The Most Beneficial Microelement for Brain Function and the Nervous System
Discover the microelement that has the most positive impact on brain function and the nervous system. Learn how this essential nutrient can help boost cognitive function and overall mental health.
Did you know that there is a microelement that plays a crucial role in brain function and the overall health of the nervous system?
Iron, magnesium, zinc – we often hear about these essential elements for our body, but one microelement that is often overlooked is selenium. While selenium is needed in small amounts, its impact on our brain and nervous system cannot be underestimated.
Selenium acts as a powerful antioxidant, protecting our brain cells from oxidative stress and damage. It also helps regulate neurotransmitter function, which is essential for cognitive function, mood regulation, and overall mental well-being.
Several studies have shown that selenium deficiency is linked to cognitive decline, memory problems, and even neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. On the other hand, adequate selenium levels have been associated with improved cognitive function and a reduced risk of neurological disorders.
In addition to its neuroprotective effects, selenium also plays a role in the synthesis of thyroid hormones, which are crucial for brain development and function. It has been found that selenium deficiency can impair thyroid function, leading to cognitive impairments and mood disorders.
So how can we ensure we are getting enough selenium for optimal brain function and nervous system health?
The good news is that selenium can be found in various food sources, including Brazil nuts, fish, poultry, eggs, and whole grains. However, the selenium content in food depends on the soil in which it is grown, so the levels can vary. If you are concerned about your selenium intake, it may be beneficial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if supplementation is necessary.
In conclusion, selenium is a microelement that should not be overlooked when it comes to brain function and the health of the nervous system. Its antioxidant properties, impact on neurotransmitter function, and role in thyroid hormone synthesis make it an essential nutrient for optimal cognitive function and mental well-being. So make sure to include selenium-rich foods in your diet and stay mindful of your selenium levels for a healthy brain and nervous system.
The Importance of Microelements for Brain Function and Nervous System
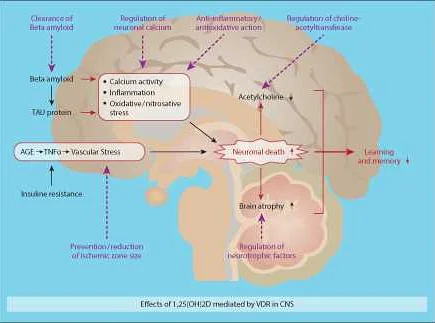
Microelements play a crucial role in the proper functioning of the brain and nervous system. These trace elements are required in small amounts, but their deficiency can have significant implications for cognitive function and overall neurological health.
One of the most important microelements for brain function is iron. Iron is involved in the production of neurotransmitters, which are chemical messengers that allow nerve cells to communicate with each other. Without adequate iron levels, the brain may not be able to produce enough neurotransmitters, leading to issues such as poor memory, difficulty concentrating, and impaired cognitive function.
Zinc is another microelement that is essential for brain health. It is involved in the regulation of neuronal activity and the maintenance of the blood-brain barrier, which protects the brain from harmful substances. Zinc deficiency has been linked to cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Selenium is a microelement that acts as an antioxidant in the brain. It helps protect neurons from oxidative stress, which can damage cell membranes and impair their function. Adequate selenium levels are necessary for the proper functioning of the nervous system and have been associated with improved cognitive performance.
Copper is another microelement that is critical for brain function. It is involved in the production of myelin, a substance that forms a protective sheath around nerve fibers. Myelin is crucial for the efficient transmission of nerve impulses. Copper deficiency can lead to demyelination and neurological symptoms such as tremors, cognitive impairment, and difficulty walking.
| Iron | Production of neurotransmitters | Red meat, poultry, beans, spinach |
| Zinc | Regulation of neuronal activity | Seafood, meat, nuts, seeds |
| Selenium | Antioxidant protection | Brazil nuts, fish, meat, eggs |
| Copper | Myelin production | Organ meats, shellfish, nuts, seeds |
In conclusion, microelements are essential for brain function and the proper functioning of the nervous system. Iron, zinc, selenium, and copper are just a few examples of microelements that play crucial roles in cognitive function and neurological health. It is important to ensure an adequate intake of these microelements through a balanced diet to support optimal brain function and overall well-being.
Understanding the Brain and Nervous System
The brain and nervous system are complex and intricate parts of the human body. The brain is the control center of the nervous system, responsible for coordinating and regulating all bodily functions. It is made up of billions of cells called neurons that communicate with each other through electrical and chemical signals.
The nervous system, on the other hand, is a network of specialized cells that transmit signals between different parts of the body. It has two main components: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS includes the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS includes the nerves that connect the CNS to the rest of the body.
The brain and nervous system work together to allow us to think, move, feel, and respond to our environment. They play a crucial role in our ability to learn, remember, and process information. Without them, we would not be able to perform even the simplest tasks.
One of the key functions of the brain and nervous system is the regulation of emotions and behaviors. They help us experience emotions such as happiness, sadness, anger, and fear, and they also control our actions and reactions to different situations.
Understanding how the brain and nervous system function is essential for maintaining optimal brain health. By knowing how these systems work, we can take steps to keep them healthy and prevent cognitive decline and neurological disorders.
In conclusion, the brain and nervous system are essential for our overall well-being. They are responsible for controlling and coordinating all bodily functions and play a crucial role in our ability to think, feel, and move. By understanding how these systems work, we can take better care of our brain and nervous system and promote a healthy and functioning mind.
The Role of Microelements in Brain Function
Microelements play a crucial role in the proper function of the brain and the nervous system. These essential nutrients are required in small amounts but have a significant impact on the cognitive abilities, memory, and overall brain health.
One of the key microelements that are vital for brain function is iron. Iron is responsible for carrying oxygen to the brain, which is essential for energy production and proper functioning of brain cells. Without sufficient iron, the brain can experience reduced oxygen levels, leading to cognitive impairment and fatigue.
Another important microelement for brain function is zinc. Zinc is involved in various processes in the brain, including neurotransmitter synthesis and synaptic signaling. It plays a crucial role in regulating the communication between brain cells and promoting optimal cognitive function.
Magnesium is also essential for brain health. It acts as a cofactor in numerous enzymatic reactions that are crucial for neurotransmitter synthesis and signaling. Magnesium deficiency has been associated with various neurological disorders, including migraine, depression, and cognitive decline.
Selenium is another microelement that plays a vital role in brain function. It acts as an antioxidant, protecting brain cells from oxidative stress and inflammation. Selenium deficiency has been linked to an increased risk of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
In addition to these microelements, other essential nutrients, such as copper, manganese, and iodine, also play important roles in brain function. Copper is involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, while manganese is essential for the production of the antioxidant enzyme superoxide dismutase, which protects the brain from oxidative damage. Iodine is necessary for the production of thyroid hormones, which are crucial for brain development and function.
In conclusion, microelements are indispensable for brain function and overall nervous system health. Including a variety of foods rich in these essential nutrients in your diet can help support optimal cognitive function, memory, and overall brain health.
The Most Beneficial Microelement: Magnesium
Magnesium is a vital microelement for brain function and the proper functioning of the nervous system. It plays a crucial role in numerous biochemical reactions that occur in the brain and helps maintain its optimal health.
Magnesium is involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, which are essential for proper brain function. It helps regulate the activity of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, serotonin, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). These neurotransmitters are responsible for various brain functions, including mood regulation, memory, and cognitive function.
Furthermore, magnesium aids in the production of energy in brain cells. It is a cofactor for many enzymes involved in energy metabolism, including those that produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary source of energy for cells.
Magnesium also acts as a natural antagonist to calcium, another essential mineral for brain function. While calcium is necessary for neurotransmitter release and signal transmission, an imbalance in its levels can lead to excitotoxicity and neuronal damage. Magnesium helps maintain the balance between calcium and magnesium ions, preventing excessive calcium influx and protecting brain cells from damage.
In addition, magnesium has anti-inflammatory properties, which can help reduce inflammation in the brain and protect it from oxidative stress. Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress contribute to the development of various neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease. By reducing inflammation, magnesium may help prevent or slow down the progression of these conditions.
It is important to ensure an adequate intake of magnesium through diet or supplementation to support optimal brain function and nervous system health. Good dietary sources of magnesium include green leafy vegetables, nuts, seeds, legumes, and whole grains.
| 1. Regulation of neurotransmitters |
| 2. Energy production in brain cells |
| 3. Balancing calcium levels |
| 4. Anti-inflammatory properties |
| 5. Protection against oxidative stress |