Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment of Vaginal Varicose Veins
Содержимое
Vaginal varicose veins are a common condition during pregnancy. This article discusses the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for vaginal varicose veins, including lifestyle changes, compression stockings, and medical procedures.
Vaginal varicose veins, also known as vulvar varicosities, are a fairly common condition that affects women during pregnancy. While varicose veins commonly occur in the legs, they can also develop in the vaginal area due to increased blood flow and hormonal changes. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for vaginal varicose veins is important for women who may be experiencing discomfort or pain in this area.
One of the main causes of vaginal varicose veins is the pressure that the growing uterus puts on the pelvic veins, which can cause them to enlarge and become twisted. Hormonal changes during pregnancy also play a role in the development of varicose veins, as they can weaken the vein walls and valves, making them more susceptible to swelling and pooling of blood.
The symptoms of vaginal varicose veins can vary from mild to severe, depending on the individual. Common symptoms include pain or discomfort in the vaginal area, aching or heaviness in the pelvis, and visible or bulging veins. Some women may also experience itching, swelling, or a feeling of fullness in the area. These symptoms can worsen with prolonged standing or sitting, and may improve with rest or elevation of the legs.
Treatment options for vaginal varicose veins focus on relieving symptoms and improving circulation. Conservative measures such as wearing compression stockings, avoiding prolonged standing or sitting, and elevating the legs can help reduce discomfort and swelling. Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding constipation can also be beneficial. In more severe cases, medical interventions such as sclerotherapy or surgery may be considered.
If you are experiencing symptoms of vaginal varicose veins, it is important to discuss them with your healthcare provider. They can provide a proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options to help alleviate your symptoms and improve your quality of life during pregnancy.
Understanding Vaginal Varicose Veins
Vaginal varicose veins are a common condition in women, but many may not be aware of their existence or symptoms. Varicose veins occur when the blood vessels in the vaginal area become swollen and twisted. This can cause discomfort and pain, as well as other symptoms.
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of vaginal varicose veins. Pregnancy is a major factor, as the growing uterus puts pressure on the veins in the pelvic area. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can also weaken the vein walls, making them more susceptible to swelling. Other factors include obesity, genetics, and hormonal changes during menopause.
The symptoms of vaginal varicose veins can vary from mild to severe. Some women may experience no symptoms at all, while others may have pain, itching, or a feeling of heaviness in the vaginal area. In some cases, the veins may be visible as blue or purple bulges on the surface of the skin.
Treatment options for vaginal varicose veins depend on the severity of the symptoms. In mild cases, self-care measures such as elevating the legs, avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, and wearing compression stockings may help alleviate symptoms. In more severe cases, medical interventions such as sclerotherapy or surgery may be necessary to remove or close off the affected veins.
If you are experiencing symptoms of vaginal varicose veins, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Understanding vaginal varicose veins can help you make informed decisions about your health and seek the care you need.
Causes of Vaginal Varicose Veins
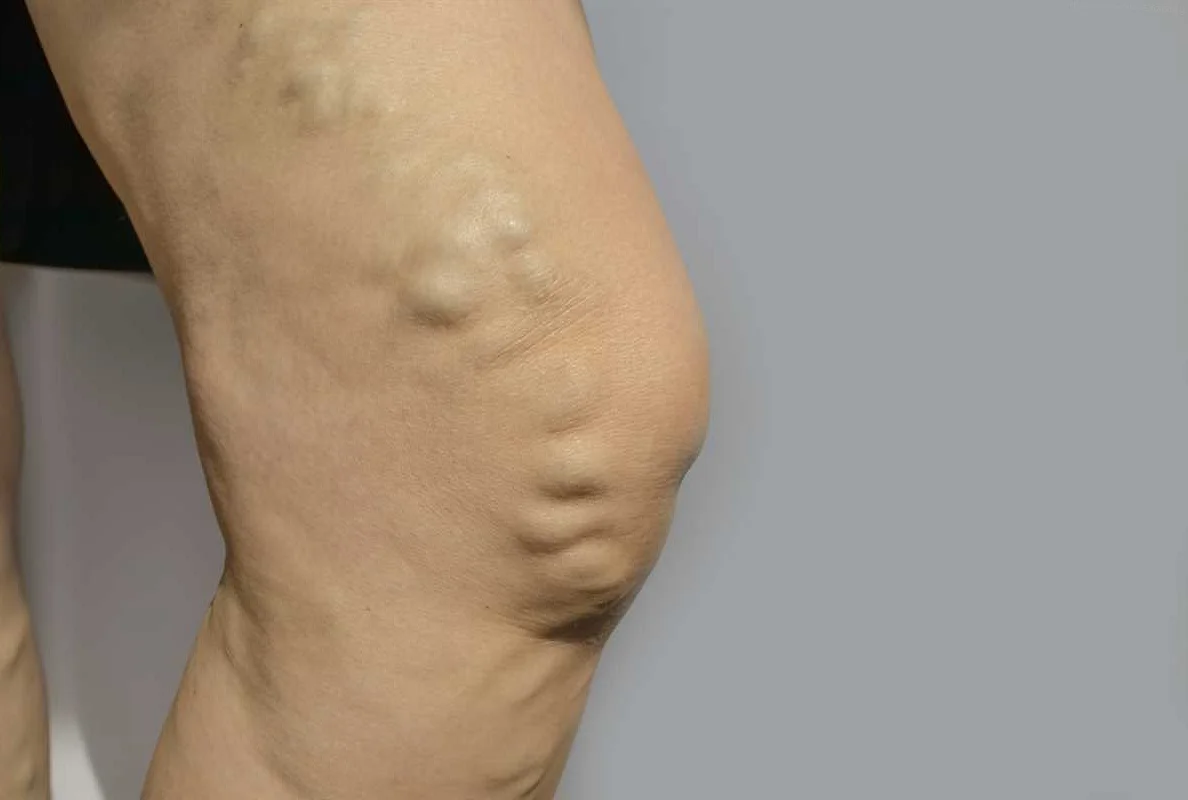
Vaginal varicose veins, also known as vulvar varicose veins, occur when the veins in the vaginal area become swollen and enlarged. While the exact cause of vaginal varicose veins is not fully understood, there are several factors that may contribute to their development:
1. Increased blood volume: During pregnancy, the volume of blood in a woman’s body increases significantly to support the growing fetus. This increase in blood volume can put additional pressure on the veins, causing them to become dilated and varicose.
2. Hormonal changes: Pregnancy hormones can also play a role in the development of vaginal varicose veins. These hormones relax the walls of the blood vessels, making it easier for them to become dilated and varicose.
3. Weakened vein walls: Some women may have naturally weaker vein walls, which can make them more prone to developing varicose veins. This weakness can be genetic or the result of previous pregnancies or medical conditions.
4. Increased pressure on the pelvic area: In addition to increased blood volume, the growing uterus can put pressure on the veins in the pelvic area, further contributing to the development of vaginal varicose veins.
5. Prolonged standing or sitting: Spending long periods of time standing or sitting can contribute to poor blood circulation and increase the risk of developing varicose veins in the vaginal area.
It is important to note that while vaginal varicose veins are often associated with pregnancy, they can also occur in women who are not pregnant. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
Symptoms of Vaginal Varicose Veins
Vaginal varicose veins are a common condition that can cause discomfort and pain for many women. While the appearance of enlarged, swollen veins in the vaginal area is one of the main symptoms, there are other signs to watch out for.
Some of the common symptoms of vaginal varicose veins include:
- Pain or discomfort in the vaginal area
- Pressure or heaviness in the pelvic region
- Itching or burning sensation in the genital area
- Visible, enlarged veins in and around the vagina
- Discomfort or pain during sexual intercourse
- In some cases, vaginal bleeding
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
While vaginal varicose veins can be a source of discomfort and concern, there are treatment options available to help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. Your healthcare provider may recommend lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise and wearing compression stockings, or may suggest more invasive treatments, such as sclerotherapy or surgery.
Overall, understanding the symptoms of vaginal varicose veins is important in order to seek proper medical attention and receive appropriate treatment. With the right care, you can manage this condition and find relief from any discomfort or pain you may be experiencing.
Treatment Options for Vaginal Varicose Veins
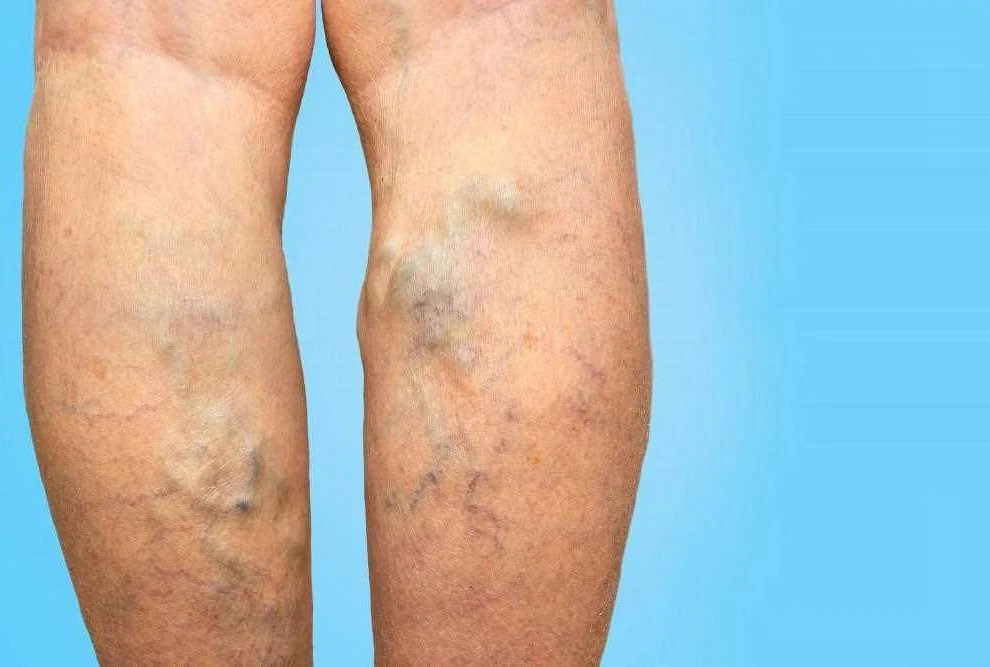
Vaginal varicose veins can be an uncomfortable and sometimes painful condition for women. Fortunately, there are several treatment options available to help manage and alleviate the symptoms associated with this condition.
Conservative Methods:
If the vaginal varicose veins are mild and not causing significant discomfort, conservative methods may be recommended. These methods aim to reduce symptoms and improve blood circulation without the need for invasive procedures. Some of the conservative treatment options include:
- Elevating the legs: Elevating the legs while resting or sleeping can help alleviate the pressure on the veins and improve blood flow.
- Wearing compression stockings: Compression stockings can help support the veins and improve blood circulation in the legs.
- Engaging in regular exercise: Gentle exercises, such as walking or swimming, can help improve blood flow and reduce symptoms.
Sclerotherapy:
Sclerotherapy is a minimally invasive procedure that involves injecting a solution directly into the affected veins. This solution irritates the vein wall, causing it to collapse and eventually be reabsorbed by the body. Sclerotherapy can be an effective treatment option for vaginal varicose veins, as it helps to reduce the size and appearance of the veins.
Laser Treatment:
Laser treatment is another option for treating vaginal varicose veins. This procedure uses laser energy to heat and close off the affected veins. Laser treatment can be effective in reducing the symptoms of vaginal varicose veins and improving blood circulation.
Surgical Options:
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to treat severe vaginal varicose veins. Surgical options include vein ligation and vein stripping, which involve tying off or removing the affected veins. These procedures are typically done under general anesthesia and may require a longer recovery period compared to less invasive treatments.
Consultation with a healthcare professional:
If you suspect you have vaginal varicose veins or experience symptoms such as pain, discomfort, or swelling in the vaginal area, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can assess your condition, provide an accurate diagnosis, and recommend the most suitable treatment options for your specific case.
Overall, with the various treatment options available, vaginal varicose veins can be effectively managed and symptoms can be reduced. It is essential to seek medical advice and discuss the best course of treatment for your individual needs.
Prevention of Vaginal Varicose Veins
While vaginal varicose veins can be a common occurrence during pregnancy, there are steps you can take to help prevent or minimize their development. Here are some preventive measures you can consider:
1. Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can improve blood circulation and help prevent the formation of varicose veins. Exercises that focus on the pelvic area, such as Kegels, can be particularly beneficial for preventing vaginal varicose veins.
2. Maintain a Healthy Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce pressure on your blood vessels and lower your risk of developing varicose veins, including those in the vaginal area. Eating a balanced diet and practicing portion control can help you achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
3. Avoid Prolonged Sitting or Standing: Prolonged periods of sitting or standing can contribute to poor blood circulation and increase the risk of developing varicose veins. If your job involves long hours of sitting or standing, try to take breaks and engage in gentle leg exercises to promote blood flow.
4. Elevate Your Legs: Elevating your legs while sitting or lying down can help improve blood flow and reduce the pressure on your veins. Prop up your legs with a pillow or use a footrest to keep them elevated whenever possible.
5. Wear Compression Stockings: Compression stockings apply pressure to your legs, which helps to improve blood flow and prevent varicose veins. Opt for compression stockings that are specifically designed for pregnancy and provide the right level of compression.
6. Avoid Tight Clothing: Wearing tight clothing, especially around the waist and groin area, can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of developing varicose veins. Opt for loose-fitting and comfortable clothing to promote healthy blood circulation.
7. Stay Hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water can help maintain blood volume and prevent dehydration, which can contribute to poor circulation. Aim to drink at least 8 cups of water per day to support optimal blood flow.
8. Avoid High Heels: Wearing high heels can impede blood flow and increase pressure on your veins. Opt for comfortable shoes with low heels or flats to promote healthy circulation.
While these preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing vaginal varicose veins, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and guidance.