The Number of St. Petersburg Residents Affected by Ticks Has Increased 4 Times
Содержимое
The number of St. Petersburg residents affected by ticks has increased fourfold, signaling a concerning trend. Stay informed on tick prevention and learn about the potential health risks associated with tick bites.
In recent years, the number of residents in St. Petersburg who have been affected by ticks has increased dramatically. According to a new report, the number of cases has quadrupled, a worrying trend that has raised concerns among local authorities and residents alike.
Ticks are small, blood-sucking parasites that can carry and transmit a variety of diseases, including Lyme disease and tick-borne encephalitis. These diseases can have serious health consequences, ranging from flu-like symptoms to neurological disorders.
The increase in tick-borne illnesses in St. Petersburg is believed to be a result of several factors. One of the main reasons is the expanding population of ticks in the area. The warm and humid climate of St. Petersburg provides a favorable environment for ticks to thrive, leading to a higher number of ticks and an increased risk of human exposure.
In addition, the growing popularity of outdoor activities, such as hiking and picnicking, has also contributed to the rise in tick-related cases. As more people venture into parks and wooded areas, they come into contact with ticks and increase their chances of being bitten.
Local authorities are taking steps to address the issue, including increased public awareness campaigns about tick prevention and control measures. Residents are being encouraged to take precautions when spending time outdoors, such as wearing long-sleeved clothing, using insect repellent, and checking their bodies for ticks after being in grassy or wooded areas.
It is hoped that these efforts will help reduce the number of tick-borne illnesses in St. Petersburg and protect the health and well-being of its residents.
Tick-borne diseases on the rise
The increasing number of St. Petersburg residents affected by ticks has led to a concerning rise in tick-borne diseases in the city. As the population of ticks grows, so does the risk of contracting diseases such as Lyme disease, tick-borne encephalitis, and babesiosis.
Lyme disease, caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, is one of the most common tick-borne diseases in the area. It can cause flu-like symptoms, joint pain, and, if left untreated, can lead to long-term health problems. The number of reported cases of Lyme disease has been steadily increasing in recent years.
Tick-borne encephalitis, on the other hand, is a viral infection that affects the central nervous system. The symptoms can range from mild flu-like symptoms to more severe cases involving inflammation of the brain. Vaccination is available for tick-borne encephalitis, but many residents remain unvaccinated.
Babesiosis is another tick-borne disease that has been on the rise. It is caused by a parasite that infects red blood cells. Symptoms can vary from mild, flu-like symptoms to severe cases that can be life-threatening, especially for individuals with weakened immune systems.
The increase in tick-borne diseases highlights the importance of taking preventive measures to protect oneself from ticks:
- Wear long sleeves and pants when spending time outdoors in areas with high tick populations.
- Use insect repellents that contain DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus.
- Check for ticks on your body and clothing after spending time outside and remove them promptly.
- Consider vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis if you live in or travel to high-risk areas.
It is crucial for residents of St. Petersburg to stay informed about tick-borne diseases and take the necessary precautions to protect their health. By being aware of the risks and taking preventive measures, individuals can reduce their chances of becoming infected with tick-borne diseases.
Factors contributing to the increase

1. Climate change: St. Petersburg has been experiencing milder winters and earlier springs, creating a longer active season for ticks. The warmer temperatures and increased humidity provide the ideal conditions for tick survival and reproduction.
2. Urbanization: The rapid growth of urban areas in St. Petersburg has led to the destruction of natural habitats, forcing wildlife and ticks to adapt to new environments. This proximity between humans, ticks, and their hosts increases the likelihood of tick encounters and subsequent bites.
3. Lack of awareness: Many residents are unaware of the risks associated with ticks and the precautions they should take. This lack of knowledge leads to a higher number of people engaging in outdoor activities without proper protection, increasing their chances of being bitten.
4. Increased outdoor activities: The growing popularity of outdoor recreational activities, such as hiking, camping, and gardening, in and around St. Petersburg has resulted in more people venturing into tick-infested areas. This increased exposure to tick habitats contributes to the higher incidence of tick bites.
5. Ticks adapting to urban environments: Ticks are adapting to urban environments, making it easier for them to survive and reproduce. They can now be found in parks, gardens, and other green spaces within the city limits, increasing the risk of tick encounters for residents.
6. Lack of effective tick control measures: The current tick control measures in St. Petersburg may not be sufficient to adequately manage the tick population. This could be due to factors such as limited funding, lack of research, or ineffective implementation of control strategies.
7. Increased pet ownership: The rising number of pet owners in St. Petersburg has also contributed to the increase in tick-related incidents. Pets can easily bring ticks into homes, increasing the likelihood of tick bites on humans.
Overall, a combination of climate change, urbanization, lack of awareness, increased outdoor activities, ticks adapting to urban environments, lack of effective tick control measures, and increased pet ownership have all been contributing factors to the quadrupling of tick-related incidents among St. Petersburg residents.
Spread of ticks in urban areas
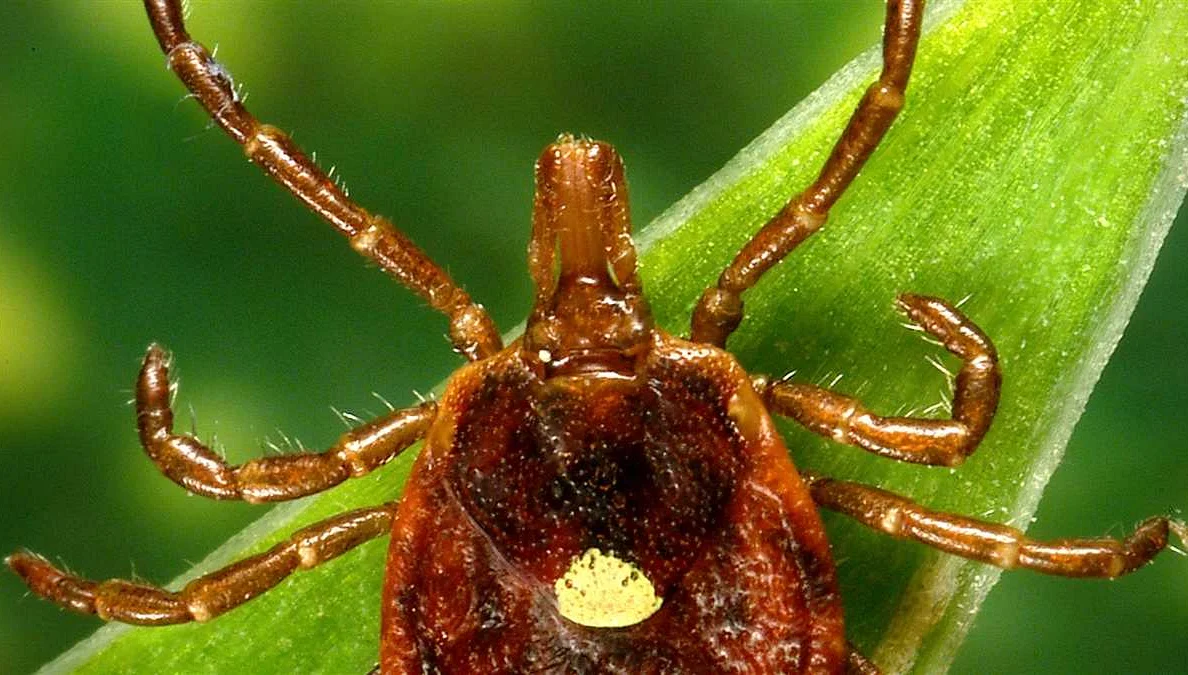

Ticks are no longer just a rural problem. In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the number of ticks found in urban areas, including St. Petersburg. This trend is concerning, as it puts more people at risk of tick-borne diseases.
The spread of ticks in urban areas can be attributed to several factors. One of the main reasons is the loss of natural habitats due to urbanization. As cities expand, forests and grasslands are being replaced by buildings and paved surfaces. This forces ticks to seek alternative hosts and increases their interaction with humans.
Climate change is another factor that is contributing to the spread of ticks. Warmer temperatures and milder winters create more favorable conditions for ticks to survive and reproduce. As a result, their populations are increasing, and they are expanding their range into new areas, including urban environments.
Human activities also play a role in the spread of ticks. Outdoor recreational activities, such as hiking and camping, bring people into closer contact with tick-infested areas. Additionally, the rise in pet ownership has led to more outdoor activities with pets, increasing the chances of ticks being brought into urban areas.
To address the spread of ticks in urban areas, it is essential to raise awareness among the public. Education about tick-borne diseases, prevention methods, and the importance of tick checks can help individuals protect themselves and their families. Furthermore, city planning should take into consideration the preservation of green spaces and the creation of tick-safe zones to reduce tick habitat and minimize the risk of tick encounters.
In conclusion, the spread of ticks in urban areas is a growing concern. It is crucial to understand the factors contributing to this spread and take proactive measures to mitigate the risk. By implementing education and prevention strategies, urban areas can minimize the impact of ticks and protect the health and well-being of their residents.
Health risks associated with tick bites
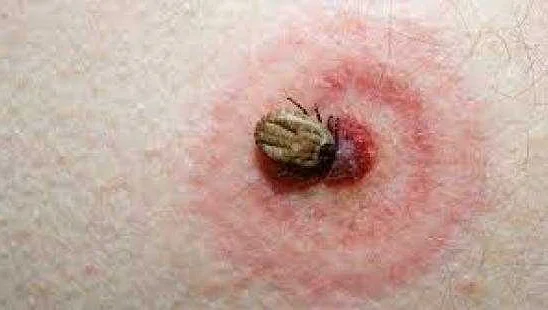
Tick bites can lead to a range of health risks, especially if the tick is a carrier of diseases. Here are some of the potential health risks associated with tick bites:
1. Lyme disease: Lyme disease is a bacterial infection that is transmitted to humans through tick bites. It can cause symptoms such as fever, fatigue, muscle aches, and joint pain. If left untreated, Lyme disease can lead to more serious complications, including neurological problems and heart disorders.
2. Tick-borne encephalitis: Tick-borne encephalitis is a viral infection that affects the central nervous system. It can cause symptoms such as headache, fever, nausea, and muscle stiffness. In severe cases, it can lead to inflammation of the brain and spinal cord, which can result in long-term neurological damage.
3. Anaplasmosis: Anaplasmosis is a bacterial infection that is transmitted through tick bites. It can cause symptoms such as fever, chills, headache, and muscle aches. In severe cases, it can lead to organ failure and even death.
4. Babesiosis: Babesiosis is a parasitic infection that is transmitted through tick bites. It can cause symptoms such as fever, fatigue, and muscle aches. In some cases, it can lead to complications such as anemia and organ failure, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems.
5. Rocky Mountain spotted fever: Rocky Mountain spotted fever is a bacterial infection that is transmitted through tick bites. It can cause symptoms such as fever, headache, and rash. If left untreated, it can lead to more severe complications such as kidney damage, respiratory failure, and even death.
It is important to take precautions to prevent tick bites and to promptly remove ticks if they are found attached to the skin. If you experience any symptoms after a tick bite, it is crucial to seek medical attention to receive appropriate diagnosis and treatment.