A 3D Printer in St. Petersburg Develops Human Tissue Printing Technology
Содержимое
A groundbreaking 3D printer has been created in St. Petersburg, Russia, which has the ability to print human tissue. This revolutionary technology has the potential to revolutionize the field of medicine by allowing scientists to create custom-made organs and tissues for transplantation.
In a groundbreaking development, scientists in St. Petersburg have unveiled a revolutionary 3D printer capable of printing human tissue. This cutting-edge technology promises to revolutionize the field of regenerative medicine and offer new hope to patients in need of organ transplants.
The 3D printer, developed by a team of experts at the prestigious St. Petersburg Research Institute, utilizes a unique bioink composed of living cells and a biocompatible polymer. This bioink is loaded into the printer, which then precisely deposits the cells layer by layer to create living tissue.
With this advanced printer, doctors will be able to create customized organs and tissues that are compatible with a patient’s body, eliminating the need for donors and reducing the risk of rejection. Furthermore, the printer has the potential to produce tissue at a much faster rate than traditional methods, making it a game-changer in the field of regenerative medicine.
Revolutionary 3D Printer in St. Petersburg
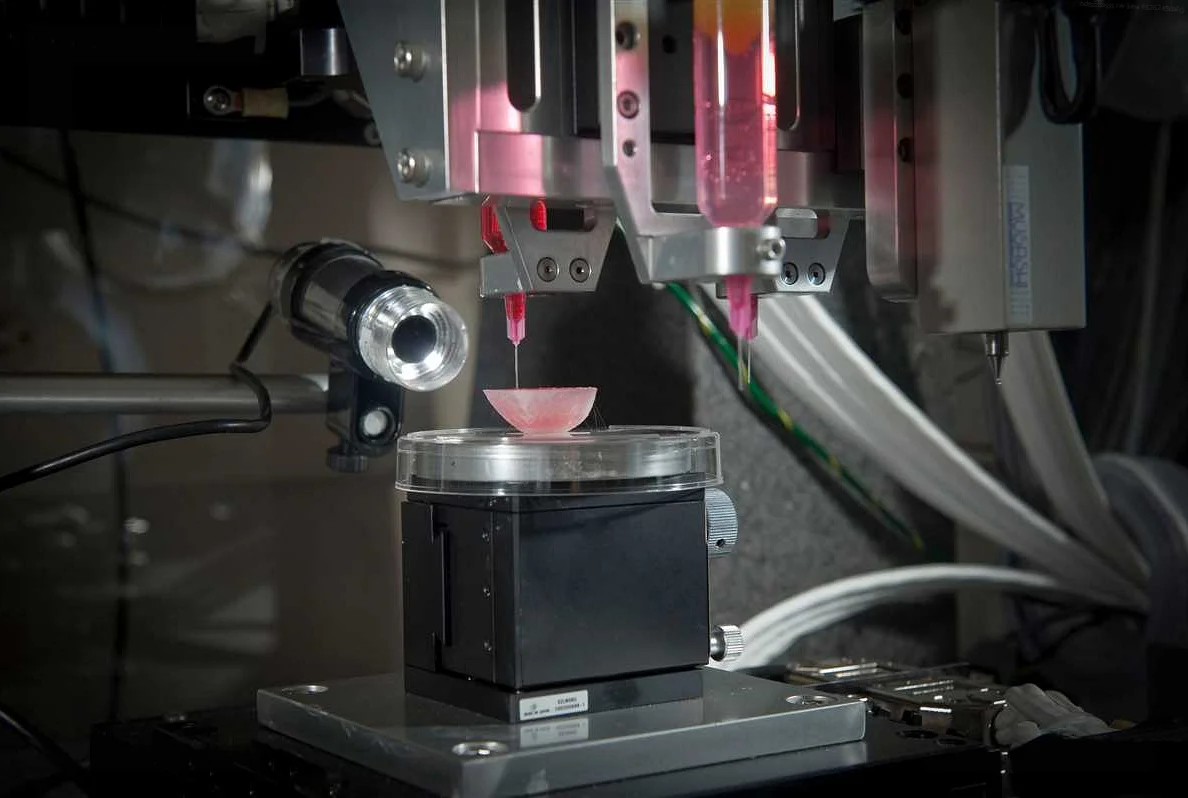

A new breakthrough in medical technology has emerged in St. Petersburg, Russia, where scientists have developed a revolutionary 3D printer capable of printing human tissue. This groundbreaking technology has the potential to revolutionize the field of medicine and transform the way we treat and replace damaged or diseased organs.
The 3D printer, developed by a team of scientists at the St. Petersburg Polytechnic University, uses a combination of bio-ink made from human stem cells and a specially designed scaffold to create intricate structures that closely resemble human tissue. The printer is capable of printing complex organs and tissues, including skin, cartilage, and even blood vessels.
This breakthrough technology not only offers hope for patients in need of organ transplants, but also provides a solution to the shortage of organ donors. By printing organs with a patient’s own stem cells, the risk of organ rejection is significantly reduced, making the transplantation process safer and more successful.
Furthermore, this 3D printer has the potential to advance the field of regenerative medicine, allowing scientists to study and test new therapies and treatments more efficiently. By printing human tissue, researchers can better understand the underlying mechanisms of diseases and develop targeted therapies that are more effective and personalized.
The development of this revolutionary 3D printer in St. Petersburg is a testament to the power of innovation and the potential of technology to improve and save lives. As this technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see more breakthroughs in the field of medicine and a brighter future for patients in need of organ replacements.
Prints Human Tissue

The revolutionary 3D printer in St. Petersburg has the capability to print human tissue, opening up a whole new world of possibilities in the field of medicine. This groundbreaking technology allows scientists and doctors to develop personalized solutions for patients, such as custom-made organs and tissues for transplant.
The printer uses a process known as bioprinting, where bioink, a mixture of living cells and biomaterials, is used as the “ink” to create the desired tissue or organ structure. The printer carefully deposits layer upon layer of bioink, following a precise design, to build the complex structures that make up human tissue.
This technology has the potential to revolutionize the field of regenerative medicine. It offers the ability to create organs and tissues that are perfectly matched to the recipient’s body, reducing the risk of rejection and creating more successful transplant outcomes. Additionally, 3D bioprinting can be used to produce tissue models for drug testing and disease research, allowing scientists to study and develop treatments more effectively.
While the technology is still in its early stages, the possibilities are promising. Researchers are optimistic that this revolutionary 3D printer will lead to significant advancements in medical science, bringing us closer to a future where custom-made organs and tissues are readily available.
State-of-the-Art Technology
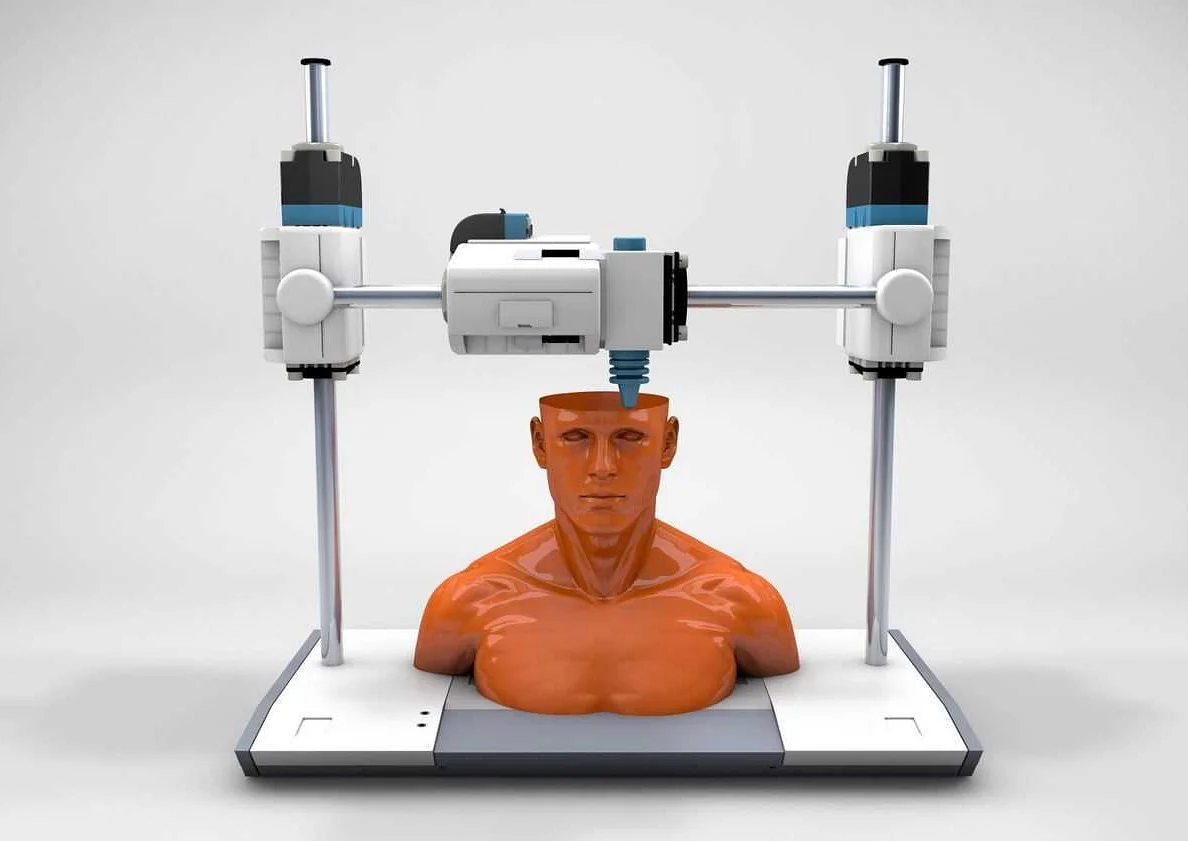
The revolutionary 3D printer in St. Petersburg represents the cutting-edge of biomedical technology. This state-of-the-art device utilizes advanced bioink formulations and precise printing techniques to create human tissue with incredible accuracy and detail.
One of the key features of this printer is its ability to print multiple types of cells simultaneously, allowing for the creation of complex tissues and organs. It also has the capability to print with a variety of biomaterials, such as hydrogels, which provide a scaffold for cell growth and development.
The printer’s high-resolution printing capabilities enable the production of intricate structures, including blood vessels and skin layers. This level of detail is crucial for creating functional tissues that closely resemble natural human tissue.
Furthermore, the printer is equipped with advanced imaging and scanning technology, which allows for precise mapping of patient-specific anatomy. This information can then be used to guide the printing process and ensure the creation of tissue that is tailored to each individual’s needs.
Overall, this state-of-the-art 3D printer is revolutionizing the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Its advanced capabilities and precision printing techniques offer new possibilities for the creation of functional human tissue, bringing us one step closer to the development of fully functional organs and personalized medical treatments.
Advancements in 3D Printing
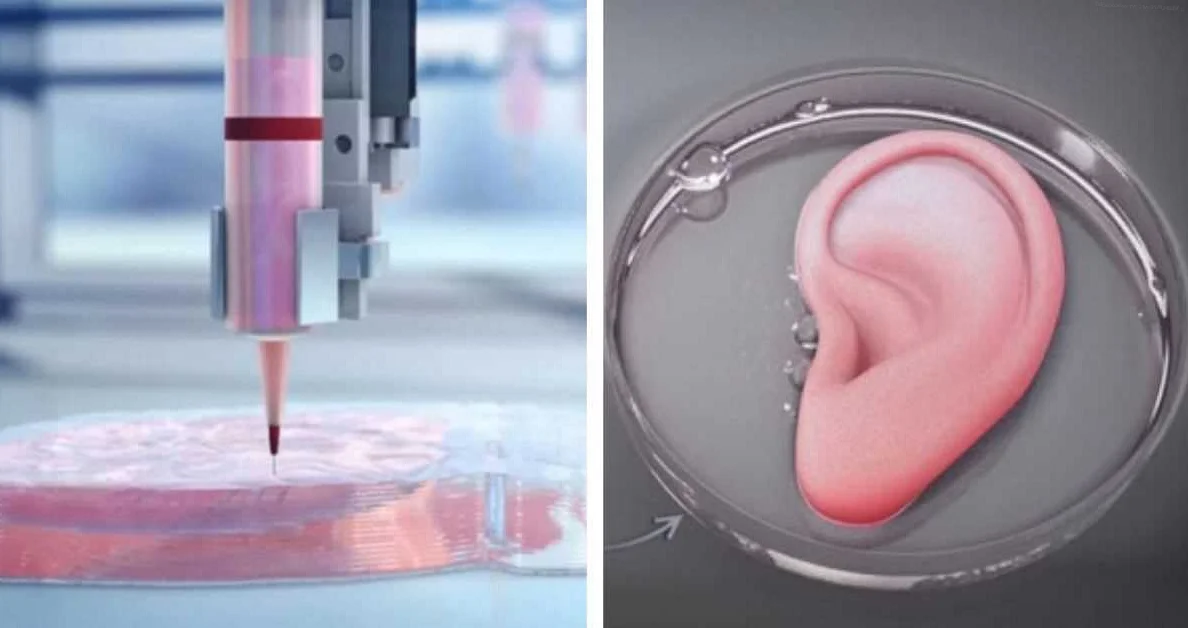
Over the past decade, there have been remarkable advancements in the field of 3D printing. This technology has revolutionized various industries, including healthcare, aerospace, and manufacturing. With its ability to create complex and customized objects, 3D printing has opened up new possibilities and has the potential to transform the way we design and produce things.
One of the most significant advancements in 3D printing is the ability to print human tissue. This breakthrough technology has the potential to redefine organ transplantation and revolutionize the medical field. By using a patient’s own cells, scientists can now 3D print organs and tissues that are a perfect match, eliminating the need for donors and the risk of rejection.
Another exciting advancement in 3D printing is the use of new materials. Initially limited to plastics, 3D printing can now be done with a wide range of materials, including metals, ceramics, and even food. This opens up new possibilities for manufacturing, allowing for the creation of stronger and more durable products.
Furthermore, the size and speed of 3D printers have greatly improved. What used to take hours or even days can now be done in a matter of minutes. This has led to increased productivity and efficiency in various industries, allowing for rapid prototyping and reduced production times.
Additionally, advancements in software and design tools have made it easier than ever to create intricate and complex objects. With the help of computer-aided design (CAD) software, designers can now create detailed 3D models that can be easily printed. This has opened up new possibilities for artists, architects, and engineers alike.
Overall, the advancements in 3D printing have had a significant impact on various industries and have the potential to revolutionize many more. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more groundbreaking applications and innovations in the future.
Groundbreaking Medical Applications
The revolutionary 3D printer in St. Petersburg has opened up a world of groundbreaking medical applications. Here are some of the most exciting possibilities:
- Organ Transplants: With the ability to print human tissue, this technology could revolutionize the field of organ transplants. Instead of waiting for a donor, patients could have their own organs printed, eliminating the need for immunosuppressant drugs and the risk of rejection.
- Customized Prosthetics: The 3D printer can create personalized prosthetics that are perfectly fitted to an individual’s body. This not only improves comfort and functionality but also reduces the cost and time involved in creating prosthetic limbs.
- Bioprinted Skin: Burn victims and patients with severe skin conditions could benefit from the ability to print bioprinted skin. This technology could provide a faster and more efficient way to heal wounds and regenerate damaged tissue.
- Tumor Models: 3D printing can be used to create accurate tumor models, which can help doctors plan surgeries and determine the most effective treatment options for cancer patients. This could lead to more successful outcomes and improved patient care.
- Drug Testing: Researchers can use 3D bioprinting to create functional human tissue models for drug testing. This allows for more accurate and reliable testing, reducing the need for animal testing and providing a more ethical approach to drug development.
These groundbreaking medical applications are just the beginning. With further advancements in 3D printing technology, the possibilities for improving healthcare and saving lives are truly limitless.
Printing Human Organs
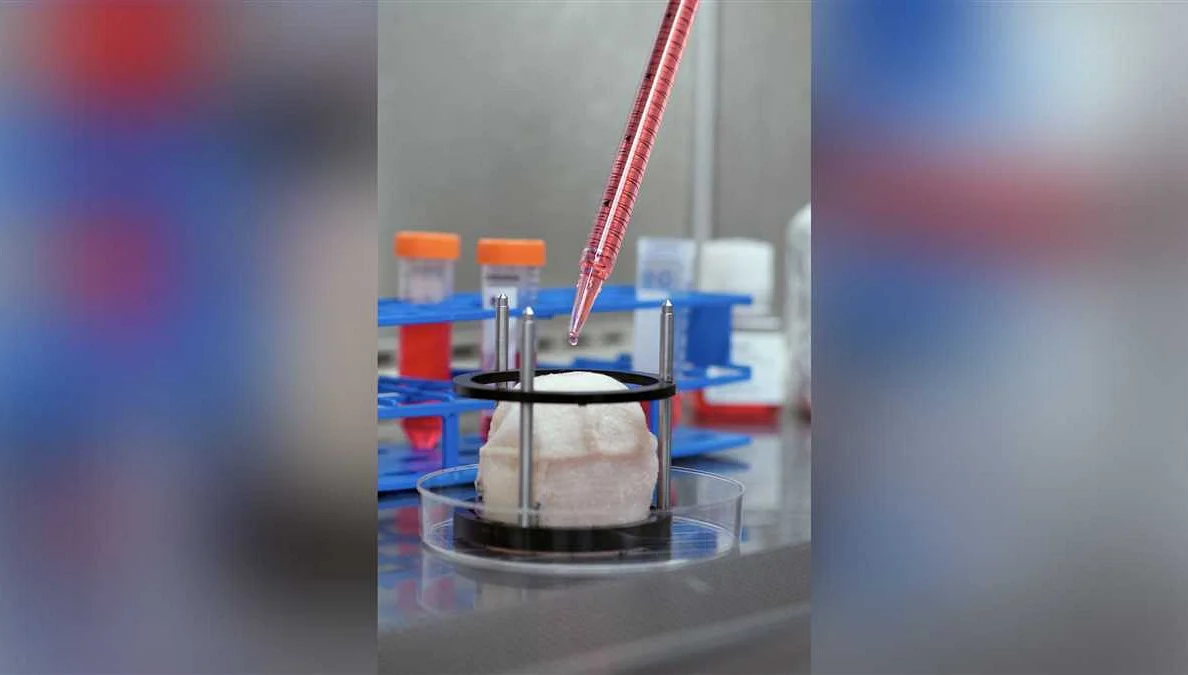

The revolutionary 3D printer in St. Petersburg is now capable of printing human organs. This groundbreaking technology has the potential to revolutionize the field of organ transplantation and save countless lives.
Using a combination of bioink and specialized cells, the 3D printer is able to create complex structures that mimic the functionality of human organs. These printed organs can be used for research and testing purposes, reducing the need for animal testing and ethical concerns.
The process of printing human organs begins with a detailed 3D model of the organ. The printer then carefully deposits layers of bioink, which contains living cells, to create the desired structure. Over time, these cells multiply and mature, creating a functional organ that can be transplanted into a patient.
One of the key advantages of 3D printed organs is that they can be customized to fit the specific needs of each patient. This personalized approach reduces the risk of organ rejection and increases the success rate of transplantation surgeries.
While the technology is still in its early stages, scientists and researchers are optimistic about its potential. The ability to print human organs has the potential to address the global organ shortage crisis and improve the quality of life for many patients.
However, challenges still remain. The process of printing complex organs with intricate vascular networks is still a major hurdle that researchers are working to overcome. Additionally, the long-term viability and functionality of printed organs need to be thoroughly tested before widespread implementation.
Despite these challenges, the development of 3D printed human organs is a major breakthrough in medical technology. It holds the promise of transforming the field of organ transplantation and offering hope to millions of patients worldwide.