Leg Amputation Rehabilitation and Possible Consequences
Содержимое
Learn about leg amputation, rehabilitation techniques, and potential consequences. Find information on coping with limb loss and regaining independence after amputation.
Amputation of a limb is a life-altering event that affects millions of individuals worldwide. In the case of leg amputation, the rehabilitation process is crucial for adapting to this new reality and regaining independence. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of the rehabilitation process after leg amputation, including the potential consequences that individuals may face.
Rehabilitation after leg amputation involves a multidisciplinary approach, combining specialized medical care, physical therapy, and psychological support. The first step in the rehabilitation process is the fitting of a prosthetic limb, which requires precise measurements and adjustments to ensure optimal comfort and functionality. Physical therapy plays a vital role in strengthening the residual limb and improving mobility, while also focusing on maintaining overall physical fitness and preventing secondary complications.
While the physical aspects of rehabilitation are essential, the psychological impact of leg amputation should not be underestimated. Many individuals face emotional challenges, such as grief, loss, and body image issues. Through counseling and support groups, patients can address these concerns and develop coping strategies to enhance their emotional well-being. It is crucial to recognize that amputation rehabilitation is a holistic process that encompasses both physical and psychological aspects.
Despite advancements in medical technology and rehabilitation techniques, individuals who have undergone leg amputation may experience certain consequences. Phantom limb pain, a sensation of pain in the amputated limb, is a common and often challenging issue. Additionally, individuals may face difficulties in adapting to the use of a prosthetic limb, as it requires significant coordination and adjustment. It is essential for healthcare professionals to provide ongoing support and assist patients in overcoming these challenges to ensure successful rehabilitation.
Importance of Leg Amputation Rehabilitation
Leg amputation rehabilitation plays a crucial role in helping individuals adjust to their new circumstances and regain their independence. It aims to improve the physical function, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life for those who have undergone leg amputation surgeries.
One of the primary goals of leg amputation rehabilitation is to help individuals adapt to their prosthetic limb and learn how to use it effectively. This process involves teaching them how to properly fit and wear their prostheses, as well as training them in gait and balance exercises. By improving their mobility and functional abilities, rehabilitation empowers individuals to regain their mobility, perform daily activities, and participate in physical activities and sports.
Furthermore, leg amputation rehabilitation addresses the psychological impact of limb loss. The emotional and mental challenges that often accompany amputation can be overwhelming and may lead to depression, anxiety, and loss of self-esteem. Rehabilitation programs provide psychological support and counseling, helping individuals cope with these emotions, adjust to their new physical appearance, and develop a positive body image.
A comprehensive rehabilitation program also focuses on pain management. Phantom limb pain, a common phenomenon among amputees, can be debilitating and interfere with their daily lives. Through various pain management techniques, such as medication, physical therapy, and psychological interventions, rehabilitation professionals aim to alleviate this pain and improve overall well-being.
Moreover, leg amputation rehabilitation addresses the importance of maintaining a healthy lifestyle. It educates individuals about proper nutrition and exercise, emphasizing the significance of maintaining a healthy weight and cardiovascular health. By adopting healthy habits, individuals can prevent additional health complications and enhance their overall well-being.
In summary, leg amputation rehabilitation is essential for promoting physical, emotional, and psychological well-being in individuals who have undergone leg amputations. It allows them to adapt to their new circumstances, regain their independence, and lead fulfilling lives. Through various strategies and interventions, rehabilitation professionals provide the necessary support and guidance to help individuals navigate the challenges of limb loss and achieve optimal outcomes.
Understanding the Rehabilitation Process
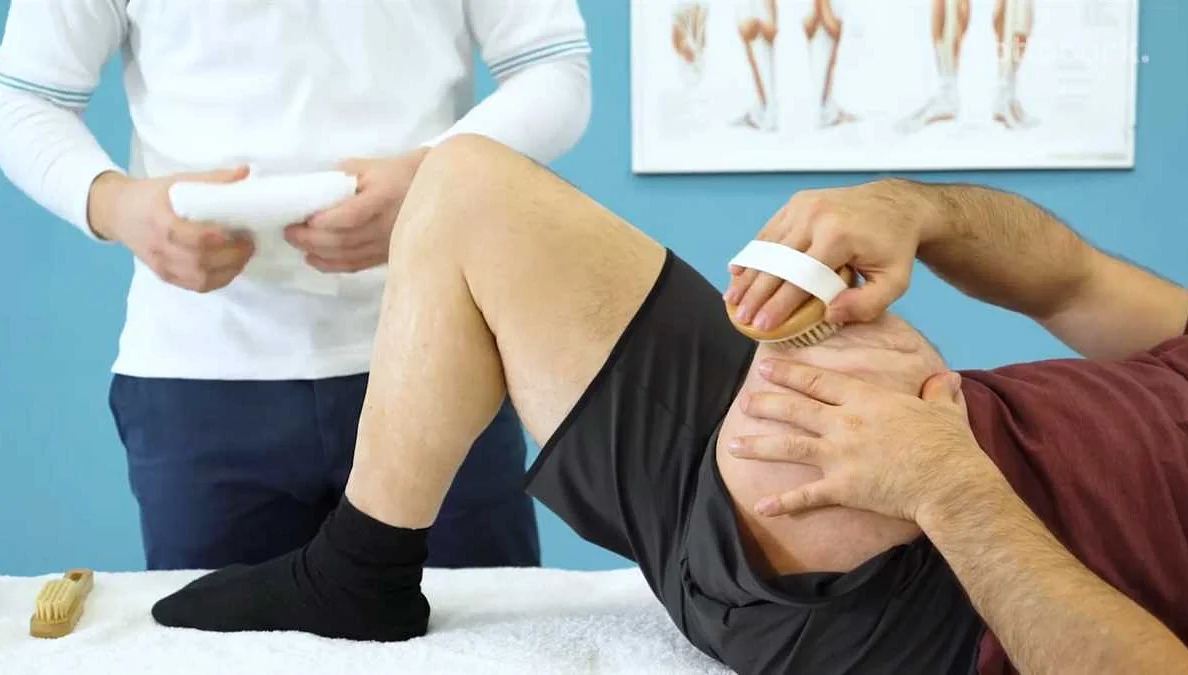
Amputation of a leg can have a significant impact on a person’s mobility, independence, and overall quality of life. However, with the right rehabilitation process, individuals can regain functionality and adapt to a new way of living.
The rehabilitation process after leg amputation typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, with healthcare professionals from various disciplines working together to provide comprehensive care. The primary goal of rehabilitation is to help individuals regain strength, improve mobility, and maximize independence.
Initially, the rehabilitation process may focus on wound healing and pain management. Physical therapists will guide individuals through exercises to promote healing, prevent complications, and reduce pain. They may also use techniques such as compression therapy and provide instruction on proper wound care.
As the wound heals, the focus of rehabilitation shifts towards mobility training and strengthening exercises. Physical therapists will work with individuals to improve their balance, gait, and overall strength. They may use assistive devices, such as crutches or prosthetics, to support mobility and help individuals regain their ability to walk.
In addition to physical therapy, occupational therapists play a crucial role in the rehabilitation process. They help individuals regain functional independence by providing training and assistance in activities of daily living, such as dressing, bathing, and household tasks. Occupational therapists may also assess the need for assistive devices, such as wheelchair modifications or adaptive equipment.
Psychological support is also an essential component of the rehabilitation process. Coping with the loss of a limb can be challenging, and individuals may experience emotional and psychological difficulties. Rehabilitation teams often include psychologists or counselors who can provide emotional support, address any mental health concerns, and help individuals adjust to their new circumstances.
Throughout the rehabilitation process, a team of healthcare professionals will closely monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. They will also educate individuals and their families about proper care techniques, self-management strategies, and available resources for ongoing support.
Rehabilitation after leg amputation is a journey that requires dedication, patience, and support. By understanding the rehabilitation process and working closely with a multidisciplinary team, individuals can achieve their maximum potential and regain a fulfilling and independent life.
Preparing for Rehabilitation
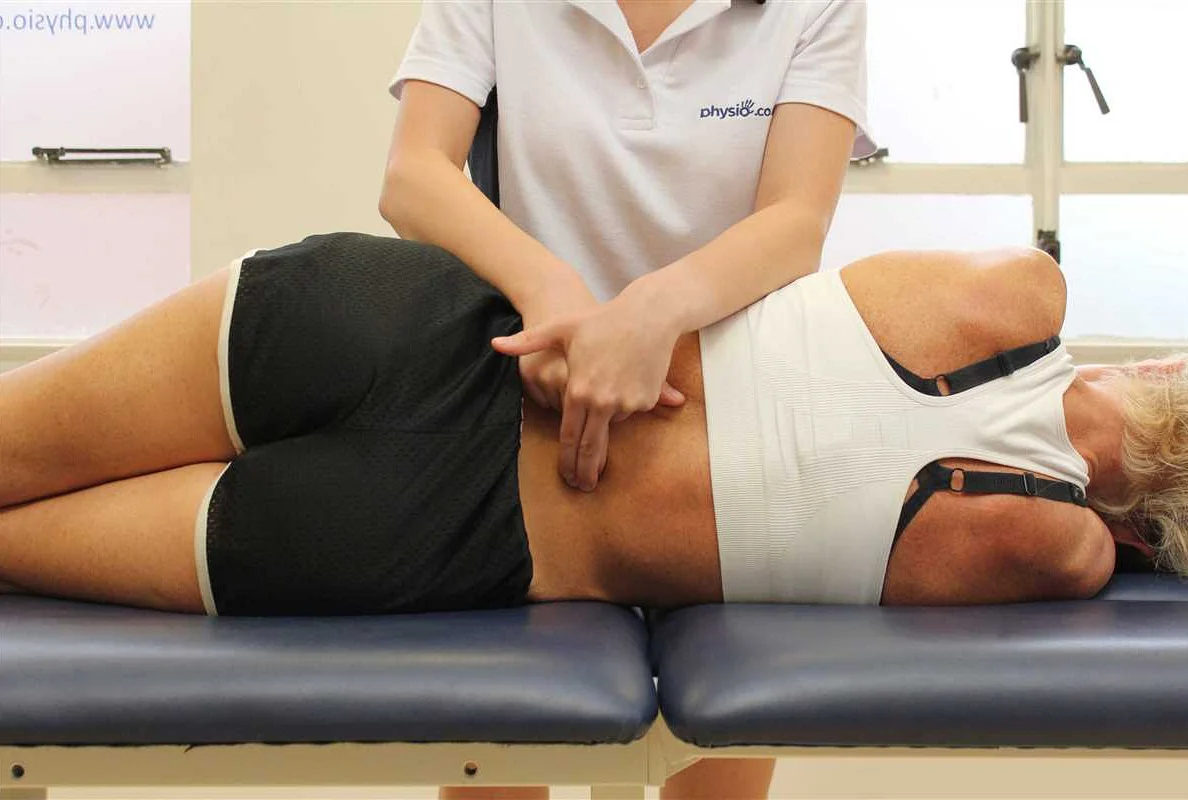
Before beginning the rehabilitation process for leg amputation, it is important to mentally and physically prepare yourself for the challenges ahead. Here are some steps you can take to ensure a successful rehabilitation:
- Educate yourself: Take the time to learn about the rehabilitation process and what to expect. Talk to your healthcare team, read informative materials, and join support groups to gain valuable insights and advice from others who have undergone similar experiences.
- Set realistic goals: Establish goals that are achievable and in line with your current abilities. Break them down into smaller, manageable steps to keep yourself motivated and on track throughout the rehabilitation journey.
- Build a support network: Surround yourself with people who can provide emotional and practical support during this challenging time. Seek out family members, friends, and healthcare professionals who can offer encouragement, advice, and assistance when needed.
- Prepare your home environment: Make necessary modifications to your home to ensure it is safe and accessible for your rehabilitation. Install handrails, remove tripping hazards, and consider purchasing assistive devices such as a wheelchair or crutches.
- Stay positive: Maintaining a positive mindset is crucial throughout the rehabilitation process. Remember that setbacks and frustrations are a normal part of the journey, but with determination and a positive attitude, you can overcome any obstacle.
- Take care of your overall well-being: Prioritize self-care by eating a balanced diet, getting enough rest, and engaging in activities that bring you joy and relaxation. Taking care of your physical and mental health will support your rehabilitation efforts.
- Communicate with your healthcare team: Stay in regular contact with your healthcare professionals to discuss your progress, address any concerns, and modify your rehabilitation plan as needed. They are there to guide you and provide the necessary medical expertise.
Remember, the rehabilitation process can be challenging, but with proper preparation and a positive mindset, you can achieve your goals and regain your independence after leg amputation.
Potential Physical Consequences
Leg amputation can result in various physical consequences that can impact an individual’s mobility and overall health. Some of these potential consequences include:
1. Loss of mobility: The loss of a limb can greatly affect an individual’s ability to walk, run, and perform everyday tasks. The absence of a leg may require the use of assistive devices such as crutches, walkers, or prosthetic limbs to regain mobility.
2. Changes in balance and stability: The loss of a leg can disrupt an individual’s sense of balance, making it more challenging to stand or perform activities that require stability. This can increase the risk of falls and injuries.
3. Muscle weakness and atrophy: After leg amputation, the muscles in the residual limb may become weak and atrophied due to disuse. Physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises are crucial to preventing further muscle deterioration and promoting strength and mobility.
4. Phantom limb pain: Many individuals experience phantom limb pain, which is the sensation of pain or discomfort in the amputated limb. This can be debilitating and may require pain management techniques or medications.
5. Increased energy expenditure: Walking or performing activities with a prosthetic limb requires more energy compared to using a natural leg. This increased energy expenditure can lead to fatigue and may require adjustments in an individual’s daily routine and lifestyle.
6. Skin problems: The residual limb may be prone to skin problems such as irritation, pressure sores, or infections. Proper hygiene, regular skin care, and the use of appropriate prosthetic devices can help prevent these complications.
7. Emotional and psychological impact: A leg amputation can have a significant emotional and psychological impact on an individual, leading to feelings of grief, loss, and body image issues. Psychological support and counseling may be necessary to cope with these challenges.
It is important for individuals who have undergone leg amputation to work closely with healthcare professionals and rehabilitation specialists to address and manage these potential physical consequences. With proper care, support, and rehabilitation, many individuals can regain their independence and lead fulfilling lives.