Step-by-Step Guide: Aspirating or Injecting the Prepatellar Bursa
Содержимое
Learn how to aspirate or inject the prepatellar bursa, a procedure commonly used to relieve pain and inflammation in the knee joint. This step-by-step guide provides detailed instructions and tips for a successful procedure.
Aspiration and injection of the prepatellar bursa is a common medical procedure performed to relieve pain and inflammation in the knee joint. The prepatellar bursa, also known as the kneecap bursa, is a small fluid-filled sac located between the skin and the patella bone. When this bursa becomes inflamed, it can cause significant discomfort and limited mobility.
This step-by-step guide aims to provide a detailed overview of the procedure for aspirating or injecting the prepatellar bursa.
Step 1: Preparation
The first step in performing the procedure is to ensure proper patient positioning and comfort. The patient should be in a supine position with the affected knee bent at approximately 30 degrees. Sterile drapes should be placed to create a sterile field, and the surrounding area should be cleaned with an antiseptic solution.
Step 2: Anesthesia
Local anesthesia is typically administered to minimize discomfort during the procedure. Lidocaine or a similar numbing agent is injected into the skin and subcutaneous tissue around the prepatellar bursa.
Step 3: Aspiration or Injection
Using a sterile needle and syringe, the healthcare provider will carefully insert the needle into the prepatellar bursa. To aspirate the bursa, the provider will gently pull back on the syringe plunger to draw out the fluid. If an injection is being performed, the medication is slowly injected into the bursa.
Step 4: Post-procedure care
After the aspiration or injection, the needle is removed, and a sterile dressing is applied to the puncture site. The patient may be advised to limit activity and apply ice to the area to reduce swelling. Pain medication may also be prescribed to manage any discomfort.
This step-by-step guide is intended to provide a general overview of the procedure for aspirating or injecting the prepatellar bursa. It is important to note that this procedure should only be performed by a qualified healthcare professional and may require additional steps or variations depending on the specific circumstances.
Step-by-Step Guide: Aspirating or Injecting the Prepatellar Bursa
The prepatellar bursa is a small sac located between the skin and the kneecap. It can become inflamed or swollen due to injury or infection, causing pain and discomfort. Aspirating or injecting the prepatellar bursa can help relieve symptoms and promote healing. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to perform this procedure:
Step 1: Prepare the patient and the equipment. Ensure that the patient understands the procedure and provides informed consent. Gather the necessary equipment, including a syringe, needle, antiseptic solution, gloves, and sterile drapes.
Step 2: Position the patient. Have the patient sit or lie down comfortably, with their knee bent at a 90-degree angle. This position allows easy access to the prepatellar bursa.
Step 3: Cleanse the area. Put on gloves and use an antiseptic solution to cleanse the skin around the prepatellar bursa. This helps reduce the risk of infection.
Step 4: Locate the prepatellar bursa. Use your fingers to palpate the area just above the kneecap. The prepatellar bursa will feel like a small fluid-filled sac.
Step 5: Insert the needle. Using a sterile technique, carefully insert the needle into the prepatellar bursa. The needle should be directed towards the center of the kneecap. Aspiration may be performed to remove fluid or inject medication, depending on the purpose of the procedure.
Step 6: Aspirate or inject. Once the needle is properly positioned, slowly aspirate fluid from the prepatellar bursa or inject the desired medication. Take caution to avoid any resistance or excessive pressure during the procedure.
Step 7: Remove the needle. Once the aspiration or injection is complete, carefully remove the needle from the prepatellar bursa.
Step 8: Apply pressure and bandage. Apply gentle pressure to the needle insertion site to prevent bleeding. Then, cover the area with a sterile bandage to protect it from contamination.
Step 9: Provide aftercare instructions. Instruct the patient on any necessary post-procedure care, such as avoiding excessive activity or applying ice to the area. Explain any potential side effects or complications they should watch for and when to follow up with a healthcare provider.
Step 10: Document the procedure. Make sure to properly document the aspiration or injection in the patient’s medical record. Include details such as the date, procedure performed, medications used, and any relevant patient responses or observations.
By following this step-by-step guide, healthcare providers can safely and effectively aspirate or inject the prepatellar bursa, helping patients find relief from pain and promote healing.
Preparation and Equipment
Before starting the procedure, it is essential to gather all the necessary equipment. This ensures that the process goes smoothly and efficiently. Here is a list of the equipment you will need:
- Gloves: It is crucial to wear sterile gloves to maintain a sterile environment and prevent infection.
- Antiseptic solution: An antiseptic solution, such as povidone-iodine or chlorhexidine, should be used to cleanse the injection site and reduce the risk of infection.
- Syringe and needle: A syringe and needle are required for both aspiration and injection. The size of the needle may vary depending on the specific procedure and patient factors.
- Local anesthetic: Local anesthesia may be necessary to minimize discomfort during the procedure. Lidocaine is commonly used for this purpose.
- Prep pads: Prep pads are used to clean the injection site before the procedure.
- Specimen container: A sterile specimen container should be ready to collect any aspirated fluid for further analysis, if necessary.
- Adhesive bandages: Adhesive bandages are used to cover the injection site after the procedure to protect it and promote healing.
Ensure that all the equipment is within reach and properly organized before starting the procedure. This helps to maintain a sterile and controlled environment throughout the process.
Cleaning and Sterilization
Proper cleaning and sterilization techniques are essential to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the procedure. Before aspirating or injecting the prepatellar bursa, it is important to follow these steps for cleaning and sterilizing the equipment:
1. Gather the necessary equipment:
Make sure you have all the required equipment ready, including syringes, needles, antiseptic solution, sterile gloves, and sterile drapes.
2. Wash your hands:
Thoroughly wash your hands with soap and water before starting the cleaning and sterilization process. This will help minimize the risk of infection.
3. Clean the work area:
Prepare a clean and well-lit work area for the procedure. Clean the surface with a disinfectant solution to eliminate any potential contaminants.
4. Clean the equipment:
Before using the equipment, make sure to clean it properly. Rinse the syringes and needles with warm soapy water, and then soak them in a disinfectant solution for the recommended amount of time. After soaking, rinse the equipment with sterile water to remove any residue.
5. Sterilize the equipment:
After cleaning, sterilize the equipment using an autoclave or another appropriate sterilization method. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the sterilization process, including the required temperature and duration.
6. Prepare the sterile field:
Place a sterile drape over the work area to create a sterile field. This will help maintain the cleanliness of the equipment and prevent contamination during the procedure.
7. Put on sterile gloves:
Before handling the equipment, put on a pair of sterile gloves. This will help minimize the risk of introducing any bacteria or other contaminants into the prepatellar bursa.
8. Follow aseptic technique:
Throughout the procedure, follow proper aseptic technique to minimize the risk of infection. Avoid touching non-sterile surfaces or equipment, and handle the needles and syringes with care to prevent contamination.
9. Dispose of used equipment:
After completing the procedure, dispose of all used equipment properly. Use a designated sharps container for needles and syringes and follow local guidelines for the disposal of other contaminated materials.
By following these cleaning and sterilization steps, you can ensure a sterile and safe environment for aspirating or injecting the prepatellar bursa. Remember, proper hygiene and sterilization are crucial to prevent infection and achieve successful outcomes.
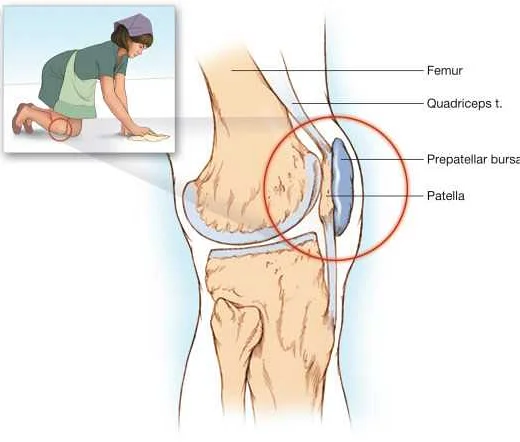
Locating the Prepatellar Bursa
The prepatellar bursa is a small sac located just above the kneecap, between the skin and the patella bone. It can be easily identified and located using a few simple steps:
1. Position the patient
Have the patient lie down on their back on an examination table or bed, with their knee bent at a 90-degree angle. This position allows for easier access and visualization of the prepatellar bursa.
2. Locate the patella
Using your fingers, find the patella bone, also known as the kneecap. It is a prominent bone located in the front of the knee. Feel for the rounded shape and follow it until you reach the upper edge of the patella.
3. Palpate for the prepatellar bursa
Once you have located the upper edge of the patella, move your fingers slightly above it and press gently. You should feel a soft, fluid-filled sac underneath the skin. This is the prepatellar bursa.
4. Confirm the location
Ask the patient if they feel any tenderness or discomfort in the area you have identified as the prepatellar bursa. If they confirm the presence of pain or swelling in this area, it further confirms the location of the bursa.
By following these steps, you can easily locate the prepatellar bursa and proceed with the aspiration or injection procedure.