Signs of Blood Clots: Important Symptoms of Thrombosis You Should Be Aware of
Содержимое
Learn the key symptoms of thrombosis and how to identify if you have a blood clot. Find out what signs to look for and when to seek medical attention to prevent serious health complications.
In today’s fast-paced world, it is essential to be aware of our health and recognize any potential signs of serious medical conditions. One such condition is thrombosis, a dangerous condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a blood vessel.
Thrombosis can occur in any part of the body, and its symptoms can vary depending on the location of the clot. If you suspect you may have a blood clot, it is crucial to recognize the signs and symptoms early to seek prompt medical attention and avoid any complications.
Common signs and symptoms of thrombosis include swelling, pain, and tenderness in the affected area. If you notice any sudden or unexplained swelling, especially in the legs or arms, it could be a sign of a blood clot. Additionally, if the area feels warm to the touch or is red or discolored, it may indicate a clotting issue.
Another symptom to be cautious of is persistent pain or discomfort. If you experience ongoing pain that does not seem to go away with rest or over-the-counter pain medication, it could be a sign of thrombosis. Pay close attention to any pain that worsens with movement or pressure, as it may suggest a blood clot.
Understanding Thrombosis
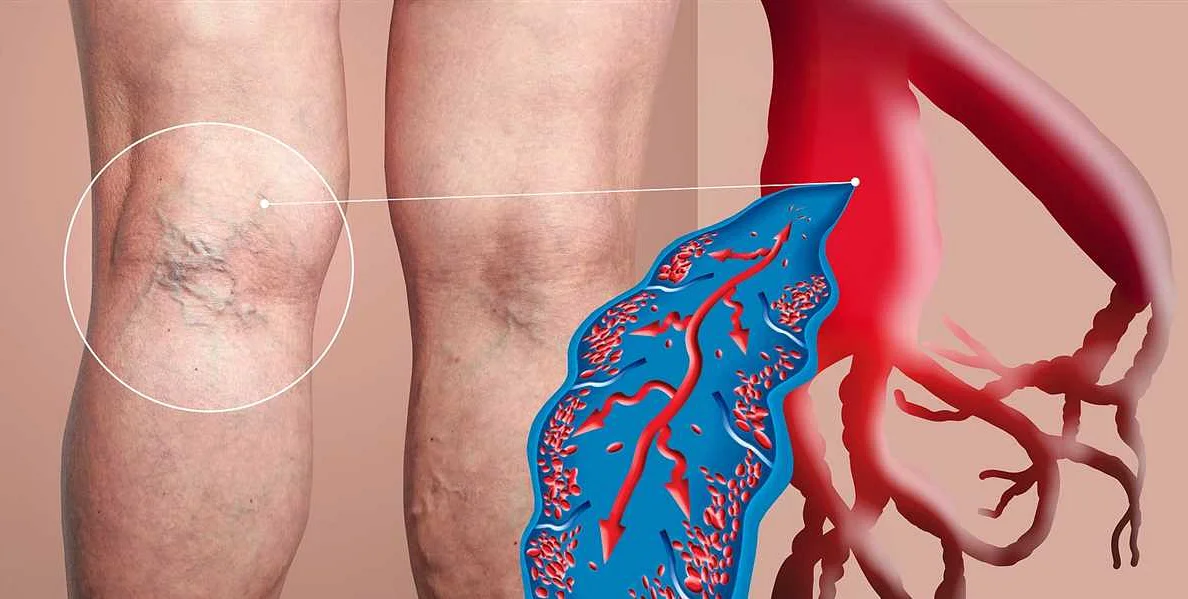
Thrombosis is a condition characterized by the formation of blood clots, also known as thrombi, within the blood vessels. These clots can obstruct blood flow and cause serious health complications if not promptly treated.
Thrombosis can occur in various parts of the body, including the deep veins of the legs (deep vein thrombosis), lungs (pulmonary embolism), brain (stroke), and heart (heart attack). It can also affect smaller blood vessels, leading to conditions such as retinal vein occlusion or peripheral artery disease.
There are several factors that can increase the risk of thrombosis, including genetic predisposition, prolonged immobility, certain medical conditions (such as cancer or heart disease), hormone therapy, pregnancy, and smoking. Additionally, surgeries, injuries, and long-distance travel can also contribute to the development of blood clots.
Common symptoms of thrombosis may include pain, swelling, and redness in the affected area. In the case of deep vein thrombosis, the leg may feel warm to the touch, and there may be visible veins. Other symptoms can vary depending on the location of the clot and may include shortness of breath, chest pain, confusion, and weakness.
If you experience any of these symptoms or suspect that you may have a blood clot, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and potentially save lives.
Understanding the signs and symptoms of thrombosis can help individuals recognize when they may be at risk and take appropriate measures to prevent blood clot formation. It is crucial to maintain a healthy lifestyle, engage in regular physical activity, avoid prolonged immobility, and discuss any concerns with a healthcare professional.
By understanding thrombosis, individuals can be proactive in protecting their health and reducing the risk of potentially serious complications associated with blood clots.
Overview of Thrombosis and its Impact on Health
Thrombosis is a medical condition characterized by the formation of blood clots within the blood vessels. These blood clots, also known as thrombi, can occur in both the veins and arteries and can have serious consequences on a person’s health.
When a blood clot forms in a vein, it can block the flow of blood, causing swelling, pain, and discoloration in the affected area. This condition, known as venous thrombosis, most commonly occurs in the deep veins of the legs, a condition called deep vein thrombosis (DVT). If a blood clot breaks free and travels to the lungs, it can block blood flow, resulting in a potentially life-threatening condition called pulmonary embolism.
Arterial thrombosis, on the other hand, occurs when a blood clot forms in an artery and restricts or blocks blood flow to an organ or body part. This can lead to serious complications, such as heart attacks or strokes. Arterial thrombosis can occur in various parts of the body, including the heart, brain, and legs.
Thrombosis can have a significant impact on a person’s health, ranging from mild discomfort to severe complications. If left untreated, blood clots can cause long-term damage to the affected organs and increase the risk of future clotting events. They can also lead to chronic conditions, such as post-thrombotic syndrome, which can cause pain, swelling, and skin ulcers.
It is important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of thrombosis to seek medical attention promptly. Common symptoms include swelling, pain, warmth, and redness in the affected area. Other warning signs may include shortness of breath, chest pain, and the sudden onset of severe headaches.
Preventing thrombosis involves making lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and avoiding prolonged periods of inactivity. In some cases, medication, such as anticoagulants or antiplatelet drugs, may be prescribed to reduce the risk of blood clot formation.
In conclusion, thrombosis is a serious medical condition that can have a significant impact on a person’s health. Understanding the signs and symptoms of thrombosis, as well as adopting a healthy lifestyle, can help prevent and manage this condition effectively. If you experience any symptoms or are at high risk for thrombosis, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment.
Common Causes of Thrombosis
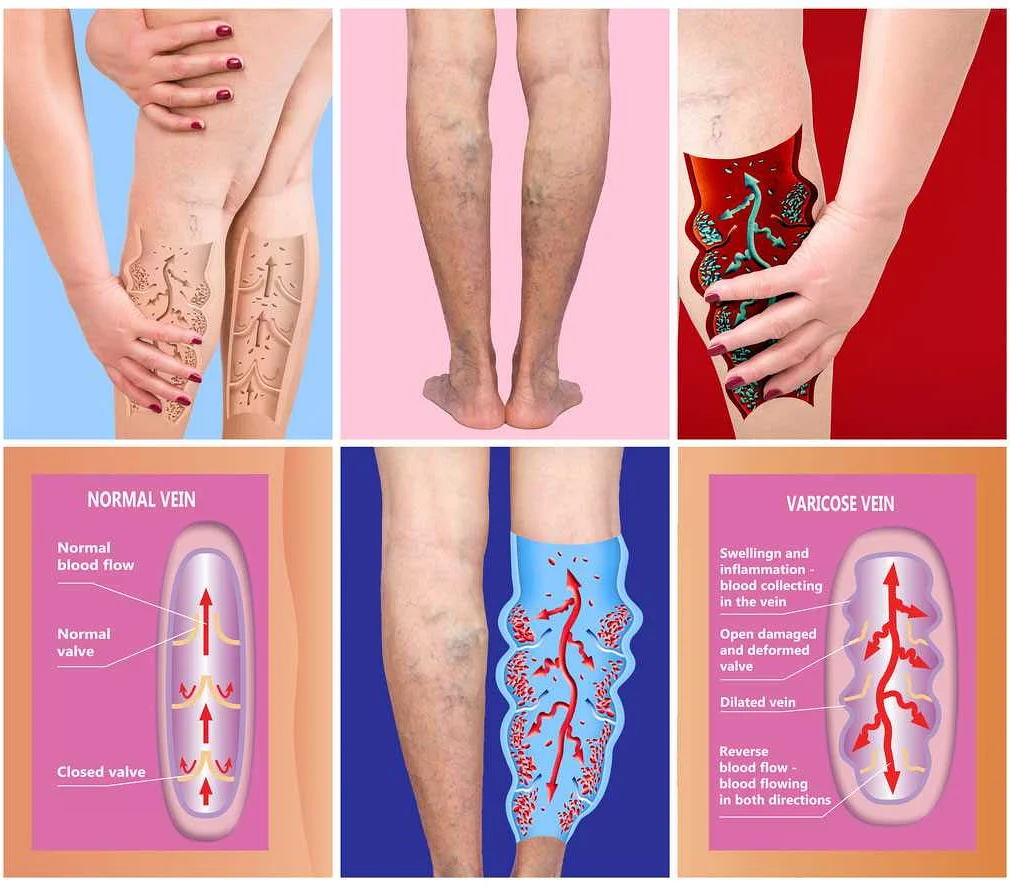
Thrombosis is a condition characterized by the formation of blood clots within the blood vessels. Several factors can contribute to the development of thrombosis, including:
1. Immobility: Prolonged periods of immobility can increase the risk of thrombosis. This is because staying still for extended periods can slow down blood flow and cause blood to pool, leading to clot formation.
2. Surgery: Surgical procedures, especially those involving the lower extremities or abdominal region, can increase the risk of developing blood clots. This is due to the trauma caused to blood vessels during surgery, as well as the immobility that often follows the procedure.
3. Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of thrombosis. Excess body fat can contribute to inflammation and affect the balance of clotting factors in the blood.
4. Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and promotes the development of atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries. This can increase the risk of thrombosis by narrowing the blood vessels and disrupting normal blood flow.
5. Hormonal changes: Certain hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy, can increase the risk of thrombosis. Hormone replacement therapy and the use of oral contraceptives can also contribute to clot formation.
6. Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as cancer, heart disease, and autoimmune disorders, can increase the risk of thrombosis. These conditions can affect blood clotting factors and promote the formation of blood clots.
7. Genetic factors: In some cases, thrombosis can be caused by genetic factors. Inherited conditions, such as Factor V Leiden mutation or deficiencies in natural anticoagulants, can increase the risk of clot formation.
It is important to note that these are just some of the common causes of thrombosis. Other factors, such as age, family history, and certain medications, can also play a role in the development of blood clots.
Key Risk Factors for Developing Thrombosis
Thrombosis occurs when blood clots form in the veins, blocking the flow of blood. There are several factors that can increase the risk of developing thrombosis:
1. Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions such as cancer, heart disease, and kidney disease can increase the risk of thrombosis.
2. Surgery or trauma: Surgery or physical trauma can disrupt the normal blood flow and increase the risk of blood clots.
3. Prolonged immobility: Sitting or lying down for long periods of time, such as during a long flight or hospital stay, can lead to blood clots.
4. Hormonal factors: Hormonal changes during pregnancy, childbirth, or while taking hormonal birth control can increase the risk of thrombosis.
5. Age: The risk of thrombosis increases with age, especially after the age of 60.
6. Family history: Having a family history of thrombosis or blood clotting disorders can increase the risk of developing thrombosis.
7. Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase the risk of thrombosis.
8. Smoking: Smoking damages the blood vessels and increases the risk of blood clots.
9. Certain medications: Certain medications, such as hormone replacement therapy and some chemotherapy drugs, can increase the risk of thrombosis.
10. Genetic factors: Inherited blood clotting disorders, such as factor V Leiden mutation or prothrombin gene mutation, can increase the risk of thrombosis.
It is important to note that having one or more of these risk factors does not necessarily mean that a person will develop thrombosis, but it does increase the likelihood. If you have any concerns about your risk of developing thrombosis, it is best to speak with a healthcare professional.