Treatment of gouty arthritis: medications and folk remedies
Содержимое
Learn about the different medications and folk remedies available for treating gouty arthritis. Discover effective treatment options to relieve symptoms and manage this painful condition for a better quality of life.
Gouty arthritis is a form of arthritis that is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. This condition can be extremely painful and debilitating, causing swelling, redness, and stiffness in the affected areas. While there is no cure for gouty arthritis, there are several treatment options available to help manage the symptoms and reduce the frequency of flare-ups.
Medications are often prescribed to treat gouty arthritis. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen can help to reduce pain and inflammation. Corticosteroids may also be prescribed to help reduce inflammation in the joints. In severe cases, colchicine may be prescribed to help alleviate the pain and prevent future flare-ups. These medications can be effective in managing the symptoms of gouty arthritis, but they may also have side effects and interactions with other medications, so it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment.
In addition to medication, there are also several folk remedies that have been used for centuries to help manage the symptoms of gouty arthritis. Some people find relief by applying ice packs to the affected joints to reduce swelling and numb the area. Others find that soaking the affected joints in warm water with Epsom salts can help to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Eating a diet low in purines, which are found in certain foods such as meat and seafood, may also help to reduce the frequency of gouty arthritis flare-ups.
It is important to note that while folk remedies may provide some relief for gouty arthritis, they should not be used as a substitute for medical treatment. If you are experiencing symptoms of gouty arthritis, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and to discuss appropriate treatment options. With the right treatment plan, gouty arthritis can be managed effectively, allowing individuals to live a full and active life.
Understanding Gouty Arthritis
Gouty arthritis is a type of arthritis that is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. Uric acid is a waste product that is normally excreted from the body through the kidneys. However, in people with gouty arthritis, the body produces too much uric acid or the kidneys are unable to excrete it properly, leading to the accumulation of uric acid in the joints.
When uric acid crystals accumulate in the joints, they can cause inflammation and severe pain. The affected joints often become red, swollen, and tender to the touch. The joint pain associated with gouty arthritis is typically sudden and intense, and episodes of pain can last for a few days to several weeks.
Gouty arthritis most commonly affects the joints in the lower extremities, such as the big toe, ankle, and knee. However, it can also affect other joints, such as those in the hands, wrists, and elbows.
There are certain risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing gouty arthritis. These include a family history of gout, being overweight or obese, having high blood pressure or diabetes, consuming a diet high in purines (substances found in certain foods), and taking certain medications, such as diuretics.
It is important to diagnose and treat gouty arthritis early to prevent further damage to the joints. Treatment options for gouty arthritis include medications to reduce inflammation and pain, as well as lifestyle changes such as weight loss and dietary modifications.
Overall, a better understanding of gouty arthritis and its causes can help individuals make informed decisions about their treatment options and lifestyle choices to manage the symptoms and prevent future flare-ups.
Medications for Gouty Arthritis
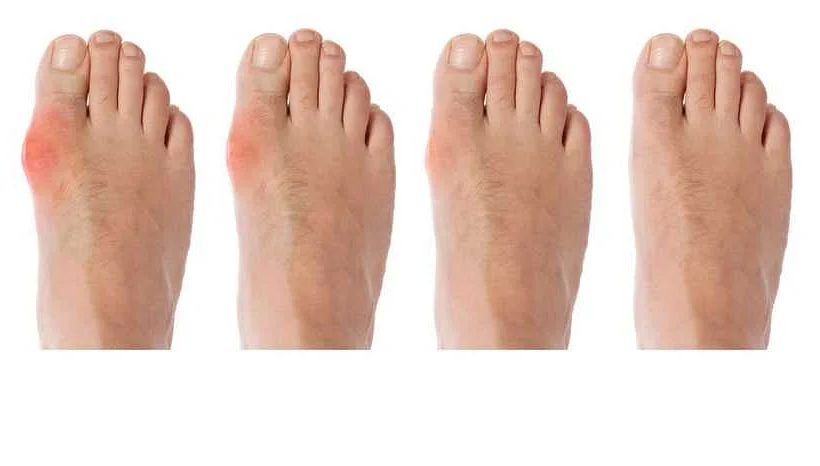
Gouty arthritis is a painful condition caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. It is a form of arthritis that can cause severe pain, swelling, and stiffness in the affected joints. While there is no cure for gouty arthritis, there are several medications that can help manage the symptoms and prevent future attacks.
1. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs are commonly used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation in gouty arthritis. They work by blocking the production of certain chemicals in the body that cause inflammation. Some examples of NSAIDs include ibuprofen, naproxen, and indomethacin.
2. Colchicine: Colchicine is an ancient remedy that has been used for centuries to treat gouty arthritis. It works by reducing the inflammation caused by uric acid crystals, and also helps to prevent future attacks. Colchicine is usually taken at the first sign of an attack, and can be an effective treatment option.
3. Corticosteroids: Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are often prescribed for gouty arthritis when NSAIDs and colchicine are not effective. These medications work by reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune system. Corticosteroids can be taken orally or injected directly into the affected joint.
4. Uric acid-lowering medications: Uric acid-lowering medications, such as allopurinol and febuxostat, are often prescribed to prevent future gout attacks. These medications work by reducing the production of uric acid in the body, and can help prevent the formation of uric acid crystals in the joints.
5. Probenecid: Probenecid is a medication that helps the kidneys eliminate uric acid from the body. It is often prescribed for gouty arthritis patients who have high levels of uric acid in their blood. Probenecid can help prevent the formation of uric acid crystals in the joints and reduce the frequency of gout attacks.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any medication for gouty arthritis. They will be able to assess your condition and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan for you. In addition to medications, making lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding alcohol and high-purine foods, and staying hydrated can also help manage gouty arthritis symptoms.
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Gouty arthritis is a condition characterized by severe pain, inflammation, and swelling of the joints. One of the commonly used medications for the treatment of gouty arthritis is non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). NSAIDs are a class of drugs that help reduce pain, inflammation, and swelling by inhibiting the production of certain chemicals in the body called prostaglandins.
NSAIDs work by blocking the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), which is responsible for the production of prostaglandins. By reducing the production of these chemicals, NSAIDs help alleviate the symptoms of gouty arthritis and provide relief from pain and inflammation.
Some commonly used NSAIDs for the treatment of gouty arthritis include ibuprofen, naproxen, indomethacin, and diclofenac. These medications are available in different forms such as tablets, capsules, creams, and gels. They can be taken orally or applied topically, depending on the severity of the symptoms and the preference of the patient.
While NSAIDs can be effective in managing the symptoms of gouty arthritis, they may also have side effects. Common side effects of NSAIDs include stomach pain, indigestion, nausea, dizziness, and increased risk of bleeding. It is important to follow the recommended dosage and consult a healthcare professional before taking NSAIDs to minimize the risk of side effects and ensure their safe and effective use.
In addition to NSAIDs, there are also other medications available for the treatment of gouty arthritis, including corticosteroids, colchicine, and urate-lowering agents. These medications work in different ways to reduce inflammation and manage the underlying causes of gout. It is important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on individual needs and medical history.
In conclusion, NSAIDs are a commonly used class of medications for the treatment of gouty arthritis. They help reduce pain, inflammation, and swelling by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins. However, it is important to use NSAIDs with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional to minimize the risk of side effects and ensure their safe and effective use.
Colchicine: A Traditional Gout Medication
Gout is a form of arthritis that is characterized by sudden and severe pain, swelling, and tenderness in the joints, most commonly in the big toe. Colchicine is one of the oldest and most traditional medications used to treat gouty arthritis.
Colchicine works by reducing the inflammation and pain associated with gout attacks. It does this by inhibiting the movement of white blood cells into the affected area, which helps to reduce the immune response and thus alleviate the symptoms of gout.
This medication is typically taken orally in the form of tablets. The dosage and frequency of colchicine will vary depending on the severity of the gout attack and the individual’s response to the medication. It is important to follow the prescribed dosing instructions and to not exceed the recommended dosage, as colchicine can have side effects such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea if taken in excessive amounts.
Colchicine is often used in combination with other medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroids, to provide more effective pain relief and reduce the duration of gout attacks. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new medication or combination of medications.
While colchicine is a commonly prescribed medication for gout, it is important to note that it may not be suitable for everyone. Individuals with certain medical conditions or who are taking certain medications may require an alternative or adjusted dosage of colchicine. It is important to discuss any potential contraindications or concerns with a healthcare professional.
In addition to medication, there are also various folk remedies and lifestyle changes that can help manage and prevent gout attacks. These may include maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding foods high in purines (such as organ meats and shellfish), staying hydrated, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations and guidance.
In conclusion, colchicine is a traditional medication that is commonly used to treat gouty arthritis. It works by reducing inflammation and pain in the affected joints. However, it is important to follow the prescribed dosing instructions and consult with a healthcare professional to ensure its safe and effective use.