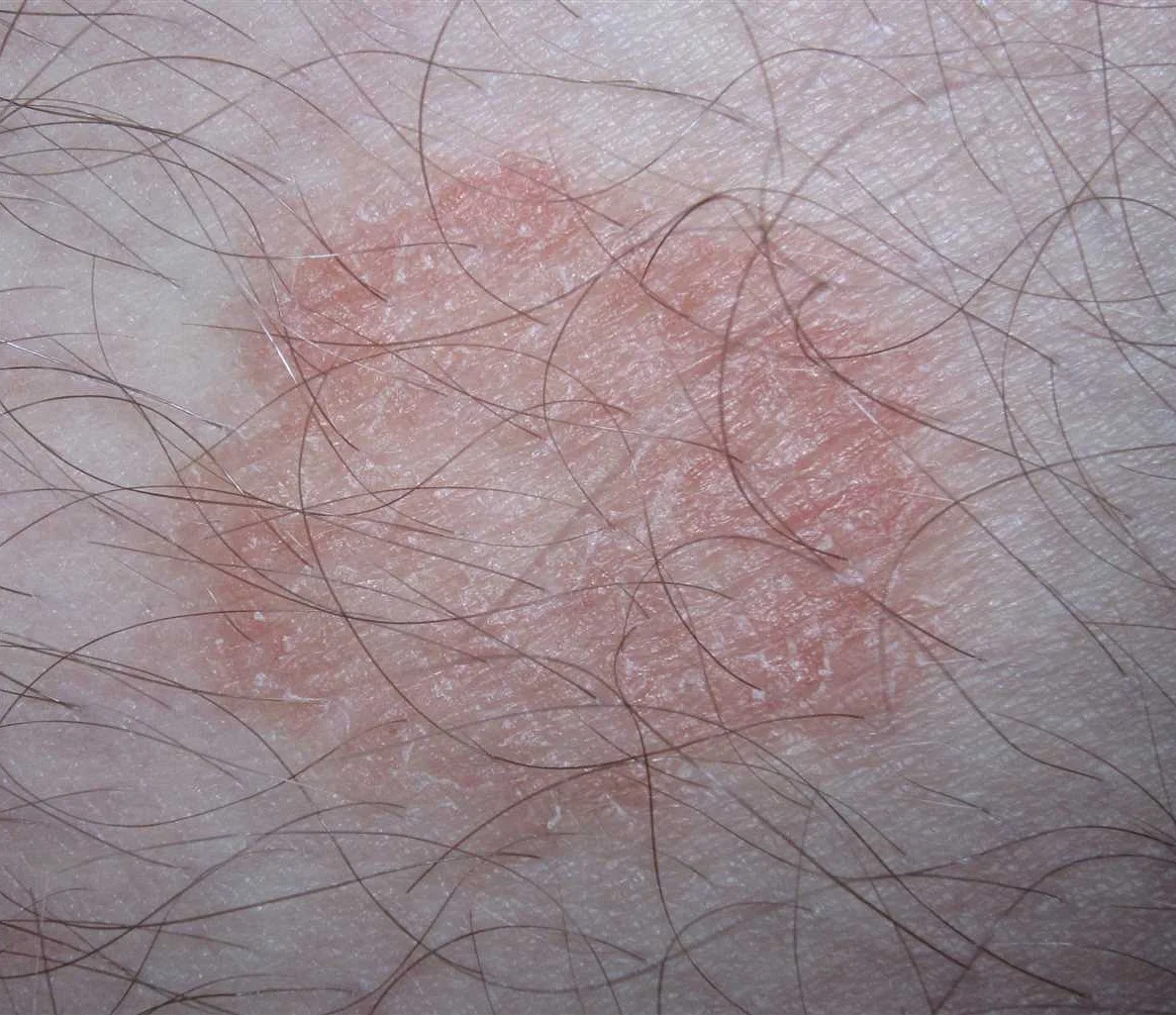
When it comes to treating inguinal dermatophytosis, there are several options available. The choice of treatment will depend on the severity of the infection and the individual’s medical history. It is always recommended to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Here are some common treatment options for inguinal dermatophytosis:
| Topical antifungal creams | These creams are applied directly to the affected area and work by killing the fungus causing the infection. They are usually used for mild to moderate cases of inguinal dermatophytosis and may need to be applied for several weeks to completely clear the infection. |
| Oral antifungal medications | In cases of severe or persistent inguinal dermatophytosis, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed. These medications work from the inside to kill the fungus causing the infection. They are typically taken for a specified period of time, often several weeks, to ensure complete eradication of the infection. |
| Antifungal powders | Antifungal powders can be used to help keep the affected area dry and free from moisture, which can promote fungal growth. These powders are often recommended in combination with other treatment methods to enhance their effectiveness. |
| Improved hygiene practices | Practicing good hygiene can help prevent the spread and recurrence of inguinal dermatophytosis. This includes keeping the affected area clean and dry, wearing clean and breathable underwear, and avoiding sharing personal items, such as towels or clothing, with others. |
| Avoiding irritants | Avoiding irritants, such as harsh soaps, perfumes, and tight-fitting clothing, can help reduce discomfort and further irritation of the affected area. |
It is important to follow the recommended treatment plan and complete the full course of medication, even if symptoms improve, to ensure the complete eradication of the fungus and prevent the recurrence of inguinal dermatophytosis.
Prevention of Inguinal Dermatophytosis
Inguinal dermatophytosis, also known as jock itch, can be prevented by following a few simple measures. It is important to maintain good personal hygiene practices and to keep the groin area clean and dry. Here are some tips to help prevent inguinal dermatophytosis:
1. Keep the groin area clean: Wash the groin area thoroughly with mild soap and water every day. Make sure to gently dry the area afterwards, using a clean towel or a hairdryer on a cool setting.
2. Wear loose-fitting clothes: Tight clothes can create a warm and moist environment, which is favorable for fungal growth. Opt for loose-fitting clothes made from breathable fabrics like cotton. Avoid wearing wet clothes for extended periods of time.
3. Use antifungal powders or creams: Applying antifungal powders or creams to the groin area can help prevent the growth of dermatophytes. These products can be purchased over-the-counter and should be used as directed by a healthcare professional.
4. Avoid sharing personal items: Do not share towels, clothes, or other personal items with others, as this can increase the risk of spreading the infection.
5. Practice good foot hygiene: Fungal infections on the feet, such as athlete’s foot, can spread to the groin area. It is important to keep the feet clean and dry, and to wear clean socks and shoes.
6. Avoid prolonged exposure to moisture: Moist environments provide a breeding ground for fungi. Avoid sitting in wet clothes or bathing suits for prolonged periods of time, and change out of sweaty clothes as soon as possible.
7. Be cautious in public areas: Use caution when using public showers, locker rooms, and saunas, as these areas may harbor fungi. Always wear sandals or flip-flops to protect your feet from coming into direct contact with potentially contaminated surfaces.
By following these preventive measures, you can reduce your risk of developing inguinal dermatophytosis and keep your groin area healthy and free from fungal infections.
Complications of Inguinal Dermatophytosis
Inguinal dermatophytosis, also known as jock itch, is a common fungal infection that affects the groin area. While it is generally a mild condition, if left untreated or not managed properly, it can lead to complications. These complications may include:
1. Secondary Infection: Scratching the affected area can break the skin barrier and create an entry point for bacteria. This can lead to a secondary bacterial infection, resulting in symptoms such as increased redness, swelling, and pus.
2. Hyperpigmentation: Chronic or recurrent cases of inguinal dermatophytosis may result in hyperpigmentation of the affected skin. This refers to the darkening of the skin due to increased melanin production. Hyperpigmentation may take several months to fade even after successful treatment.
3. Psychological Impact: Inguinal dermatophytosis can be uncomfortable and embarrassing for individuals, especially if it affects sensitive areas like the groin. This can lead to psychological distress, lowered self-esteem, and decreased quality of life.
4. Spread to Other Body Parts: If proper hygiene and preventive measures are not followed, the infection can spread to other body parts or to other people. Direct contact with infected skin or sharing contaminated clothing or towels can facilitate the spread of the fungi responsible for inguinal dermatophytosis.
5. Recurrence: Without appropriate treatment and preventive measures, inguinal dermatophytosis can recur. Factors such as weakened immune system, excessive sweating, and tight clothing can increase the risk of recurrence. Recurrent episodes may require a more aggressive treatment approach.
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have inguinal dermatophytosis or if you experience any complications. A healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options to prevent complications and manage the condition effectively.