Missing or Incompletely Formed Limbs
Содержимое
Learn about missing or incompletely formed limbs, including types, causes, and treatment options. Find support and resources for individuals and families affected by limb differences.
Human body, with its intricate design and remarkable functionality, is a product of millions of years of evolution. However, sometimes this incredible process can result in missing or incompletely formed limbs, leaving individuals facing unique challenges. This condition, known as limb deficiency, can occur due to various causes and can affect different parts of the body.
There are several reasons why limb deficiency may occur. Genetic factors can play a significant role, with certain conditions, such as Amelia or Phocomelia, being present at birth. Acquired limb deficiency can also result from accidents, infections, or medical interventions, such as amputations. Additionally, environmental factors, such as exposure to harmful substances during pregnancy, can contribute to the development of limb abnormalities.
While limb deficiency can present physical and emotional hurdles, there are various treatments and support systems available to improve the quality of life for individuals affected by this condition. Prosthetic limbs and orthotic devices offer mobility and functionality, enabling individuals to lead fulfilling lives. Physical and occupational therapy can also play a crucial role in helping individuals adapt to their circumstances, enhancing their independence and well-being.
Education and advocacy are essential in ensuring that individuals with limb deficiency receive the support they need. Organizations and support groups provide resources, information, and emotional support to individuals and their families. By raising awareness and promoting inclusion, we can create a society that celebrates diversity and provides equal opportunities for everyone, regardless of their physical differences.
While limb deficiency can present unique challenges, it is important to remember that individuals with missing or incompletely formed limbs are capable of achieving great things. With the right support, treatment, and mindset, they can overcome obstacles and lead fulfilling lives, proving that our differences are what make us truly extraordinary.
Causes of Missing or Incompletely Formed Limbs
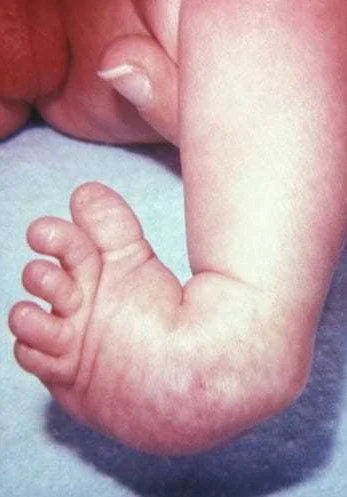
Missing or incompletely formed limbs can occur due to various factors, including genetic and environmental factors. Here are some common causes:
- Genetic mutations: In some cases, missing or incompletely formed limbs can be attributed to genetic mutations. These mutations can affect the development of limbs during early stages of pregnancy.
- Chromosomal abnormalities: Certain chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome or Turner syndrome, can increase the risk of having missing or incompletely formed limbs.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain environmental factors during pregnancy, such as infections, toxins, or medications, can increase the risk of limb abnormalities in the developing fetus.
- Maternal conditions: Certain maternal conditions, such as uncontrolled diabetes or inadequate prenatal care, can also contribute to limb abnormalities in the fetus.
- Amniotic band syndrome: This condition occurs when bands of tissue inside the womb restrict the normal development of limbs, leading to missing or incompletely formed limbs.
- Amniotic fluid abnormalities: Uneven levels of amniotic fluid can disrupt limb development and result in limb abnormalities.
It’s important to note that the exact cause of missing or incompletely formed limbs may vary on a case-by-case basis. In some instances, the cause may be unknown.
Further research and understanding of these causes are essential for improving prevention strategies and developing effective treatment options for individuals with missing or incompletely formed limbs.
Genetic Factors
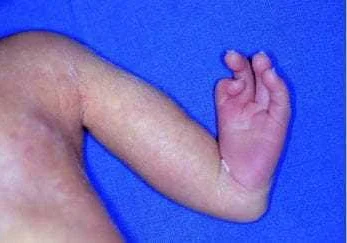
Missing or incompletely formed limbs can be caused by a variety of genetic factors. These genetic factors can be inherited from parents or occur spontaneously during pregnancy.
One common genetic factor is a mutation in a gene that is responsible for limb development. This mutation can disrupt the normal formation of limbs, leading to missing or incomplete limbs. Genetic testing can help identify these mutations and provide information about the chances of passing them on to future generations.
Another genetic factor is chromosomal abnormalities. Certain chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome or Turner syndrome, can increase the risk of missing or incompletely formed limbs. These abnormalities can affect the development of various body systems, including the limbs.
Furthermore, some genetic syndromes are associated with missing or incompletely formed limbs. For example, Amelia and Phocomelia are genetic syndromes characterized by the absence of one or more limbs. These syndromes can be caused by mutations in specific genes or chromosomal abnormalities.
Genetic counseling and testing are important for individuals and families affected by missing or incompletely formed limbs. They can provide information about the underlying genetic factors, help determine the risks of recurrence in future pregnancies, and guide treatment and support options.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a significant role in the development of missing or incompletely formed limbs. These factors can include exposure to certain chemicals, toxins, or drugs during pregnancy. For example, studies have shown that exposure to thalidomide, a medication used in the 1950s and 1960s to treat morning sickness, can lead to limb abnormalities in infants.
In addition to chemical exposures, certain infections during pregnancy can also increase the risk of limb malformations. For instance, rubella (German measles) infection during the first trimester has been linked to a higher incidence of limb defects in newborns.
Other environmental factors that may contribute to the development of missing or incompletely formed limbs include maternal smoking, alcohol consumption, and poor nutrition during pregnancy. Smoking and alcohol use have been associated with an increased risk of limb malformations. Nutritional deficiencies, such as a lack of folic acid, can also impact limb development.
It is important for expectant mothers to be aware of these environmental factors and take steps to minimize their exposure. This can include avoiding certain medications and chemicals, practicing good hygiene to prevent infections, and following a healthy diet rich in essential nutrients.
| Exposure to thalidomide | Rubella infection | Smoking during pregnancy | Lack of folic acid |
| Other medications, toxins, or drugs | Other infections | Alcohol consumption during pregnancy | Poor nutrition during pregnancy |
By understanding the role of environmental factors in limb development, healthcare professionals can provide appropriate support and education to expectant mothers, helping to minimize the risk of missing or incompletely formed limbs in newborns.
Developmental Disorders
Developmental disorders are a group of conditions that affect the normal growth and development of a person’s body. These disorders can result in missing or incompletely formed limbs. They can be caused by genetic factors, environmental factors, or a combination of both.
One common developmental disorder is called Amelia, which is the absence of one or more limbs. Another disorder is called Meromelia, which is the partial absence of a limb. These disorders can occur in isolation or as part of a larger syndrome.
Developmental disorders can have a significant impact on a person’s life. They can affect their ability to perform daily activities, such as dressing, eating, or writing. They can also impact their mobility and independence.
Treatment for developmental disorders varies depending on the specific condition and its severity. In some cases, prosthetic limbs or assistive devices can be used to improve function and mobility. Physical therapy and occupational therapy may also be helpful in developing skills and adapting to living with a limb difference.
It is important for individuals with developmental disorders to have access to support and resources. Support groups, counseling, and educational programs can provide valuable information and emotional support. These resources can also help individuals and their families navigate the challenges and opportunities that come with a limb difference.
Treatment for Missing or Incompletely Formed Limbs
Treatment for individuals with missing or incompletely formed limbs can vary depending on the specific condition and the individual’s needs. The main goal of treatment is to improve functionality, mobility, and quality of life for the affected individual.
One common treatment option is the use of prosthetics. Prosthetic limbs can help individuals with missing limbs regain some degree of mobility and independence. These artificial limbs are custom-made to fit the individual’s body and are designed to mimic the movement and function of a natural limb as closely as possible.
In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to address the underlying cause of the limb abnormality or to improve functionality. These surgeries can range from minor procedures, such as tendon transfers, to more complex reconstructive surgeries.
Physical and occupational therapy are also important components of treatment for missing or incompletely formed limbs. These therapies focus on strengthening and conditioning the muscles surrounding the affected limb, as well as teaching individuals how to use their limbs effectively in daily activities.
Additionally, individuals with missing or incompletely formed limbs may benefit from psychological support and counseling. Dealing with a limb abnormality can be emotionally challenging, and having a support system in place can help individuals cope with any psychological or social difficulties they may face.
It is important to note that treatment for missing or incompletely formed limbs is highly individualized. It is essential for individuals to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses their unique needs and goals.