Preoperative assessment
Содержимое
Preoperative assessment is the evaluation of a patient’s physical and medical condition prior to surgery. It involves a comprehensive examination and testing to determine the patient’s fitness for the procedure, identify any potential risks or complications, and develop an appropriate plan for anesthesia and postoperative care. This article provides an overview of the preoperative assessment process and its importance in ensuring safe and successful surgical outcomes.
Before undergoing surgery, a comprehensive preoperative assessment is essential to ensure the safety and success of the procedure. This assessment involves a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. The goal is to identify any potential risks or complications that may arise during or after surgery, and to develop a personalized plan for anesthesia and perioperative care.
One of the key steps in the preoperative assessment is obtaining a detailed medical history. This includes information about the patient’s current medications, allergies, previous surgeries, and any underlying medical conditions such as diabetes or heart disease. It is important to identify any factors that may increase the patient’s risk for surgical complications, such as smoking, obesity, or a history of blood clots.
In addition to the medical history, a thorough physical examination is necessary to assess the patient’s overall health and fitness for surgery. This includes evaluating the patient’s vital signs, checking for any signs of infection or other abnormalities, and assessing the patient’s lung and heart function. Any findings that may affect the surgical outcome, such as an elevated blood pressure or a heart murmur, should be further investigated and managed prior to surgery.
Diagnostic tests are another important component of the preoperative assessment. These may include blood tests, imaging studies such as X-rays or CT scans, and electrocardiograms (ECGs) to evaluate the patient’s cardiac function. These tests can help identify any underlying conditions that may impact the surgical procedure, such as anemia or an abnormal heart rhythm. Based on the results of these tests, the surgical team can make informed decisions about the best approach for anesthesia and perioperative care.
In conclusion, a comprehensive preoperative assessment is crucial in ensuring the safety and success of any surgical procedure. By thoroughly evaluating the patient’s medical history, conducting a physical examination, and performing necessary diagnostic tests, the surgical team can identify and manage any potential risks or complications. This personalized approach allows for optimal anesthesia and perioperative care, leading to better surgical outcomes and improved patient satisfaction.
Preoperative Assessment: Key Steps and Considerations for Surgery
When preparing for surgery, a thorough preoperative assessment is crucial to ensure the safety and success of the procedure. This assessment involves a series of key steps and considerations that help to identify any potential risks or complications that may arise during surgery.
One of the first steps in the preoperative assessment is the collection of a patient’s medical history. This includes information about any past surgeries, medical conditions, and medications that the patient may be taking. It is important to gather as much detail as possible, as certain medications or conditions may increase the risk of complications during surgery.
Another important aspect of the preoperative assessment is a physical examination. This allows the healthcare team to evaluate the patient’s overall health and identify any potential issues that may require further investigation or treatment before the surgery. The physical examination may include checking the patient’s vital signs, assessing their cardiovascular and respiratory systems, and conducting a general examination of their overall health.
In addition to the medical history and physical examination, preoperative testing is often conducted to further assess the patient’s health status. This may include blood tests, imaging studies (such as X-rays or MRI scans), and other diagnostic procedures. These tests can help to identify any underlying conditions or abnormalities that may impact the surgical procedure or its outcomes.
| Collect medical history | Evaluate risk factors |
| Perform physical examination | Assess overall health status |
| Conduct preoperative tests | Identify underlying conditions |
| Evaluate anesthesia needs | Ensure appropriate anesthesia plan |
| Review surgical consent | Ensure patient understanding and agreement |
| Provide preoperative instructions | Prevent complications and ensure patient compliance |
Furthermore, the preoperative assessment includes an evaluation of the patient’s anesthesia needs. This involves assessing the patient’s tolerance for anesthesia and developing an appropriate anesthesia plan for the surgery. The anesthesia team will review the patient’s medical history and perform additional tests if necessary to ensure a safe administration of anesthesia.
Before the surgery, it is important to review the surgical consent with the patient. This ensures that the patient understands the risks, benefits, and alternatives associated with the procedure. The surgical consent process also allows the patient to ask any questions or voice any concerns they may have before proceeding with the surgery.
Finally, the preoperative assessment involves providing the patient with preoperative instructions. These instructions may include guidelines for fasting, medication management, and other preoperative preparations. Following these instructions is essential for preventing complications and ensuring a successful surgery.
In conclusion, a thorough preoperative assessment is essential for the safe and successful completion of a surgical procedure. By following the key steps and considerations outlined in this assessment, healthcare professionals can identify any potential risks or complications and take the necessary steps to mitigate them.
Importance of Preoperative Assessment
Preoperative assessment plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and success of surgical procedures. It involves a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, physical condition, and the specific requirements of the planned surgery. This assessment helps to identify any potential risks or complications that may arise during or after the surgery.
One of the key benefits of preoperative assessment is the ability to optimize the patient’s overall health prior to the surgery. By identifying and addressing any underlying medical conditions or lifestyle factors that could impact the surgery, healthcare professionals can take necessary measures to minimize risks and enhance surgical outcomes.
Furthermore, preoperative assessment allows for the identification of any specific precautions or additional tests that may be required before the surgery. This ensures that the patient is well-prepared and that all necessary resources are available to support a smooth surgical process.
Another important aspect of preoperative assessment is the evaluation of the patient’s mental and emotional well-being. Surgery can be a stressful and anxiety-inducing experience, and addressing any fears or concerns beforehand can significantly improve the patient’s experience and overall satisfaction.
In summary, preoperative assessment is a critical step in the surgical process. It helps to ensure the safety and success of the procedure by identifying and addressing any potential risks or complications. By optimizing the patient’s health, addressing any specific requirements, and addressing mental and emotional well-being, preoperative assessment plays a vital role in facilitating a positive surgical experience for the patient.
Patient History and Physical Examination
Obtaining a comprehensive patient history and conducting a thorough physical examination are essential steps in the preoperative assessment process. This information helps to gather important baseline data, identify potential risks, and tailor an individualized plan of care for the patient.
The patient history should include a detailed account of the patient’s medical, surgical, and medication history. It is important to inquire about any chronic medical conditions, previous surgeries, allergies, and current medications. Additionally, any family history of surgical complications or anesthesia-related issues should be documented.
During the physical examination, the surgeon and anesthesiologist will assess the patient’s general appearance, vital signs, and overall physical health. This includes evaluating the patient’s cardiovascular system, respiratory system, and neurological status. Special attention should be paid to any abnormalities or potential contraindications for surgery.
Furthermore, the physical examination may involve specific assessments based on the planned surgical procedure. For example, if the patient is undergoing abdominal surgery, the surgeon may perform a focused abdominal examination to assess for any pre-existing hernias or other pathologies.
In addition to the patient history and physical examination, it is important to review any relevant diagnostic tests, such as laboratory results or imaging studies. These tests can provide further insight into the patient’s overall health and help guide the perioperative management plan.
In summary, obtaining a detailed patient history and conducting a thorough physical examination are key steps in the preoperative assessment process. This information, along with any relevant diagnostic tests, helps to identify potential risks and develop an individualized plan of care for the surgical patient.
Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests
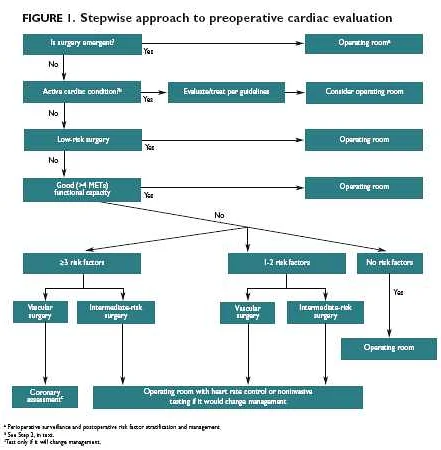
Before undergoing surgery, patients typically undergo a series of laboratory and diagnostic tests to assess their overall health and ensure they are prepared for the procedure. These tests provide valuable information to the surgical team and help guide decision-making.
Some common laboratory tests that may be ordered include:
- Complete blood count (CBC): This test measures various components of the blood, such as red and white blood cells, hemoglobin, and platelets. It can help identify potential anemia, infection, or other blood-related conditions.
- Electrolyte panel: This test measures the levels of important electrolytes in the blood, such as sodium, potassium, and calcium. Imbalances in electrolyte levels can affect various bodily functions and may need to be corrected prior to surgery.
- Liver function tests: These tests assess the health and function of the liver by measuring levels of enzymes, proteins, and other substances. Abnormal liver function can indicate underlying liver disease or dysfunction.
- Renal function tests: These tests evaluate kidney function by measuring levels of creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and other markers. Impaired kidney function can impact the body’s ability to process and eliminate medications used during surgery.
In addition to laboratory tests, diagnostic imaging may also be ordered to provide further information about a patient’s condition. Common diagnostic tests include:
- X-rays: X-rays use radiation to create images of the body’s internal structures. They can help identify bone fractures, abnormalities, or the presence of foreign objects.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan: CT scans use a series of X-ray images to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. They can provide information about the size, shape, and location of abnormalities or tumors.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the body’s organs and tissues. It can be particularly useful for evaluating soft tissues and identifying abnormalities.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the body’s internal structures. It is commonly used to assess organs like the liver, kidneys, and gallbladder and can help identify abnormalities or blockages.
These laboratory and diagnostic tests, along with a thorough medical history and physical examination, provide important information to the surgical team and help ensure that patients are prepared for surgery. They can help identify any potential risks or complications and guide the development of an appropriate surgical plan.