Step-by-Step Guide: Orotracheal Intubation with Video Laryngoscopy
Содержимое
Learn how to perform orotracheal intubation using video laryngoscopy, a modern technique that provides improved visualization and easier intubation. This article provides step-by-step instructions and valuable tips for successful intubation using this method.
Intubation is a critical procedure in emergency medicine and anesthesia. It involves the insertion of a flexible plastic tube into the trachea to establish an airway and facilitate ventilation. Orotracheal intubation, specifically, refers to the placement of the endotracheal tube through the mouth.
Video laryngoscopy is a technique that uses a specialized device to provide a visual guide during intubation. This technology offers several advantages over traditional direct laryngoscopy, including improved visualization of the airway and easier tube placement.
In this step-by-step guide, we will walk you through the process of orotracheal intubation using video laryngoscopy. Whether you are a seasoned medical professional looking to refresh your skills or a novice practitioner seeking to learn this procedure, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive overview.
Before we begin, it is important to note that orotracheal intubation is an advanced procedure that should only be performed by trained healthcare professionals who have received appropriate education and clinical experience. This guide is intended for educational purposes only and should not replace proper training and supervision.
Importance of Video Laryngoscopy in Intubation
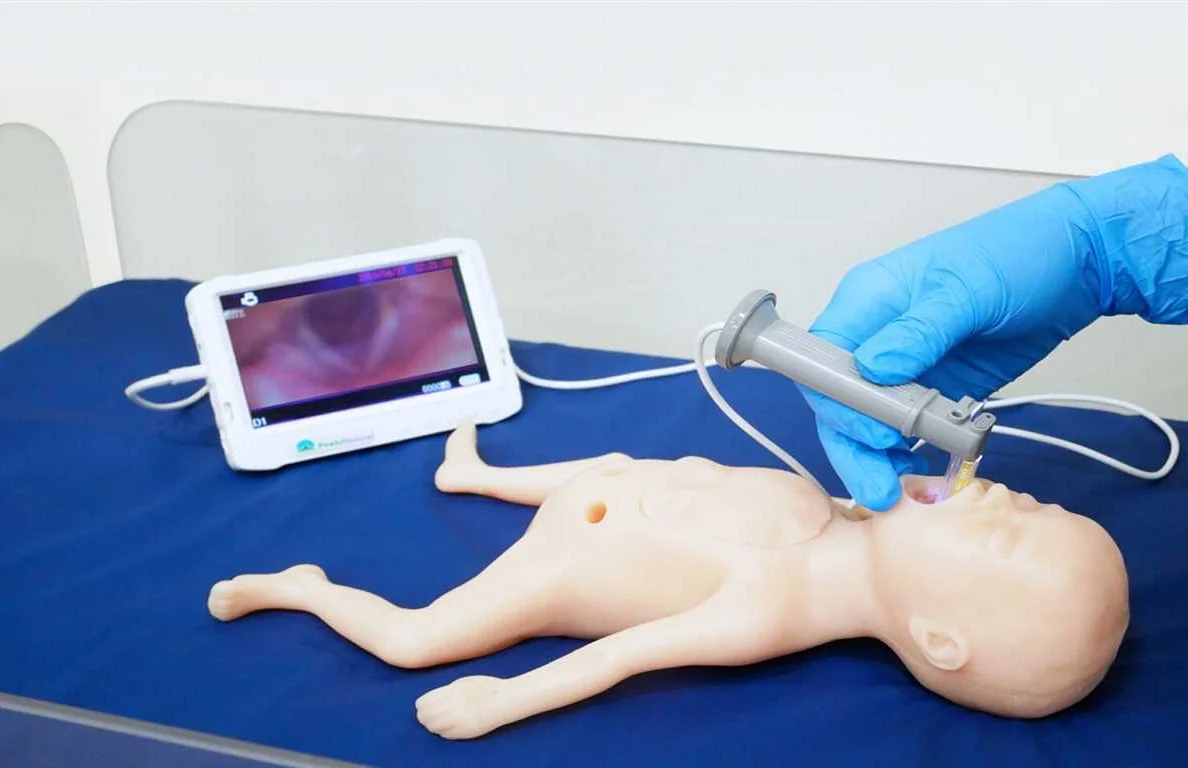
Video laryngoscopy has revolutionized the field of airway management, particularly in the context of intubation. Compared to traditional direct laryngoscopy, video laryngoscopy provides numerous advantages that make it an essential tool for healthcare professionals.
One of the key benefits of video laryngoscopy is the improved visualization it offers. With the use of a camera and a high-resolution screen, providers can obtain a clear and magnified view of the patient’s airway structures. This enhanced visibility allows for better identification of anatomical landmarks and a more accurate placement of the endotracheal tube.
Furthermore, video laryngoscopy allows for better visualization in difficult airway scenarios. Patients with limited mouth opening, significant neck immobilization, or distorted airway anatomy can pose challenges during intubation. However, with video laryngoscopy, these obstacles can be overcome as it provides an indirect view of the airway, reducing the need for a direct line of sight.
Another advantage of video laryngoscopy is the ability to record the procedure. This feature is especially useful for educational purposes and quality improvement initiatives. It allows for the review of intubation techniques, identification of areas for improvement, and training of new healthcare providers.
In addition, video laryngoscopy can enhance patient safety. By minimizing the need for excessive manipulation of the airway structures, it reduces the risk of trauma and potential complications associated with intubation. The improved visualization also enables providers to avoid complications such as esophageal intubation and accidental extubation.
Overall, video laryngoscopy has become an indispensable tool in the realm of intubation. Its ability to provide superior visualization, overcome difficult airway scenarios, facilitate education and training, and enhance patient safety makes it a valuable asset for healthcare professionals.
Preparing for Orotracheal Intubation
Before performing orotracheal intubation, it is essential to properly prepare for the procedure. This helps ensure patient safety and increases the chances of a successful intubation. Here are some important steps to follow:
1. Gather all the necessary equipment: Ensure that you have all the required equipment ready and easily accessible. This includes the endotracheal tube, laryngoscope, stylet, syringe, and suction device.
2. Check the equipment for functionality: Inspect the equipment to ensure that it is in proper working condition. Check the laryngoscope for a functional light source, make sure the endotracheal tube is the correct size and is not damaged, and ensure that the suction device is functional.
3. Prepare the patient: Position the patient properly, ensuring proper alignment of the head and neck. Apply appropriate monitoring devices, such as pulse oximetry and ECG leads, to monitor the patient’s vital signs during the procedure.
4. Gather the necessary personnel: Ensure that you have an assistant available to help with the procedure. This can include assisting with patient positioning, holding equipment, or providing support during intubation.
5. Administer pre-intubation medications: If necessary, administer any pre-intubation medications, such as sedatives or muscle relaxants, as prescribed by the physician.
6. Prepare the laryngoscope and endotracheal tube: Attach the appropriate blade to the laryngoscope and ensure that the light source is functioning properly. Lubricate the endotracheal tube to aid in its smooth insertion.
By following these steps and properly preparing for orotracheal intubation, you can help ensure a smooth and successful procedure.
Performing Orotracheal Intubation with Video Laryngoscopy
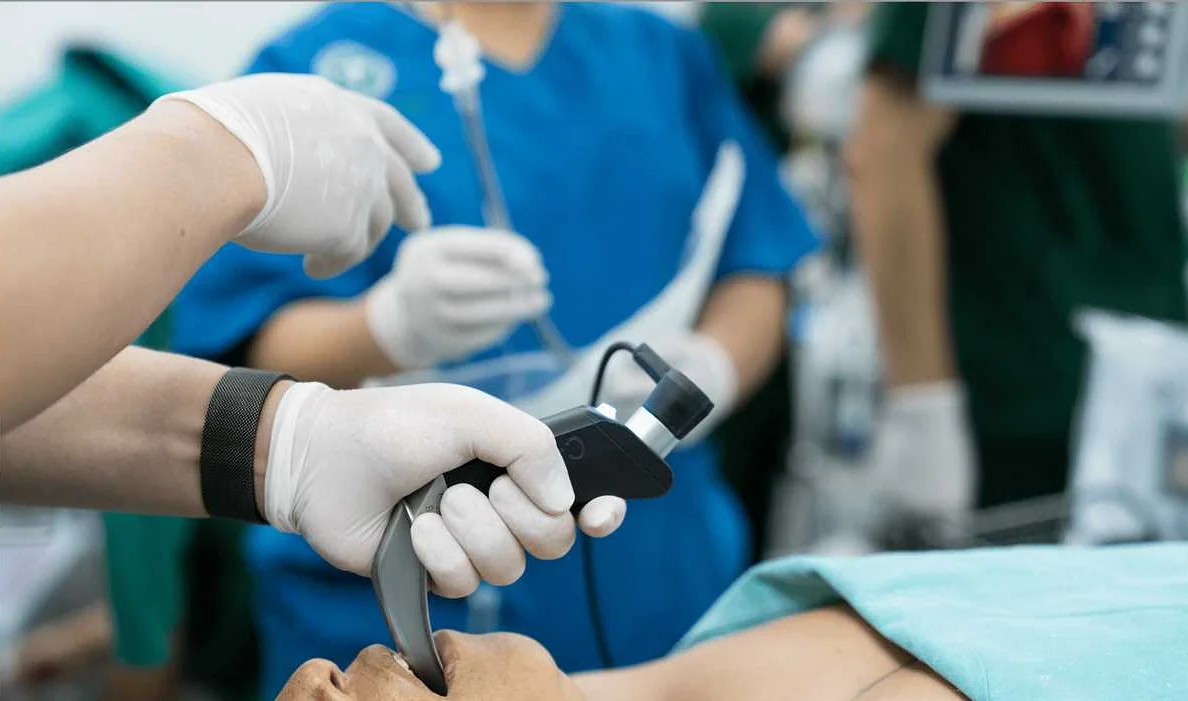
Orotracheal intubation is a procedure used to establish an airway in patients who are unable to breathe on their own or require mechanical ventilation. Video laryngoscopy is a technique that uses a camera and monitor to visualize the vocal cords during intubation, making it easier to navigate the airway and reduce the risk of complications.
Before beginning the procedure, it is important to gather all the necessary equipment. This includes a video laryngoscope, endotracheal tube, stylet, laryngoscope blade, lubricating jelly, suction device, and bag-valve-mask device.
Once the equipment is prepared, the patient should be positioned properly with the head in a sniffing position to align the oral, pharyngeal, and laryngeal axes. It is important to ensure adequate muscle relaxation before starting the procedure.
| 1 | Pre-oxygenation: Administer high-flow oxygen to the patient for several minutes to increase their oxygen reserves. |
| 2 | Preparation: Assemble the video laryngoscope and ensure the camera is clear and functioning properly. Preoxygenate the patient if necessary. |
| 3 | Insertion: Insert the laryngoscope blade into the mouth and sweep the tongue aside to visualize the epiglottis. Advance the blade until the vocal cords are visible on the monitor. |
| 4 | Intubation: Carefully pass the endotracheal tube through the vocal cords while watching the screen for guidance. Withdraw the laryngoscope blade once the tube is in place. |
| 5 | Confirmation: Confirm proper tube placement by auscultating bilateral breath sounds, observing chest rise, and monitoring end-tidal carbon dioxide levels. |
| 6 | Securing the tube: Secure the endotracheal tube in place using tape or a commercial device, ensuring it is at the proper depth. |
| 7 | Post-intubation care: Assess the patient’s vital signs, oxygen saturation, and end-tidal carbon dioxide levels. Provide sedation and analgesia as needed. |
It is important to regularly assess the patient’s airway, breathing, and circulation after the procedure. Complications such as tube dislodgement or obstruction should be promptly addressed.
Performing orotracheal intubation with video laryngoscopy requires training and proficiency to ensure the safety and success of the procedure. Regular practice and continuing education are important for maintaining skill and staying up to date with advancements in airway management.
Troubleshooting Common Issues during Intubation
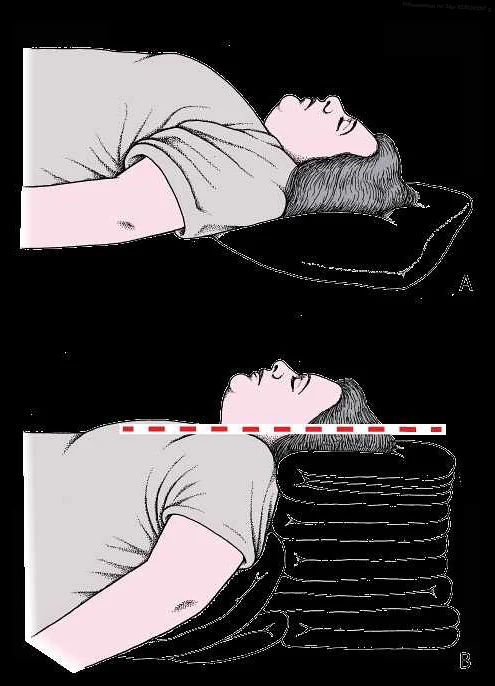
Intubation is a critical procedure that requires carefully following the steps to ensure successful placement of the endotracheal tube. However, there are several common issues that may arise during intubation, which can impede the process. Below, we have outlined these issues and provided troubleshooting strategies to overcome them.
| Poor visualization of the vocal cords | 1. Adjust the position of the patient’s head and neck 2. Optimize the angle and depth of insertion of the video laryngoscope blade 3. Apply gentle backward pressure on the laryngoscope blade to lift the epiglottis 4. Use a different blade size or type if needed |
| Inability to pass the endotracheal tube | 1. Confirm proper alignment of the anatomy and tube 2. Lubricate the endotracheal tube to reduce friction 3. Consider using a stylet to guide the tube 4. Select a smaller or larger tube size if necessary 5. Assess for any airway obstructions or anatomical abnormalities |
| Difficulty advancing the endotracheal tube beyond the vocal cords | 1. Slowly rotate the tube while applying gentle forward pressure 2. Confirm proper positioning of the tube within the trachea using capnography or chest rise 3. Ensure the tube cuff is not inflated while passing through the vocal cords 4. Consider withdrawing the tube slightly and attempting reinsertion 5. Seek assistance from a more experienced provider if needed |
| Inadvertent esophageal intubation | 1. Confirm correct tube placement by visualization of the tube passing through the vocal cords 2. Use capnography to monitor end-tidal CO2 levels 3. Auscultate the chest bilaterally for breath sounds 4. Remove the tube and attempt re-intubation if esophageal intubation is confirmed 5. Consider using a bougie or stylet for better visualization and guidance |
By being aware of these common issues and having troubleshooting strategies in place, healthcare providers can successfully overcome challenges during orotracheal intubation. It is crucial to remain calm, focused, and to seek assistance if necessary to ensure patient safety and optimal airway management.