Urinary control
Содержимое
Learn about urinary control and how to improve bladder function. Discover tips and techniques to manage urinary incontinence and regain control of your bladder. Find resources and support for managing urinary control issues.
Are you experiencing difficulties with urinary control?
Urinary incontinence can be caused by a variety of factors, such as pregnancy, childbirth, aging, and certain medical conditions. It can significantly impact your daily life and overall well-being.
If you’re struggling with symptoms like frequent urination, sudden urges to urinate, or urine leakage, it’s important to seek treatment options that can help improve your quality of life.
Understanding Urinary Control
Urinary control is the body’s ability to regulate the release of urine from the bladder. It is a vital function that allows us to empty our bladder at the appropriate time and place.
Causes of Urinary Control Problems:
There are several factors that can contribute to urinary control problems. These include:
- Weak pelvic floor muscles
- Nerve damage
- Urinary tract infections
- Hormonal changes
- Side effects of medications
- Obstruction in the urinary tract
Symptoms of Urinary Control Problems:
Common symptoms of urinary control problems include:
- Urinary leakage or incontinence
- Frequent urination
- Urgency to urinate
- Weak urinary stream
- Pain or discomfort during urination
Treatment Options for Urinary Control Problems:
There are various treatment options available for urinary control problems. These include:
- Strengthening the pelvic floor muscles through exercises such as Kegels
- Medications to manage symptoms
- Behavioral therapies, such as bladder training
- Surgical procedures in severe cases
If you are experiencing urinary control problems, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
What is Urinary Control?
Urinary control refers to the ability to control the release of urine from the bladder. It is an essential function of the urinary system and an important aspect of overall health and well-being.
When we have full urinary control, we can choose when and where to empty our bladder. However, certain factors can disrupt this control, leading to urinary incontinence or the involuntary leakage of urine.
There are several causes of urinary control problems, including weakened pelvic floor muscles, hormonal changes, nerve damage, and certain medical conditions like urinary tract infections or prostate problems.
Symptoms of urinary control issues may vary, but common signs include frequent urination, a sudden and strong urge to urinate, urinating during sleep, or difficulty starting or stopping urination.
Treatment options for urinary control problems depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Non-invasive approaches such as lifestyle changes, pelvic floor exercises, and bladder training can often help improve urinary control.
In some cases, medications or medical devices may be prescribed to manage symptoms. For more severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to address the underlying issue and restore urinary control.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional if you are experiencing urinary control problems. They can help determine the cause and recommend the most appropriate treatment options for your specific situation.
Don’t let urinary control issues limit your daily activities and quality of life. Take control and seek the help you need to maintain optimal urinary control and overall well-being.
The Causes of Urinary Control Issues
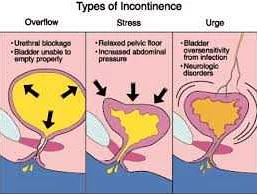
Urinary control issues, also known as urinary incontinence, can be caused by a variety of factors. Understanding these causes is essential in order to effectively manage and treat the issue.
Some of the common causes of urinary control issues include:
| Age | As individuals age, the muscles and nerves that control the bladder may weaken, leading to urinary control issues. |
| Pregnancy and Childbirth | During pregnancy and childbirth, the pelvic floor muscles may stretch or weaken, resulting in urinary incontinence. |
| Menopause | Changes in estrogen levels during menopause can cause the tissues of the urethra and bladder to become less elastic, leading to urinary control issues. |
| Prostate Problems | Enlarged prostate or prostate surgery can cause urinary control issues in men. |
| Neurological Disorders | Conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and stroke can affect the nerves that control the bladder, resulting in urinary incontinence. |
| Urinary Tract Infections | Infections of the urinary tract, such as bladder or kidney infections, can cause temporary urinary control issues. |
| Medications | Certain medications, such as diuretics or muscle relaxants, can interfere with bladder control and lead to urinary incontinence. |
| Obesity | Excess weight can put pressure on the bladder and surrounding muscles, contributing to urinary control issues. |
If you are experiencing urinary control issues, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of urinary control issues is the first step towards finding a suitable treatment option. It’s important to be aware of the signs and symptoms to ensure prompt medical attention and intervention. Here are some common symptoms to watch out for:
- Frequent urination: If you find yourself needing to urinate more often than usual, especially during the night, it could be a sign of urinary control problems.
- Urgency: Feeling a strong and sudden need to urinate, often with little or no warning, may indicate an issue with urinary control.
- Leakage: Accidental leakage of urine, especially during activities such as coughing, sneezing, laughing, or exercising, can be a symptom of urinary control problems.
- Incomplete emptying: Difficulty fully emptying the bladder or feeling like there is still urine left after urination can be a sign of urinary control issues.
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs): Recurrent UTIs may be a red flag for underlying urinary control problems.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and to explore your treatment options. Remember, early recognition and intervention can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with urinary control issues.
Exploring Treatment Options
When it comes to managing urinary control issues, there are several treatment options available. The right approach for you will depend on the underlying cause of your symptoms, as well as your individual needs and preferences. Here are some common treatment options to consider:
| Behavioral Techniques | These techniques involve making changes to your daily habits and routines to improve bladder control. This may include timed voiding, pelvic floor exercises, and fluid management. |
| Medications | There are various medications available that can help manage urinary control issues. These may include anticholinergics, alpha blockers, and topical estrogen therapy. |
| Physical Therapy | Physical therapy can be beneficial in strengthening the pelvic floor muscles and improving bladder control. This may involve exercises, biofeedback, and electrical stimulation. |
| Surgical Interventions | In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to treat urinary control issues. This may include procedures such as bladder suspension, sling surgery, or artificial urinary sphincter implantation. |
| Alternative Therapies | There are also alternative therapies that some individuals find helpful in managing urinary control issues. These may include acupuncture, herbal remedies, and bladder training. |
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment option for you. They will be able to assess your symptoms, perform any necessary tests, and provide personalized recommendations based on your individual circumstances. With the right treatment plan, you can regain control and improve your quality of life.
Improving Urinary Control
While urinary control issues can be distressing, there are various measures you can take to improve your condition. Here are some tips to help you regain control of your bladder:
- Practice Kegel exercises: Kegel exercises involve contracting and relaxing the pelvic floor muscles. These exercises can help strengthen your pelvic floor, which plays a key role in urinary control.
- Stay hydrated: It may seem counterintuitive, but staying well-hydrated can actually improve urinary control. Aim to drink enough water throughout the day to keep your urine a light, pale yellow color.
- Avoid bladder irritants: Certain foods and drinks can irritate the bladder and worsen urinary control issues. Try to limit or avoid alcohol, caffeine, carbonated beverages, spicy foods, and citrus fruits.
- Manage your weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can help improve urinary control. Excess weight can put additional pressure on the bladder, leading to leakage or difficulty controlling urine flow.
- Use the bathroom regularly: Holding your urine for long periods of time can contribute to urinary control issues. Make sure to empty your bladder regularly, even if you don’t feel the need to go.
- Manage constipation: Constipation can put pressure on the bladder, making urinary control more difficult. Make sure to eat a diet high in fiber, drink plenty of water, and consider using a stool softener if necessary.
- Consider pelvic floor therapy: In some cases, working with a pelvic floor physical therapist can help improve urinary control. They can provide guidance on exercises and techniques to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.
- Talk to your doctor: If you’re struggling with urinary control, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider. They can help determine the underlying causes of your symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Remember, improving urinary control may take time and patience. Be consistent with your efforts and don’t hesitate to seek professional help if needed. With the right approach, you can regain control and improve your quality of life.