Understanding the Causes and Treatment of Prostatitis Pain in Men
Содержимое
Learn about the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for prostatitis pain in men. Find out how to manage and alleviate the discomfort associated with this condition.
If you’re a man experiencing discomfort and pain in your pelvic region, you may be suffering from prostatitis. This condition occurs when the prostate gland becomes inflamed, causing a variety of symptoms that can significantly impact your quality of life.
Causes: Prostatitis can be caused by various factors, including bacterial infections, autoimmune disorders, and nerve damage. It can also develop as a result of previous urinary tract infections or prostate procedures.
Symptoms: Common symptoms of prostatitis include pain or burning sensation during urination, frequent urination, difficulty urinating, pain in the groin or lower back, and sexual dysfunction. These symptoms can be debilitating and affect your daily activities.
Treatment: If you suspect you have prostatitis, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly. Your healthcare provider will evaluate your symptoms, conduct tests if necessary, and develop a personalized treatment plan. Treatment options may include antibiotics, pain relievers, alpha-blockers, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
Don’t let prostatitis pain control your life. Take the first step towards relief by seeking proper diagnosis and treatment. Remember, early intervention is key to managing this condition effectively and improving your overall well-being.
Understanding Prostatitis
Prostatitis is a condition that affects the prostate gland, a small gland located just below the bladder in men. It is characterized by inflammation and swelling of the prostate, which can cause a range of symptoms and discomfort.
There are several types of prostatitis, including acute bacterial prostatitis, chronic bacterial prostatitis, chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS), and asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis. Each type has its own causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Acute bacterial prostatitis is caused by a bacterial infection in the prostate gland. It can cause symptoms such as fever, chills, pain or burning during urination, frequent urination, and pain in the lower back or pelvic area. Treatment usually involves antibiotics to eliminate the infection.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis is a recurrent infection of the prostate gland. It can cause similar symptoms to acute bacterial prostatitis, but the symptoms are usually less severe. Treatment involves long-term antibiotic therapy.
CP/CPPS is the most common type of prostatitis. Its exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to be related to an autoimmune reaction or dysfunction of the pelvic nerves. Symptoms include pain or discomfort in the pelvis, lower back, or genitals, frequent urination, and pain or discomfort during ejaculation. Treatment may involve a combination of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
Asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis is the least common type of prostatitis and often does not cause any symptoms. It is usually detected during routine medical tests. Treatment may not be necessary unless symptoms develop.
If you are experiencing any symptoms of prostatitis, it is important to see a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Prostatitis can be a chronic condition, but with the right management, symptoms can be controlled and quality of life can be improved.
Causes of Prostatitis Pain

Prostatitis pain in men can be caused by a variety of factors. These include:
| Bacterial Infection | Prostatitis can be caused by a bacterial infection, which occurs when bacteria enter the prostate gland. This can happen through the urethra or through the bloodstream. |
| Non-Bacterial Inflammation | Not all cases of prostatitis are caused by bacterial infection. In some cases, the inflammation of the prostate can be due to non-bacterial causes, such as an autoimmune reaction or chemical irritation. |
| Structural Abnormalities | Prostatitis pain can also be caused by structural abnormalities in the prostate gland or the urinary tract. These abnormalities can lead to blockages, urinary retention, and inflammation. |
| Sexually Transmitted Infections | Sexually transmitted infections can also contribute to prostatitis pain. Infections such as gonorrhea or chlamydia can spread to the prostate gland and cause inflammation and pain. |
| Urinary Tract Infections | Urinary tract infections (UTIs) can sometimes lead to prostatitis pain. Bacteria from a UTI can travel to the prostate gland and cause infection and inflammation. |
It’s important to identify the underlying cause of prostatitis pain in order to develop an effective treatment plan. If you are experiencing symptoms of prostatitis pain, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Identifying Symptoms of Prostatitis
To effectively manage and treat prostatitis, it is essential to be able to identify the symptoms associated with this condition. While the symptoms may vary depending on the type of prostatitis, there are several common signs to look out for:
| Urinary Problems | Prostatitis can cause various urinary issues such as frequent urination, difficulty starting or stopping urination, weak urine flow, and a feeling of incomplete bladder emptying. |
| Pelvic Pain | Many men with prostatitis experience pain or discomfort in the pelvic region, which can range from mild to severe. This pain may also radiate to the lower back, groin, or thighs. |
| Sexual Dysfunction | Prostatitis can lead to sexual problems including erectile dysfunction, painful ejaculation, and decreased sexual desire. |
| Flu-like Symptoms | In some cases, prostatitis may cause flu-like symptoms such as fever, chills, body aches, and fatigue. |
| Psychological Symptoms | Men with prostatitis may also experience psychological symptoms like anxiety, depression, and irritability. |
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a medical professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Early detection and intervention can help prevent complications and improve your overall quality of life.
Prostatitis Treatment Options
When it comes to treating prostatitis, there are several options available. The choice of treatment will depend on the underlying cause of the condition and the severity of the symptoms. Here are some common treatment options:
| 1. Antibiotics | Antibiotics are often prescribed to treat bacterial prostatitis. They work by killing the bacteria causing the infection and reducing inflammation in the prostate gland. It is important to take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by your healthcare provider. |
| 2. Alpha-blockers | Alpha-blockers are medications that help relax the muscles in the prostate gland and the bladder neck, making it easier to urinate. They can help relieve urinary symptoms associated with prostatitis, such as difficulty urinating and frequent urination. |
| 3. Pain Medications | If you are experiencing pain or discomfort due to prostatitis, your doctor may recommend pain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or acetaminophen, to help alleviate the symptoms. |
| 4. Physical Therapy | In some cases, physical therapy may be recommended to help relax the muscles and tissues in the pelvic area. This can help improve blood flow to the prostate gland and reduce pain and inflammation. |
| 5. Lifestyle Changes | Making certain lifestyle changes can also help manage the symptoms of prostatitis. This may include avoiding caffeine and alcohol, staying hydrated, practicing relaxation techniques, and avoiding prolonged sitting or cycling. |
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific condition. They can provide a comprehensive evaluation and help tailor a treatment strategy that will work best for you.
Preventing Prostatitis Pain
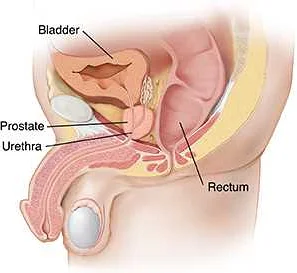
While there is no foolproof way to prevent prostatitis pain, there are several steps you can take to help reduce your risk. By adopting healthy habits and practicing good hygiene, you can significantly lower your chances of developing this condition. Here are some tips to help you prevent prostatitis pain:
- Practice safe sex: Engaging in safe sexual practices, such as using condoms and limiting the number of sexual partners, can help reduce your risk of contracting a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that may lead to prostatitis.
- Maintain good hygiene: Keep your genital area clean and dry. Wash your penis regularly with warm water and mild soap, and dry thoroughly afterward. Avoid using harsh soaps or products that may irritate the skin.
- Urinate regularly: Make sure to empty your bladder regularly, especially after sexual activity. Holding in urine for extended periods can increase the risk of bacterial growth and infection.
- Avoid urinary tract infections (UTIs): Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and promote regular urination. Urinate before and after sexual activity to flush out any bacteria that may have entered the urethra.
- Avoid prolonged sitting: Sitting for long periods, especially on hard surfaces, can put pressure on the prostate and contribute to inflammation. Take breaks and try to avoid sitting for extended periods.
- Stay physically active: Regular exercise helps improve blood circulation and overall prostate health. Engage in activities such as walking, jogging, or cycling to promote a healthy prostate.
- Eat a healthy diet: Incorporate a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins into your diet. Avoid excessive consumption of alcohol, caffeine, and spicy foods, as they can irritate the prostate.
- Manage stress: Chronic stress can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of developing prostatitis pain. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques, exercising, or seeking support from loved ones.
- Regular check-ups: Schedule regular visits with your healthcare provider to monitor your prostate health. Early detection of any potential issues can lead to prompt treatment and better outcomes.
By following these preventative measures, you can take an active role in reducing your risk of prostatitis pain. Remember, maintaining good overall health and hygiene is key to promoting a healthy prostate.