MRI of the liver with contrast
Содержимое
MRI of the liver with contrast is a diagnostic imaging technique that uses a contrast agent to enhance the visibility of liver structures and detect abnormalities. This non-invasive procedure helps in the evaluation of liver diseases, such as tumors, cysts, and infections, providing detailed information for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
The liver is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in our overall health and well-being. It is responsible for various important functions, including filtering toxins from the blood, producing bile to aid in digestion, and storing essential vitamins and minerals. When there is a problem with the liver, it is essential to accurately diagnose and assess the extent of the condition. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) with contrast is a powerful diagnostic tool that can provide detailed images of the liver, helping doctors to better understand and manage various liver diseases.
MRI with contrast involves the use of a special dye called a contrast agent that is injected into the patient’s bloodstream before the scan. This contrast agent helps to enhance the visibility of certain structures and tissues in the liver, making it easier for doctors to identify abnormalities. During the scan, a strong magnetic field and radio waves are used to create detailed images of the liver and surrounding areas. These images can reveal important information about the liver’s size, shape, and overall function, as well as detect any signs of tumors, inflammation, or abnormal blood vessels.
So why is MRI of the liver with contrast important? Firstly, it provides valuable information that can help doctors diagnose various liver conditions accurately. For example, MRI with contrast can help identify and differentiate between different types of liver tumors, such as hepatocellular carcinoma and metastatic liver cancer. Additionally, it can help determine the stage and extent of liver diseases, such as cirrhosis or fatty liver disease, which can guide treatment decisions and prognosis. Moreover, MRI with contrast is a non-invasive procedure that does not involve exposure to ionizing radiation, making it a safe option for patients, including those who may have contraindications for other imaging techniques.
In conclusion, MRI of the liver with contrast is a valuable diagnostic tool that can provide detailed images of the liver and aid in the accurate diagnosis and management of various liver diseases. By enhancing the visibility of certain structures and tissues, MRI with contrast allows doctors to gather essential information about the liver’s size, shape, and function, as well as detect any abnormalities. Not only does it help in diagnosing conditions such as liver tumors and cirrhosis, but it is also a safe and non-invasive procedure. With the help of MRI with contrast, doctors can make more informed decisions about the treatment and prognosis of their patients with liver diseases.
Understanding MRI
MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, is a noninvasive medical imaging technique that uses magnetism, radio waves, and a computer to produce detailed images of the body’s internal structures. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, which use ionizing radiation, MRI uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to create images.
During an MRI scan, the patient lies on a table that is moved into the MRI machine. The machine contains a large magnet, which creates a magnetic field around the patient’s body. Radio waves are then used to manipulate the magnetic field and create images of the body’s tissues and organs.
One of the key advantages of MRI is its ability to provide clear and detailed images of soft tissues, such as the liver. This is particularly important in the case of liver imaging, as it allows healthcare providers to detect tumors, cysts, and other abnormalities that may not be visible with other imaging techniques.
MRI of the liver with contrast involves the use of a contrast agent, which is typically a dye that is injected into the patient’s bloodstream. This contrast agent helps to enhance the visibility of certain structures or abnormalities in the liver, making it easier for healthcare providers to make an accurate diagnosis.
In conclusion, understanding how MRI works is important for patients and healthcare providers alike. MRI allows for detailed imaging of the body’s internal structures, including the liver, and the use of contrast agents can further enhance the visibility of certain abnormalities. By providing clear and accurate images, MRI plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and treatment of various conditions.
Importance of Contrast
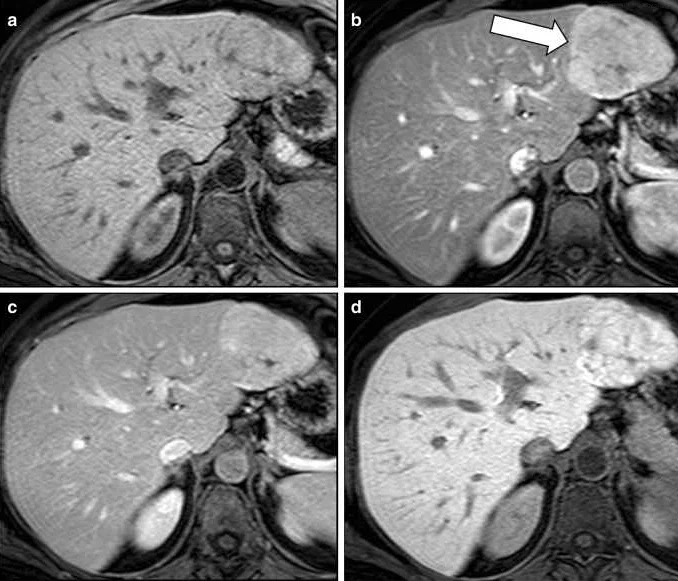
An MRI of the liver with contrast is an important diagnostic tool that allows for enhanced imaging of the liver. By using a contrast agent, such as gadolinium, the radiologist can better visualize the blood vessels, organs, and tissues in the liver.
The contrast agent helps to highlight areas of concern, such as tumors or lesions, making them more distinguishable from the surrounding healthy tissue. This allows for a more accurate assessment of the liver’s condition and the ability to detect abnormalities that may not be visible on a non-contrast MRI.
In addition to aiding in the detection of liver abnormalities, a contrast-enhanced MRI can also help in the planning and monitoring of treatment. The improved visualization provided by the contrast agent can assist in guiding procedures such as biopsies or surgeries, allowing for more precise targeting and a better understanding of the extent of the disease.
It is important to note that not all liver MRI exams require contrast. The decision to use contrast is based on the specific clinical scenario and the information needed by the healthcare provider. Your healthcare team will determine if a contrast-enhanced MRI is necessary for your particular situation.
While a contrast-enhanced MRI of the liver can provide valuable information, it is essential to discuss the risks and benefits with your healthcare provider before the procedure. Some individuals may have allergies or other conditions that make the use of contrast agents potentially unsafe. Your healthcare provider will consider these factors and determine the most appropriate course of action for your specific situation.
Overall, the use of contrast in an MRI of the liver plays a crucial role in improving the accuracy and diagnostic capabilities of the imaging exam. It allows for better visualization of the liver and helps to detect and monitor liver abnormalities, aiding in the provision of optimal patient care.
How MRI with Contrast Works
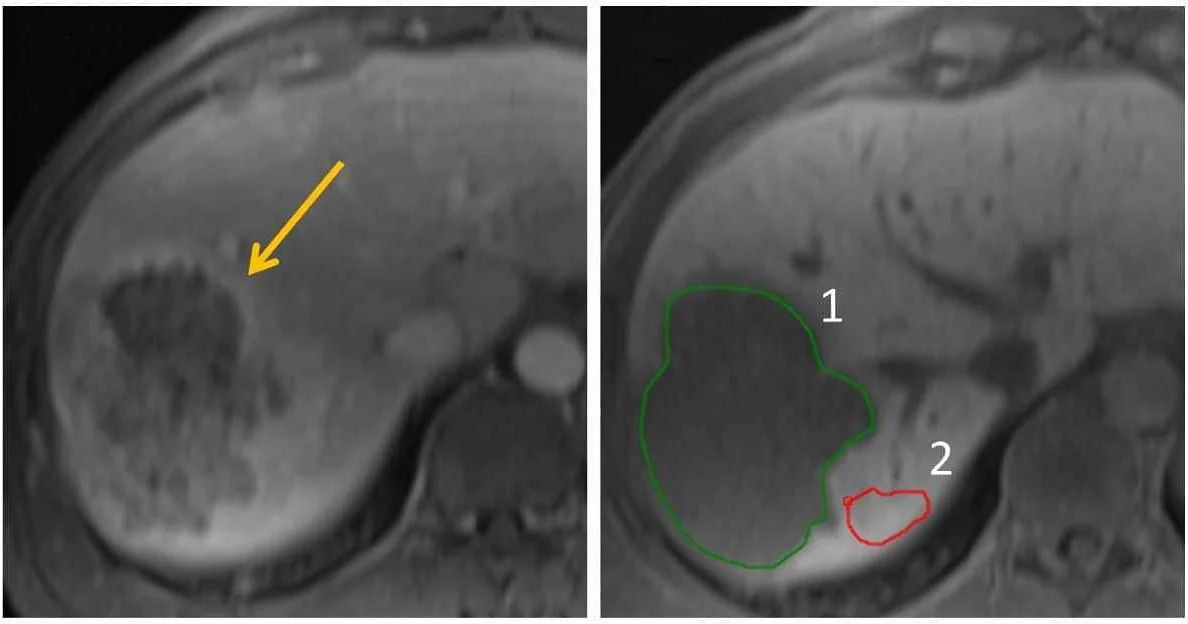
MRI with contrast is a diagnostic imaging technique that uses a contrast agent to enhance the visibility of certain structures or abnormalities in the liver. This procedure helps doctors identify and diagnose liver diseases, such as tumors, cysts, or areas of inflammation.
The contrast agent used in MRI is typically a gadolinium-based substance that is injected into the patient’s bloodstream prior to the scan. Gadolinium is a paramagnetic substance, which means it interacts with the magnetic field of the MRI machine and produces a signal that can be detected by the scanner.
Once the contrast agent is injected, it circulates throughout the body and accumulates in certain tissues or blood vessels, depending on the specific characteristics of the liver disease being evaluated. The contrast agent helps highlight these areas of interest, making them easier to identify and analyze.
During the MRI scan, the patient lies on a table that slides into a cylindrical machine. The machine generates a strong magnetic field and pulses of radio waves, which cause the hydrogen atoms in the body’s tissues to align and then realign. As the atoms realign, they emit signals that are detected by the scanner and converted into detailed images of the liver.
The injected contrast agent enhances the signal from the liver and surrounding structures, providing a clearer and more detailed view of any abnormalities. This allows radiologists to accurately diagnose and stage liver diseases, determine treatment options, and monitor the effectiveness of therapies.
| 1. Provides excellent soft tissue contrast. | 1. Not suitable for patients with severe kidney problems. |
| 2. Non-invasive and does not involve ionizing radiation. | 2. Allergic reactions to the contrast agent can occur, although rare. |
| 3. Can detect subtle changes in liver tissue. | 3. MRI with contrast may not be appropriate for all patients. |
| 4. Can provide multiplanar images for comprehensive evaluation. | 4. MRI with contrast can be more expensive compared to other imaging techniques. |
In conclusion, MRI with contrast is a valuable tool in the diagnosis and evaluation of liver diseases. By enhancing the visibility of abnormalities in the liver, it helps doctors make more accurate diagnoses and determine appropriate treatment options for their patients.
Benefits of MRI with Contrast
An MRI with contrast is a valuable tool in diagnosing and monitoring liver conditions. By using a contrast agent, the liver and any abnormalities can be highlighted, providing clear and detailed images for accurate diagnosis.
One of the main benefits of MRI with contrast is its ability to detect tumors and lesions in the liver. The contrast agent enhances the image of these abnormalities, making them easier to identify and evaluate. This is especially important for early detection of liver cancer, as early diagnosis can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
Additionally, MRI with contrast allows for better characterization of liver lesions. Differentiating between benign and malignant lesions can be challenging with conventional imaging techniques, but contrast-enhanced MRI provides additional information that aids in accurate diagnosis.
Furthermore, MRI with contrast is non-invasive and does not involve radiation exposure, making it a safe option for patients. This is particularly beneficial for individuals who require frequent imaging or those who cannot undergo other imaging modalities due to contraindications or allergies.
In conclusion, MRI with contrast offers many benefits in the evaluation of liver conditions. It provides detailed images, aids in the detection and characterization of liver tumors and lesions, and is a safe option for patients. These advantages make it an essential tool in the field of liver imaging.