Salpingoophoritis is an inflammation of the ovarian appendages
Содержимое
Salpingoophoritis is a condition in which the ovaries and fallopian tubes become inflamed, leading to pain and potential fertility issues. Learn about the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for salpingoophoritis.
Salpingoophoritis, also known as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), is a common condition that affects the female reproductive system. It occurs when the fallopian tubes and ovaries become inflamed due to an infection. This condition can cause a range of symptoms and can lead to complications if left untreated.
There are several potential causes of salpingoophoritis. It is most commonly caused by a bacterial infection, usually transmitted through sexual contact. The bacteria can enter the reproductive system and cause inflammation and infection. Other potential causes include infections from childbirth or abortion, the use of intrauterine devices (IUDs), or certain procedures such as endometrial biopsy.
The symptoms of salpingoophoritis can vary from mild to severe. Common symptoms include pelvic pain, abdominal pain, abnormal vaginal discharge, painful intercourse, and fever. In some cases, the infection may spread to other parts of the reproductive system, leading to more serious symptoms such as infertility, chronic pelvic pain, and ectopic pregnancy.
Treatment for salpingoophoritis typically involves antibiotics to fight the infection. The specific antibiotics prescribed will depend on the type of bacteria causing the infection. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary, especially if the infection is severe or if there are complications. It is also important to identify and treat any sexual partners who may be infected to prevent reinfection.
In conclusion, salpingoophoritis is a common condition that affects the female reproductive system. It is important to recognize the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition in order to seek appropriate medical care. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and improve outcomes for individuals with salpingoophoritis.
What is Salpingoophoritis?
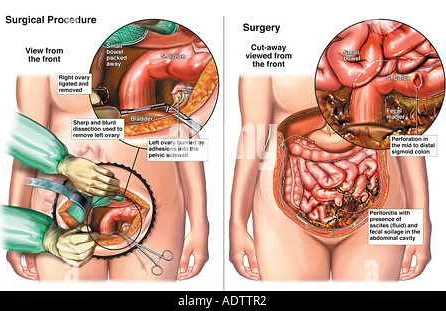
Salpingoophoritis, also known as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), is an infection and inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries. It is commonly caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as chlamydia and gonorrhea. This condition can also result from other bacteria spreading from the vagina and cervix to the upper reproductive organs.
Salpingoophoritis can lead to a variety of symptoms, including lower abdominal pain, abnormal vaginal discharge, painful urination, and pain during intercourse. If left untreated, it can cause serious complications such as infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and chronic pelvic pain.
Diagnosis of salpingoophoritis is typically made through a combination of physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. Treatment usually involves a course of antibiotics to eliminate the infection. In severe cases, hospitalization and surgical intervention may be necessary.
It is important for individuals who suspect they may have salpingoophoritis to seek medical attention promptly in order to prevent complications and protect their reproductive health.
Causes of Salpingoophoritis
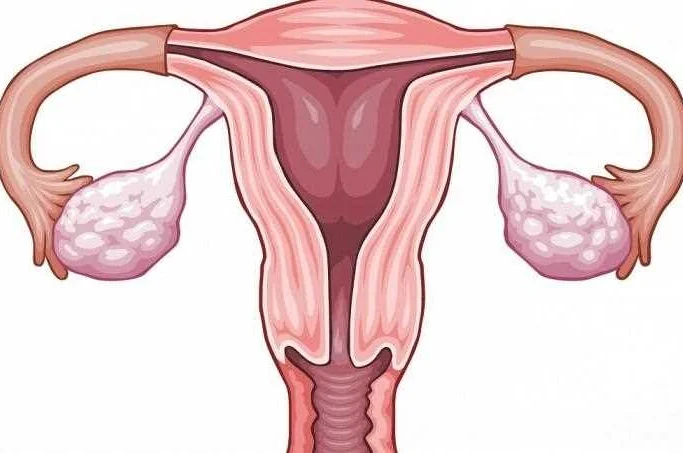
Salpingoophoritis, also known as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), is typically caused by an infection that spreads from the vagina and cervix to the fallopian tubes and ovaries. The most common cause of salpingoophoritis is a bacterial infection, usually resulting from sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as chlamydia or gonorrhea.
Other bacteria, such as E. coli or streptococcus, can also cause salpingoophoritis when they enter the reproductive organs through the bloodstream or during invasive procedures like childbirth or abortion.
In some cases, salpingoophoritis can be caused by non-infectious factors, such as a ruptured appendix or the presence of foreign bodies in the reproductive organs. These factors can lead to inflammation and infection in the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
It’s important to note that women at a higher risk of developing salpingoophoritis include those who have multiple sexual partners, engage in unprotected sex, or have a history of sexually transmitted infections. Additionally, douching, which disrupts the natural balance of bacteria in the vagina, can also increase the risk of developing salpingoophoritis.
If left untreated, salpingoophoritis can lead to serious complications such as infertility, chronic pelvic pain, and ectopic pregnancy. It is crucial to seek medical attention at the first sign of symptoms to prevent long-term damage to the reproductive organs.
Always consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment options if you suspect you have salpingoophoritis or any other medical condition.
Symptoms of Salpingoophoritis
Salpingoophoritis, also known as pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), is an infection of the fallopian tubes and ovaries. It can cause a variety of symptoms, which can vary in severity from mild to severe. If left untreated, salpingoophoritis can lead to complications, such as infertility and chronic pelvic pain. It is important to recognize the symptoms and seek medical attention if you suspect you may have salpingoophoritis.
Common symptoms of salpingoophoritis include:
- Lower abdominal pain
- Pelvic pain
- Pain during intercourse
- Painful urination
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Irregular menstrual bleeding
- Fever
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
- Generalized body weakness
In some cases, salpingoophoritis may not cause any noticeable symptoms or the symptoms may be mild and go unnoticed. This can make diagnosis and treatment challenging, as the infection can progress without intervention. It is important to see a healthcare provider if you experience any of the above symptoms or if you have concerns about your reproductive health.
Early diagnosis and treatment of salpingoophoritis is crucial to prevent complications and preserve fertility. If you suspect you may have salpingoophoritis, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Diagnosis and Testing for Salpingoophoritis
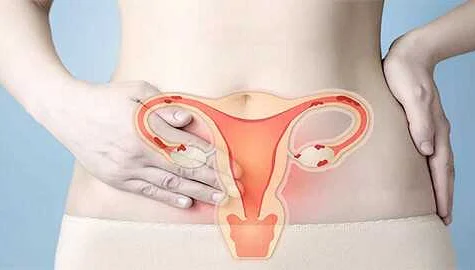
Diagnosing salpingoophoritis involves a combination of medical history assessment, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. If you experience symptoms such as pelvic pain, fever, abnormal vaginal discharge, or pain during intercourse, it is important to seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis.
During the medical history assessment, your doctor will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and any risk factors that may contribute to salpingoophoritis. It is crucial to provide accurate information to help the doctor make an accurate diagnosis.
During the physical examination, the doctor will perform a pelvic exam to check for any abnormalities in the reproductive organs. They may also check for tenderness or swelling in the lower abdomen or pelvic region.
In addition to the medical history assessment and physical examination, your doctor may order certain diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis of salpingoophoritis. These tests may include:
- Blood tests: A complete blood count (CBC) may be done to check for signs of infection, such as an elevated white blood cell count.
- Urinalysis: A urinalysis may be performed to rule out other possible causes of the symptoms.
- Pelvic ultrasound: An ultrasound may be done to visualize the reproductive organs and identify any signs of inflammation or infection.
- Endometrial biopsy: In some cases, your doctor may recommend an endometrial biopsy to rule out other conditions and to evaluate the lining of the uterus.
- Swab tests: Swab tests may be taken from the cervix, vagina, or fallopian tubes to check for the presence of bacteria or other infectious agents.
Once a diagnosis of salpingoophoritis is confirmed, your doctor will discuss the appropriate treatment options based on the severity of the infection and your overall health. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent complications and promote recovery.
Treatment Options for Salpingoophoritis
Treatment for salpingoophoritis usually involves a combination of medication and lifestyle changes. The goals of treatment are to reduce inflammation and pain, eliminate the infection, and prevent future episodes.
1. Antibiotics: The primary treatment for salpingoophoritis is antibiotics. These medications are used to kill the bacteria causing the infection. The specific antibiotic prescribed will depend on the severity of the infection and may be taken orally or administered intravenously.
2. Pain medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. If the pain is severe, stronger prescription pain medication may be recommended.
3. Rest and self-care: It is important to rest and take care of yourself while recovering from salpingoophoritis. Avoid strenuous activities that could worsen the symptoms and follow your healthcare provider’s instructions on self-care measures, such as applying heat or cold packs to the affected area.
4. Treatment of sexual partners: If the infection is caused by a sexually transmitted infection, it is crucial for sexual partners to receive treatment to prevent reinfection. It is recommended to abstain from sexual activity until both partners have completed treatment.
5. Surgical intervention: In severe cases or when other treatment options have failed, surgery may be necessary. This could involve removing the infected fallopian tubes and ovaries, a procedure called salpingo-oophorectomy. However, surgery is typically considered a last resort and is only recommended in certain situations.
It is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Following the treatment plan, taking all prescribed medications, and attending follow-up appointments are crucial for successful recovery from salpingoophoritis.