Venous insufficiency of the lower extremities: symptoms, treatment, drugs
Содержимое
Learn about venous insufficiency of the lower extremities, its symptoms, and available treatment options, including medications. Find out how to manage and prevent this condition for better leg health.
Venous insufficiency of the lower extremities is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the veins in the legs are unable to efficiently return blood back to the heart. This can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications, including pain, swelling, and skin changes.
One of the main causes of venous insufficiency is a condition called chronic venous insufficiency (CVI), which is often a result of damaged or weakened valves in the veins. These valves are responsible for preventing blood from flowing backwards, but when they become damaged, blood can pool in the veins and lead to venous insufficiency.
Symptoms of venous insufficiency can vary from mild to severe and may include leg pain, swelling, heaviness, and fatigue. Skin changes, such as varicose veins, spider veins, and skin ulcers, may also occur in more advanced cases of the condition. If left untreated, venous insufficiency can cause serious complications, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and leg ulcers.
Treatment for venous insufficiency focuses on improving blood flow and reducing symptoms. Lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, elevating the legs, and wearing compression stockings, can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further progression of the condition. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation or to promote blood thinning.
In more severe cases, procedures such as sclerotherapy, endovenous laser treatment, or surgical interventions may be recommended to remove or close off damaged veins and improve circulation. Your healthcare provider will determine the best treatment plan based on the severity of your condition and your individual needs.
Overall, venous insufficiency of the lower extremities is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management. By understanding the symptoms, treatment options, and available medications, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and improve their quality of life.
Understanding Venous Insufficiency
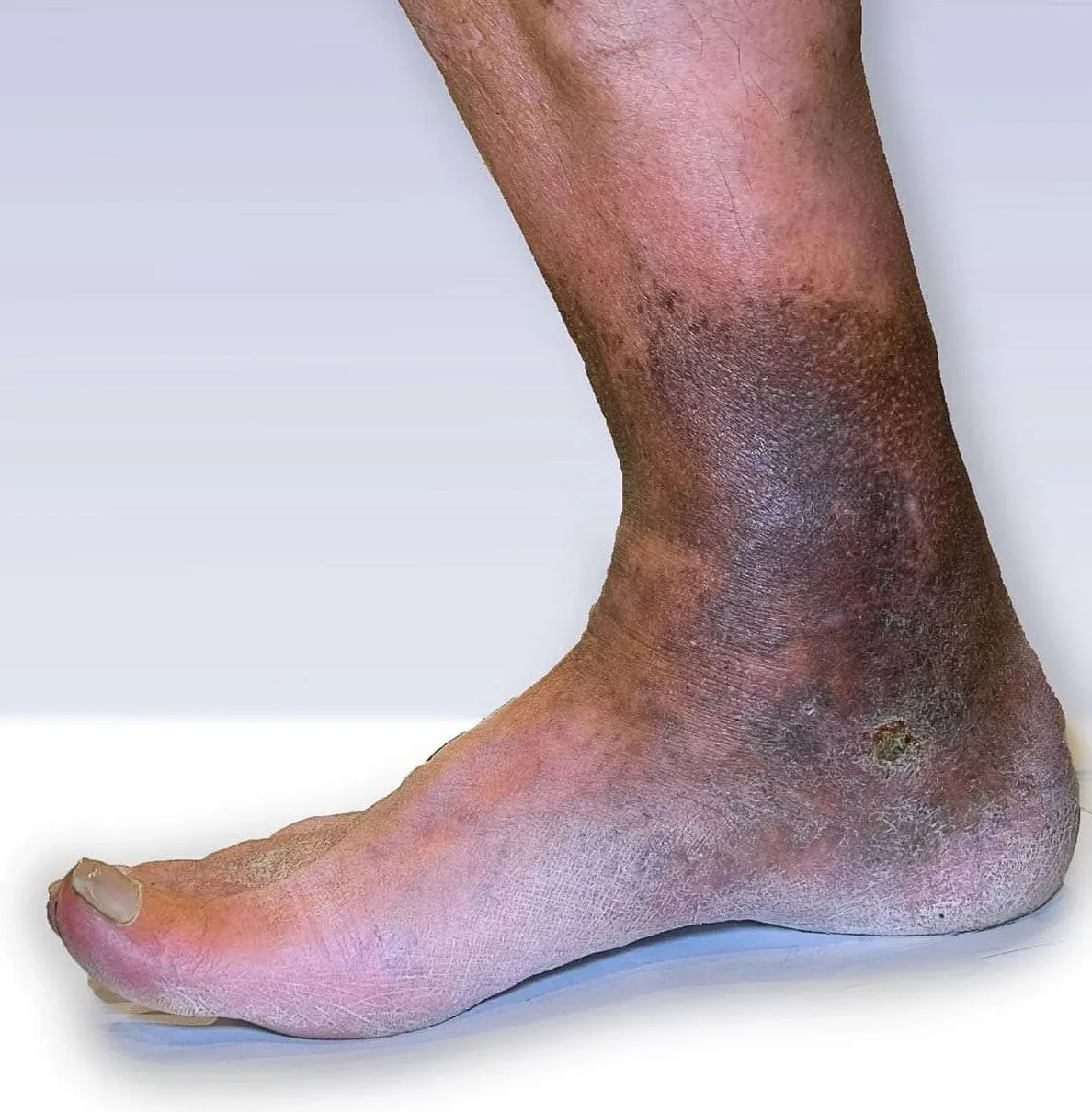
Venous insufficiency refers to a condition where the veins in the lower extremities, such as the legs and feet, are unable to efficiently return blood back to the heart. This can lead to a variety of symptoms and complications, ranging from mild discomfort to severe pain and ulcers.
The veins in the legs have valves that help prevent blood from flowing in the wrong direction. When these valves become damaged or weakened, blood can pool in the veins, causing them to become swollen and enlarged. This pooling of blood is known as venous insufficiency.
The main causes of venous insufficiency include:
| 1. | Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): a blood clot in the deep veins |
| 2. | Varicose veins: enlarged, twisted veins near the surface of the skin |
| 3. | Previous leg injury or surgery |
| 4. | Obesity: excess weight puts added pressure on the veins |
| 5. | Pregnancy: hormonal changes and increased blood volume can affect vein function |
Common symptoms of venous insufficiency include:
- Pain or aching in the legs, especially after long periods of standing or sitting
- Swelling in the legs and ankles
- Visible varicose veins
- Leg cramps
- Itching or tingling sensation
- Changes in skin color and texture
Without proper treatment, venous insufficiency can lead to more serious complications, such as venous ulcers, skin infections, and deep vein thrombosis. Therefore, it is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of venous insufficiency.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Venous insufficiency of the lower extremities can manifest itself through a variety of symptoms. It is important to be able to recognize these symptoms in order to seek timely medical attention and receive appropriate treatment.
One common symptom of venous insufficiency is swelling in the legs and ankles. This swelling, also known as edema, occurs due to the buildup of fluid in the tissues. It may be more pronounced at the end of the day or after prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
Another symptom is the development of varicose veins. These are enlarged, twisted veins that can appear blue or purple in color. They often protrude from the skin surface and can be painful or tender to the touch. Varicose veins are caused by the weakening of the vein walls and the pooling of blood in the affected veins.
Individuals with venous insufficiency may also experience leg pain or aching, especially after physical activity. This pain can be described as a dull, throbbing sensation that may improve with leg elevation or rest.
Other symptoms may include skin changes in the affected area, such as dryness, itchiness, or a brownish discoloration. The skin may become thin and fragile, and wounds or ulcers may develop. These skin changes are a result of the poor circulation and reduced oxygen supply to the tissues.
In some cases, venous insufficiency can lead to restless legs syndrome. This condition is characterized by an uncontrollable urge to move the legs, particularly at night. It can disrupt sleep and cause discomfort.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Early recognition and intervention can help prevent complications and improve overall quality of life.
Diagnosis and Tests
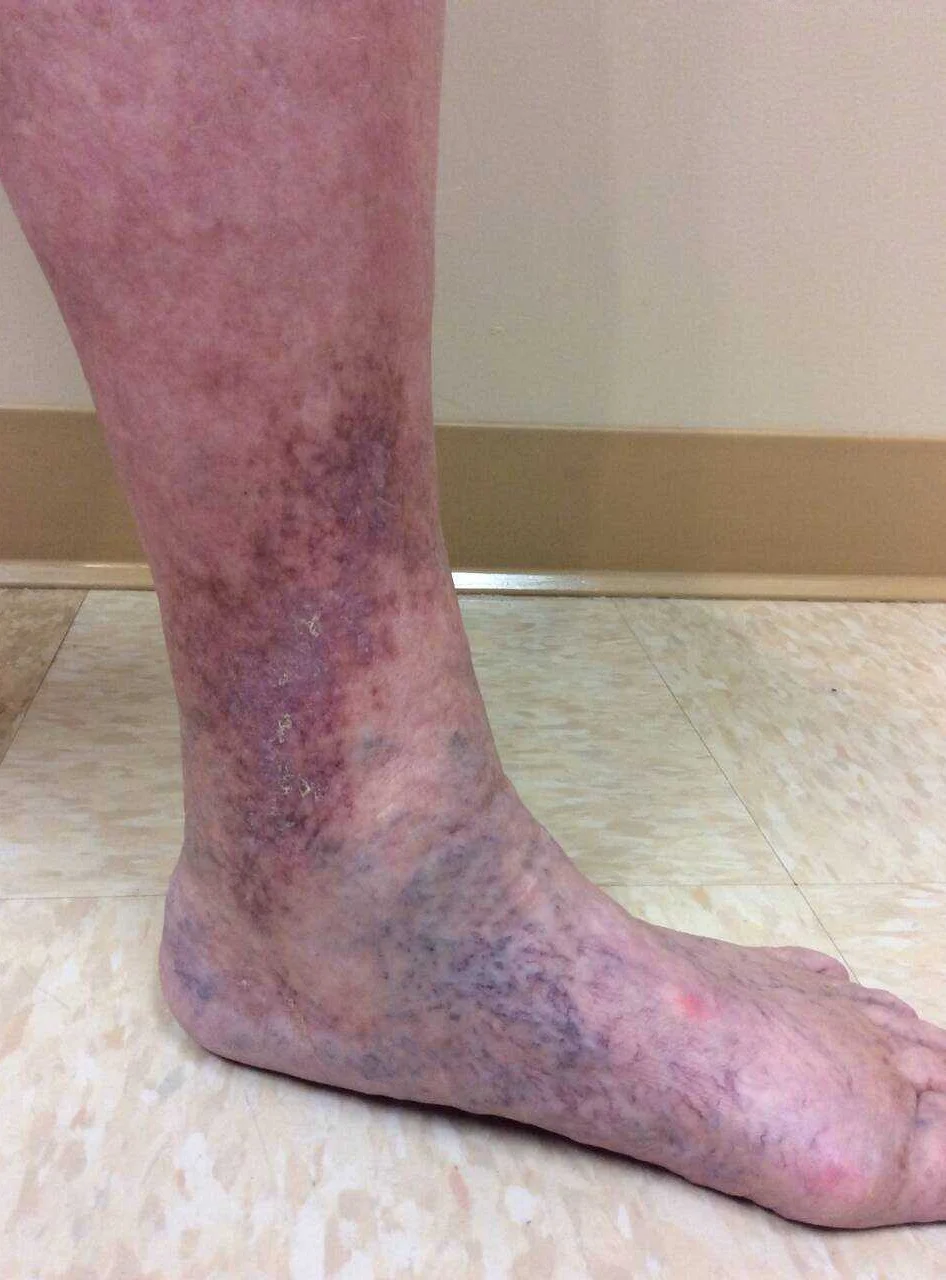
To diagnose venous insufficiency of the lower extremities, a thorough medical history and physical examination are typically performed. The doctor will ask about the patient’s symptoms, such as leg pain, swelling, and skin changes. They will also inquire about any risk factors, such as a family history of venous disease or a sedentary lifestyle.
During the physical examination, the doctor will visually inspect the patient’s legs for any signs of venous insufficiency, such as varicose veins or ulcers. They may also perform a manual assessment called the Trendelenburg test, which involves compressing certain veins to check for abnormal blood flow.
In addition to the medical history and physical examination, various tests may be used to confirm the diagnosis, assess the severity, and determine the underlying cause of venous insufficiency. These tests may include:
| Duplex ultrasound | This non-invasive test uses sound waves to create images of the veins in the legs. It allows the doctor to evaluate the blood flow and identify any blockages or valve abnormalities. |
| Doppler ultrasound | Similar to duplex ultrasound, this test measures the speed and direction of blood flow in the veins using sound waves. |
| Venography | This invasive test involves injecting a contrast dye into the veins and taking X-ray images. It provides detailed information about the veins and their function. |
| CT scan or MRI | In some cases, imaging tests like CT scan or MRI may be ordered to get a more detailed view of the veins and surrounding structures. |
| Blood tests | Occasionally, blood tests may be done to rule out other medical conditions that could be causing the symptoms. |
These diagnostic tests can help the doctor determine the appropriate treatment plan for the patient. They can also help identify any complications or coexisting conditions that may need to be addressed.
Treatment Options
There are several treatment options available for venous insufficiency of the lower extremities. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the patient’s symptoms.
In mild cases, conservative treatment measures may be recommended. This may include lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, elevation of the legs, and wearing compression stockings. These measures can help improve blood flow and reduce symptoms.
If conservative treatment measures are not sufficient, medical interventions may be necessary. One common treatment option is the use of medications to improve blood flow and reduce inflammation. Some commonly prescribed medications include diuretics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and anticoagulants.
In more severe cases, surgical interventions may be required. These procedures aim to remove or repair the damaged veins and restore proper blood flow. Some surgical options include vein ligation and stripping, endovenous laser treatment, and sclerotherapy.
| Conservative Measures | Non-invasive, can be done at home | May not be effective in all cases |
| Medications | Can help improve blood flow and reduce inflammation | Possible side effects and drug interactions |
| Surgical Interventions | Can provide long-term relief | Risk of complications and longer recovery time |
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment option for individual cases of venous insufficiency of the lower extremities.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
If you have venous insufficiency of the lower extremities, there are several lifestyle changes and home remedies that you can incorporate into your daily routine to help manage your symptoms and improve your overall vascular health.
1. Exercise regularly: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can help promote blood flow and improve circulation in your legs. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
2. Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight can put added pressure on your veins and exacerbate venous insufficiency symptoms. Eating a balanced diet and maintaining a healthy weight can help alleviate some of the symptoms associated with this condition.
3. Elevate your legs: Elevating your legs above heart level for 15-20 minutes several times a day can help reduce swelling and improve blood flow. You can use pillows or a reclining chair to elevate your legs comfortably.
4. Wear compression stockings: Compression stockings can provide support to your veins and help improve circulation in your legs. These stockings apply pressure to your legs, helping to prevent blood from pooling and reducing swelling.
5. Avoid prolonged sitting or standing: If your job requires long periods of sitting or standing, try to take breaks and move around as often as possible. This can help prevent blood from pooling in your legs and alleviate symptoms.
6. Practice leg exercises: Simple leg exercises, such as ankle pumps and leg lifts, can help improve circulation in your legs. These exercises can be done while sitting or lying down and can be incorporated into your daily routine.
7. Manage stress: Stress can worsen symptoms of venous insufficiency. Practice stress management techniques, such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga, to help relax your body and mind.
8. Avoid tight clothing: Wearing tight clothing, especially around your waist, groin, and thighs, can restrict blood flow and worsen symptoms. Opt for loose-fitting clothing that allows for proper circulation.
9. Stay hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water can help keep your blood volume at a healthy level and prevent dehydration, which can affect blood flow. Aim to drink at least 8 cups of water per day.
10. Quit smoking: Smoking can constrict blood vessels and worsen symptoms of venous insufficiency. Quitting smoking can improve your overall vascular health and reduce the risk of complications associated with this condition.
While these lifestyle changes and home remedies can help alleviate symptoms and improve your vascular health, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.