Polysegmental pneumonia in adults
Содержимое
Polysegmental pneumonia in adults is a severe respiratory infection that affects multiple segments of the lungs. This article provides an overview of the causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention of polysegmental pneumonia. Learn about the risk factors and complications associated with this condition and find out when to seek medical attention. Stay informed about the latest research and medical advancements in the field of respiratory infections.
Pneumonia is a common respiratory infection that affects millions of adults worldwide. It is characterized by inflammation of the lungs, leading to symptoms such as coughing, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. While most cases of pneumonia are mild and can be easily treated, there are certain types that are more severe and require specialized care. One such type is polysegmental pneumonia, which affects multiple segments of the lungs simultaneously.
Polysegmental pneumonia is a serious condition that can have a significant impact on a person’s health. It is usually caused by bacterial or viral infections, such as Streptococcus pneumoniae or influenza. The infection spreads to multiple segments of the lungs, leading to widespread inflammation and damage. This can result in severe symptoms, including high fever, rapid breathing, and the production of large amounts of phlegm.
The diagnosis of polysegmental pneumonia is usually made based on a combination of symptoms, physical examination, and imaging tests, such as chest X-rays or CT scans. Treatment typically involves a combination of antibiotics to combat the underlying infection, as well as supportive care to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. In severe cases, hospitalization may be required to provide intensive care and ensure proper monitoring.
Prevention plays a crucial role in reducing the risk of polysegmental pneumonia. Vaccinations can help protect against common bacterial and viral infections that can cause pneumonia, such as the pneumococcal vaccine and the influenza vaccine. Good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing and avoiding close contact with sick individuals, can also help prevent the spread of infectious agents.
In conclusion, polysegmental pneumonia is a serious condition that affects multiple segments of the lungs and can lead to severe symptoms. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial for a successful recovery. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for polysegmental pneumonia, individuals can take steps to protect their respiratory health and reduce their risk of developing this condition.
Polysegmental Pneumonia in Adults
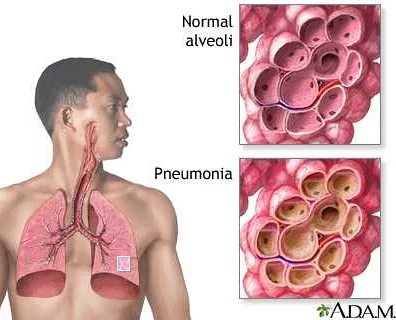
Polysegmental pneumonia in adults is a type of pneumonia that affects multiple segments of the lungs. It is characterized by inflammation and infection in two or more lobes of the lung.
This condition can be caused by various factors, including bacterial, viral, or fungal infections. Common pathogens associated with polysegmental pneumonia include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Staphylococcus aureus.
Patients with polysegmental pneumonia often experience symptoms such as coughing, shortness of breath, chest pain, and fever. The severity of symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause and the extent of lung involvement.
Diagnosis of polysegmental pneumonia is typically made through a combination of physical examination, chest X-ray, and laboratory tests. Imaging studies can reveal the presence of consolidation in multiple lung segments, while laboratory tests can help identify the causative organism.
Treatment for polysegmental pneumonia usually involves the use of antibiotics, antiviral medications, or antifungal drugs, depending on the identified pathogen. Supportive measures, such as rest, hydration, and pain management, are also important for recovery.
In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary for close monitoring and intravenous administration of medications. The prognosis for polysegmental pneumonia is generally good with prompt and appropriate treatment.
Preventive measures, such as vaccination against common pathogens, practicing good respiratory hygiene, and avoiding exposure to environmental pollutants, can help reduce the risk of developing polysegmental pneumonia.
In conclusion, polysegmental pneumonia in adults is a serious condition that requires timely diagnosis and treatment. Awareness of the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options is essential for managing this respiratory infection effectively.
Causes of Polysegmental Pneumonia
Polysegmental pneumonia can be caused by a variety of factors, including infectious agents, environmental exposures, and underlying health conditions.
Infectious Agents: Bacterial, viral, and fungal infections can all lead to polysegmental pneumonia. Common pathogens include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and Influenza viruses.
Environmental Exposures: Exposure to certain environmental factors can increase the risk of developing polysegmental pneumonia. These factors may include air pollution, cigarette smoke, and chemical irritants.
Underlying Health Conditions: People with certain underlying health conditions may be more susceptible to developing polysegmental pneumonia. These conditions can weaken the immune system and make it easier for infectious agents to cause pneumonia. Examples of such health conditions include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, diabetes, and heart disease.
Aspiration: Aspiration pneumonia occurs when foreign substances, such as food particles or gastric contents, are inhaled into the lungs. This can lead to inflammation and infection in multiple lung segments.
Immunosuppression: Individuals with weakened immune systems, either due to medications or medical conditions such as HIV/AIDS, are at a higher risk of developing polysegmental pneumonia.
It is important to identify the underlying cause of polysegmental pneumonia in order to provide appropriate treatment and prevent complications.
Symptoms of Polysegmental Pneumonia
Polysegmental pneumonia, also known as multi-segmental pneumonia, is a severe respiratory infection that affects multiple segments of the lungs. The symptoms of this condition can vary but typically include:
|
|
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention as polysegmental pneumonia can be a serious and potentially life-threatening condition. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial for a better outcome.
Treatment Options for Polysegmental Pneumonia
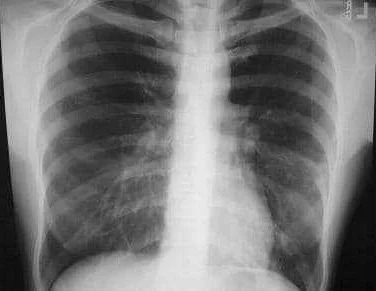
Polysegmental pneumonia is a serious condition that requires prompt and appropriate treatment. The choice of treatment options depends on the underlying cause of the pneumonia, the severity of the symptoms, and the patient’s overall health.
1. Antibiotics: Antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment for bacterial pneumonia, which is the most common cause of polysegmental pneumonia. The type of antibiotic prescribed will depend on the specific bacteria causing the infection. It is important to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by the healthcare provider.
2. Antiviral medications: If the pneumonia is caused by a viral infection, antiviral medications may be prescribed. These medications can help reduce the severity and duration of the symptoms, but they are not effective against bacteria.
3. Respiratory support: In severe cases of polysegmental pneumonia, respiratory support may be necessary. This can include the use of supplemental oxygen, mechanical ventilation, or other methods to help the patient breathe more easily.
4. Fluids and rest: It is important for patients with polysegmental pneumonia to stay hydrated and get plenty of rest. Adequate fluids can help thin mucus and make it easier to cough up, while rest allows the body to heal and recover.
5. Pain relievers and fever reducers: Over-the-counter pain relievers and fever reducers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help alleviate discomfort and reduce fever associated with polysegmental pneumonia. However, it is important to follow the recommended dosage and consult a healthcare provider if symptoms worsen or persist.
6. Follow-up care: After initial treatment, it is important for patients with polysegmental pneumonia to follow up with their healthcare provider. This allows for monitoring of symptoms, evaluation of treatment effectiveness, and adjustment of the treatment plan if necessary.
Note: This article is for informational purposes only and should not replace the advice of a healthcare professional. If you suspect you have polysegmental pneumonia, seek medical attention immediately.
Prevention of Polysegmental Pneumonia
Polysegmental pneumonia is a serious condition that can be caused by various factors, including viral and bacterial infections. While it may not always be possible to prevent polysegmental pneumonia, there are several steps that individuals can take to reduce their risk of developing the condition.
1. Vaccinations: Getting vaccinated against common respiratory infections, such as influenza and pneumonia, can significantly lower the risk of polysegmental pneumonia. Vaccinations can help the immune system recognize and fight off specific pathogens, reducing the likelihood of developing severe respiratory infections.
2. Good hygiene practices: Practicing good hygiene, such as regular handwashing with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand sanitizers, can help prevent the transmission of respiratory infections. Avoiding close contact with individuals who have respiratory symptoms and covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing can also help reduce the risk of infection.
3. Healthy lifestyle choices: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can boost the immune system and reduce the risk of developing infections. This includes eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, getting enough sleep, managing stress levels, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
4. Avoiding exposure to pollutants: Exposure to pollutants, such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, and occupational hazards, can increase the risk of developing respiratory infections. Minimizing exposure to these pollutants is essential in preventing polysegmental pneumonia and other respiratory conditions.
5. Regular check-ups: Regular medical check-ups can help identify any underlying health conditions or risk factors that may contribute to the development of polysegmental pneumonia. It is important to seek medical advice if experiencing persistent respiratory symptoms or if at higher risk due to age or pre-existing health conditions.
While these preventive measures can reduce the risk of polysegmental pneumonia, it is important to remember that no prevention strategy is foolproof. It is always advisable to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and recommendations based on individual circumstances.