Juvenile osteochondrosis: symptoms, features of the disease, treatment
Содержимое
Learn about juvenile osteochondrosis, its symptoms, and the specific features of this disease. Explore the available treatment options and find out how to manage this condition effectively.
Osteochondrosis is a condition that affects the growth plates of children and adolescents. It is characterized by the abnormal development of bone and cartilage, leading to pain and limited mobility. Juvenile osteochondrosis specifically refers to cases that occur during childhood and adolescence.
One of the main symptoms of juvenile osteochondrosis is pain, which can be localized or spread throughout the affected area. This pain is often worse during physical activity and can limit a child’s ability to participate in sports or other activities. Other symptoms may include swelling, tenderness, and decreased range of motion. In some cases, there may also be visible deformities or changes in the affected area.
Treatment for juvenile osteochondrosis depends on the severity of the condition and the specific affected area. In some cases, conservative methods such as rest, physical therapy, and pain management may be sufficient. However, more severe cases may require surgical intervention to correct the underlying bone and cartilage abnormalities.
It is important to diagnose and treat juvenile osteochondrosis early to prevent long-term complications and ensure optimal growth and development. Regular check-ups with a pediatrician or orthopedic specialist can help identify any potential issues and allow for early intervention. With proper treatment and management, the symptoms of juvenile osteochondrosis can be minimized, and children can resume their normal activities in a healthy manner.
Symptoms of Juvenile Osteochondrosis
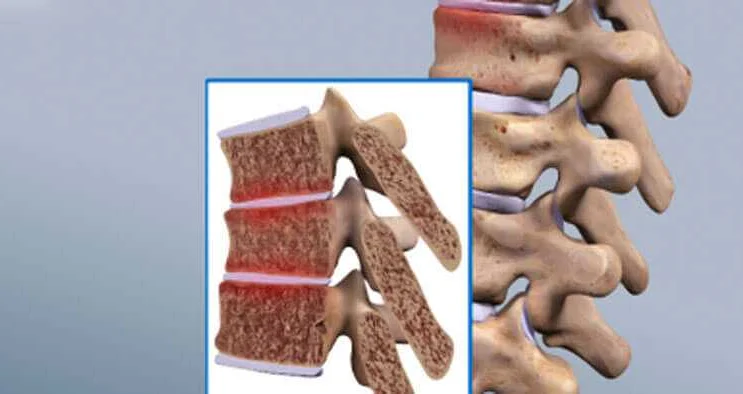
Juvenile osteochondrosis is a condition that primarily affects children and adolescents. It is characterized by a disturbance in the growth and development of the bones and cartilage, particularly in the joints.
The symptoms of juvenile osteochondrosis can vary depending on the specific joint affected. However, some common symptoms include:
| Pain | Children may complain of pain in the affected joint, which can range from mild to severe. The pain may worsen with physical activity or at the end of the day. |
| Swelling | Swelling around the affected joint may be present, making it appear larger than usual. The swelling can be accompanied by redness and warmth. |
| Limited Range of Motion | The affected joint may have reduced flexibility and a decreased range of motion. This can make it difficult for children to perform certain movements or activities. |
| Joint Stiffness | Children may experience stiffness in the affected joint, particularly after periods of rest or in the morning. The stiffness may improve with movement. |
| Joint Clicking or Popping | Some children with juvenile osteochondrosis may notice a clicking or popping sound when they move the affected joint. This can be a result of loose pieces of cartilage or bone within the joint. |
| Muscle Weakness | Due to the pain and limited range of motion, children with juvenile osteochondrosis may experience muscle weakness in the affected area. This can affect their ability to perform certain activities or exercises. |
If your child is experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Early intervention can help manage the symptoms and prevent further progression of the condition.
Distinctive Features of Juvenile Osteochondrosis
Juvenile osteochondrosis is a condition that primarily affects growing children and adolescents. It is characterized by the abnormal development of the bone and cartilage in the joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and limited movement. While the exact cause of juvenile osteochondrosis is still unknown, there are several distinctive features that can help identify this condition.
Age: Juvenile osteochondrosis typically occurs in children and adolescents between the ages of 5 and 16. It is more common during periods of rapid growth, such as puberty, when the bones and cartilage are undergoing significant changes.
Joint Involvement: Juvenile osteochondrosis commonly affects the weight-bearing joints, such as the knees, ankles, and hips. However, it can also affect other joints in the body, including the shoulders, elbows, and wrists.
Pain and Stiffness: One of the key symptoms of juvenile osteochondrosis is pain in the affected joint. The pain may be localized or radiate to other parts of the body. Stiffness and limited range of motion are also common, especially after periods of rest or inactivity.
Visible Deformities: In some cases, juvenile osteochondrosis can cause visible deformities in the affected joints. These deformities may include swelling, redness, and an abnormal shape or alignment of the joint.
Activity Limitations: Children and adolescents with juvenile osteochondrosis may experience limitations in their physical activities. They may have difficulty participating in sports, walking long distances, or performing simple movements that require joint flexibility and strength.
Diagnosis and Treatment: Diagnosis of juvenile osteochondrosis typically involves a physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRI scans. Treatment options may include pain management, physical therapy, bracing, and in severe cases, surgery.
In conclusion, recognizing the distinctive features of juvenile osteochondrosis can help in its timely diagnosis and management. If your child or adolescent is experiencing persistent joint pain, stiffness, or limited movement, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options for Juvenile Osteochondrosis

The treatment options for juvenile osteochondrosis depend on the specific condition and its severity. In most cases, conservative treatments are recommended to manage symptoms and promote healing. However, in severe cases or when conservative treatments fail, surgical intervention may be necessary.
| 1. Rest and Activity Modification: Resting the affected area and avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms can help reduce pain and inflammation. |
| 2. Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can provide exercises and techniques to improve mobility, strengthen muscles, and support proper joint alignment. |
| 3. Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain medications or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be recommended to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. |
| 4. Orthotic Devices: Braces, shoe inserts, or other orthotic devices can help support the affected joint and reduce stress on the affected area. |
| 5. Lifestyle Modifications: Specific lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding repetitive stress on the affected area, may be recommended to improve overall joint health. |
In cases where conservative treatments are not effective or the condition worsens, surgical intervention may be considered. Surgical options for juvenile osteochondrosis include:
| 1. Arthroscopy: During arthroscopy, a small incision is made, and a thin tube with a camera is inserted into the joint. This allows the surgeon to visualize and treat the affected area. |
| 2. Osteotomy: In some cases, an osteotomy may be performed to reshape the bone and relieve pressure on the affected area. |
| 3. Joint Fusion: If the condition has progressed to severe arthritis, joint fusion may be considered to stabilize the joint and alleviate pain. |
| 4. Joint Replacement: In rare cases of advanced joint damage, joint replacement surgery may be necessary to replace the damaged joint with an artificial joint. |
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for juvenile osteochondrosis based on individual circumstances and the specific condition.
Preventive Measures for Juvenile Osteochondrosis
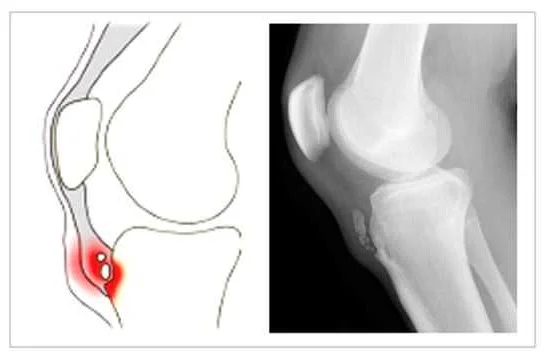
Preventing juvenile osteochondrosis involves several key measures that can help reduce the risk of developing this condition or manage its progression. These preventive measures include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight can put additional strain on the joints, increasing the risk of osteochondrosis. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help prevent this condition.
- Practicing good posture: Maintaining proper posture while sitting, standing, and lifting can help distribute weight and pressure evenly on the joints, reducing the risk of osteochondrosis.
- Engaging in regular physical activity: Regular exercise, such as swimming, biking, and walking, can help strengthen the muscles and improve joint stability, reducing the likelihood of osteochondrosis.
- Avoiding excessive stress on the joints: Activities that put excessive stress on the joints, such as high-impact sports or repetitive movements, should be avoided or limited to reduce the risk of osteochondrosis.
- Using proper equipment: Using appropriate sports equipment, such as well-fitting shoes and protective gear, can help minimize the risk of joint injuries that can lead to osteochondrosis.
- Taking regular breaks: Taking frequent breaks during activities that involve prolonged sitting or repetitive motions can help reduce the risk of osteochondrosis by allowing the joints and muscles to rest and recover.
- Practicing proper ergonomics: Ensuring that workstations, chairs, and other equipment are ergonomically designed can help maintain proper posture and reduce the strain on the joints, preventing osteochondrosis.
It is important to note that these preventive measures may not guarantee the complete prevention of juvenile osteochondrosis, but they can significantly reduce the risk and manage its progression. Individuals should consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations based on their specific needs and risk factors.