The first cases of tick-borne encephalitis this season have been registered in Russia
Содержимое
The first cases of tick-borne encephalitis have been reported in Russia, signaling the start of the season. Stay informed and take precautions to protect yourself against this potentially serious illness.
The first cases of tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) have been registered in Russia this season, sparking concerns among health officials. TBE is a viral infection that is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected ticks, and it can cause severe neurological symptoms.
The country’s health authorities have been closely monitoring the situation, as TBE cases tend to increase during the spring and summer months when ticks are most active. Experts recommend taking precautions to avoid tick bites, such as wearing long-sleeved clothing, using insect repellent, and checking for ticks after spending time outdoors.
Tick-borne encephalitis can be a serious illness, with symptoms ranging from fever, headache, and fatigue to more severe complications such as meningitis and encephalitis. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in preventing long-term neurological damage.
While TBE is endemic in certain regions of Russia, including the Siberian and Far Eastern areas, the recent cases have raised concerns because they occurred outside of these traditional endemic areas. Health officials are urging the public to be vigilant and seek medical attention if they experience any symptoms or suspect a tick bite.
The First Cases
The first cases of tick-borne encephalitis have been registered in Russia this season. Tick-borne encephalitis is a viral infection transmitted through the bite of infected ticks. It can cause inflammation of the brain, leading to neurological symptoms and, in severe cases, even death.
The first cases were reported in several regions of Russia, including Moscow, Saint Petersburg, and Novosibirsk. Health authorities are urging people to take precautions against tick bites, such as wearing protective clothing and using insect repellent.
In addition to tick-borne encephalitis, ticks are also known to transmit other diseases, such as Lyme disease. It is important for people to be aware of the risks and to seek medical attention if they have been bitten by a tick and develop symptoms such as fever, headache, and muscle and joint aches.
| Moscow | 10 |
| Saint Petersburg | 5 |
| Novosibirsk | 3 |
Authorities are working to prevent the spread of tick-borne encephalitis by conducting tick control measures, such as treating wooded areas with insecticides and providing information on tick prevention to the public.
It is important for people to be vigilant and take precautions to protect themselves against tick bites, especially during the peak tick season, which typically occurs in spring and summer. By being aware of the risks and taking appropriate measures, individuals can reduce their risk of tick-borne diseases.
Tick-Borne Encephalitis
Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is a viral infection that affects the central nervous system. It is transmitted through the bite of infected ticks, primarily found in wooded and grassy areas. TBE is endemic in certain regions of Europe and Asia, including Russia.
The symptoms of TBE can range from mild flu-like symptoms to more severe neurological symptoms, such as meningitis or encephalitis. In some cases, TBE can be life-threatening or result in long-term neurological complications.
Prevention is key in reducing the risk of TBE. Vaccination is available and recommended for individuals living in or travelling to endemic areas. It is also important to take precautions to avoid tick bites, such as wearing protective clothing, using insect repellent, and checking for ticks after spending time outdoors.
Early diagnosis and treatment are important in managing TBE. If you suspect you have been infected, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.
With the first cases of tick-borne encephalitis registered in Russia this season, it serves as a reminder of the importance of awareness and prevention in avoiding this potentially serious disease.
Registered in Russia
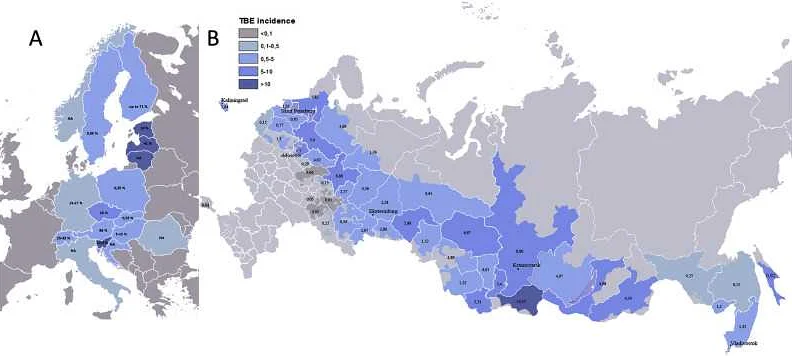
Tick-borne encephalitis is a serious viral infection that affects the central nervous system. It is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected ticks, usually found in wooded areas. The first cases of tick-borne encephalitis have been registered in Russia this season, raising concerns among public health officials.
The exact number of cases has not been disclosed, but it is believed to be higher than previous years. This is a cause for alarm as tick-borne encephalitis can lead to severe complications, including inflammation of the brain and spinal cord.
Authorities are urging the public to take precautions when spending time outdoors, such as wearing long sleeves and pants, using insect repellent, and checking for ticks after being in wooded areas. Vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis is also recommended, especially for those living in or traveling to high-risk areas.
Efforts are being made to raise awareness about tick-borne encephalitis and educate the public on how to protect themselves from ticks. This includes distributing informational materials, conducting educational campaigns, and providing resources for healthcare professionals.
It is important to stay vigilant and take the necessary precautions to protect against tick-borne encephalitis. By being aware of the risks and taking preventive measures, we can minimize the spread of this potentially harmful disease.
This Season
This season, the first cases of tick-borne encephalitis have been registered in Russia. Tick-borne encephalitis is a viral infection transmitted through tick bites. It can cause inflammation of the brain, leading to symptoms such as fever, headache, and muscle pain.
According to the latest data, there have been several cases of tick-borne encephalitis reported in different regions of Russia. The affected individuals have been hospitalized and are currently receiving treatment.
The increase in tick-borne encephalitis cases this season is a cause for concern. Health authorities are advising the public to take precautions to prevent tick bites, such as wearing protective clothing, using insect repellent, and conducting regular tick checks after outdoor activities.
| Moscow | 6 |
| St. Petersburg | 4 |
| Vladimir | 3 |
These numbers are expected to rise as the tick season continues. It is important for individuals to be aware of the risks and take appropriate measures to protect themselves from tick-borne diseases.
Risk of Tick-Borne Encephalitis

Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is a viral infection transmitted by ticks. It is a serious illness that can affect the central nervous system and lead to neurological complications. TBE is most commonly found in regions of Europe and Asia, including Russia.
The risk of contracting TBE is highest in areas where infected ticks are prevalent, such as forests, woodlands, and grassy areas. Ticks are most active during the warmer months, typically from spring to autumn, when people are more likely to be outdoors. Therefore, individuals who spend time in these areas are at a higher risk of exposure to infected ticks.
It is important to note that not all ticks carry the TBE virus. However, it is difficult to determine which ticks are infected without testing. Therefore, it is recommended to take precautions against tick bites regardless of the area and time of year.
To reduce the risk of tick-borne encephalitis:
- Wear long-sleeved clothing and pants to minimize exposed skin.
- Use insect repellent on exposed skin and clothing.
- Regularly check for ticks while in tick-prone areas and remove them promptly.
- Avoid walking through tall grass or brush where ticks may be present.
- Consider vaccination against TBE for individuals living in or traveling to high-risk areas.
If you develop symptoms such as fever, headache, muscle aches, or fatigue after a tick bite, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
Overall, being aware of the risk of tick-borne encephalitis and taking necessary preventive measures can help protect against this potentially serious infection.
Infections in Humans
Tick-borne encephalitis is a viral infection that is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected ticks. The infection primarily affects the central nervous system and can result in severe neurological complications.
Symptoms of tick-borne encephalitis in humans can vary, but typically include fever, headache, fatigue, muscle aches, and stiffness in the neck. In more severe cases, individuals may experience neurological symptoms such as confusion, paralysis, and seizures.
It is important for individuals living in or visiting areas where tick-borne encephalitis is prevalent to take precautions to prevent tick bites. This includes wearing protective clothing, using insect repellent, and avoiding areas with high tick populations.
If a person is bitten by an infected tick, it is crucial to seek medical attention as soon as possible. Early treatment with antiviral medication can help reduce the severity of symptoms and prevent complications.
Prevention and timely treatment are essential in reducing the spread of tick-borne encephalitis and protecting individuals from this potentially dangerous infection.
Prevention Measures
Tick-borne encephalitis is a serious disease that can have long-term effects on a person’s health. Fortunately, there are several preventive measures that individuals can take to reduce their risk of contracting the virus.
Here are some important prevention measures:
| 1. Vaccination | Getting vaccinated against tick-borne encephalitis is the most effective way to prevent the disease. It is recommended to receive the vaccine before the start of the tick season. |
| 2. Avoid Tick-Infested Areas | Avoiding tick-infested areas, such as forests and grassy fields, can help reduce the risk of tick bites. If you need to be in these areas, wear long sleeves, long pants, and closed-toe shoes to cover your skin. |
| 3. Use Insect Repellents | Apply insect repellents containing DEET or permethrin to exposed skin and clothing to repel ticks. Follow the instructions on the product label carefully. |
| 4. Perform Regular Tick Checks | After spending time outdoors, thoroughly check your body for ticks. Pay special attention to the hairline, armpits, groin area, and behind the ears. If you find a tick, remove it promptly with tweezers. |
| 5. Avoid Tick Hosts | Ticks often attach themselves to animals like deer and rodents. Avoid contact with these animals and their habitats to reduce the risk of tick bites. |
| 6. Educate Yourself | Learn more about tick-borne encephalitis and the risks associated with it. Understanding the disease and its symptoms can help you take necessary precautions. |
By following these prevention measures, individuals can greatly reduce their risk of tick-borne encephalitis and enjoy a safer outdoor experience.