Breast Infection: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Содержимое
Breast infection, also known as mastitis, is a painful condition that can occur in breastfeeding women. It is caused by bacteria entering the breast tissue, leading to inflammation and infection. Symptoms include breast pain, redness, swelling, and fever. Treatment typically involves antibiotics, pain medication, and frequent breastfeeding or pumping to help clear the infection. It is important to seek medical attention promptly to prevent complications and ensure a swift recovery.
A breast infection, also known as mastitis, is a condition that occurs when bacteria enters the breast tissue, causing inflammation and infection. This condition is most commonly seen in breastfeeding women, but it can also occur in women who are not breastfeeding. Breast infections can be painful and uncomfortable, but with prompt treatment, they can be effectively managed.
The most common cause of breast infection is bacteria entering the breast tissue through a cracked or sore nipple. This can happen during breastfeeding when the baby’s mouth comes into contact with the cracked skin. Other factors that can contribute to the development of a breast infection include poor breast hygiene, a weakened immune system, and blocked milk ducts. It’s important to note that not all women who experience these factors will develop a breast infection, as the presence of bacteria is also a key factor.
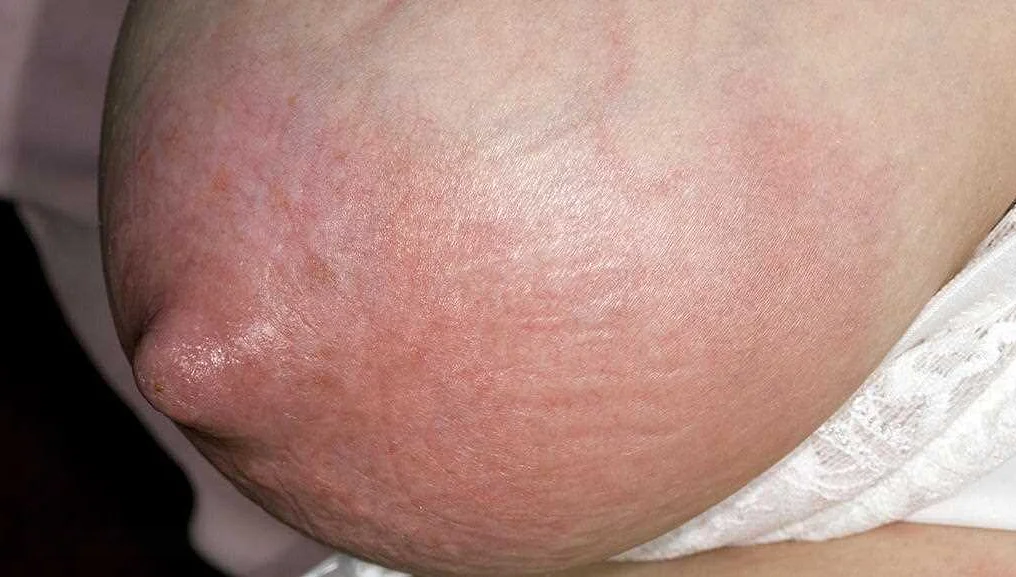
Signs and symptoms of a breast infection may include redness, swelling, and warmth in the affected breast, as well as pain or tenderness. Some women may also experience flu-like symptoms such as fever, chills, and fatigue. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms, as they may indicate a breast infection that requires treatment.
Treatment for breast infection usually involves a combination of antibiotics to address the underlying bacterial infection, as well as pain medication to manage discomfort. It’s also important to continue breastfeeding or pumping breast milk to help alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications. In some cases, if an abscess (a pocket of pus) develops, it may need to be drained through a minor surgical procedure. It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions and complete the full course of antibiotics to ensure effective treatment.
In conclusion, breast infection is a common condition that can occur in breastfeeding and non-breastfeeding women. Prompt treatment with antibiotics and management of symptoms is crucial to prevent complications and promote a full recovery. If you suspect you have a breast infection, it’s important to seek medical attention to receive the appropriate care and guidance.
Causes of Breast Infection
A breast infection, also known as mastitis, can be caused by a variety of factors. Some common causes of breast infection include:
| Bacterial infection | Bacteria can enter the breast tissue through cracks or breaks in the skin, especially during breastfeeding. This can lead to an infection. |
| Milk duct blockage | When a milk duct becomes blocked, milk may build up and create an environment favorable for bacterial growth, leading to an infection. |
| Weak immune system | If the immune system is weakened, it may be less able to fight off infections, including breast infections. |
| Poor breastfeeding technique | If the baby doesn’t latch on properly during breastfeeding, it may not drain the breast completely, increasing the risk of infection. |
| Injury to the breast | An injury to the breast, such as a bruise or cut, can make it more susceptible to infection. |
| Previous breast infection | Having had a previous breast infection increases the likelihood of developing another infection. |
| Diabetes | Women with diabetes are more prone to developing infections, including breast infections. |
It’s important to note that breast infections are not contagious and cannot be passed from one person to another.
Symptoms of Breast Infection
A breast infection, also known as mastitis, can cause a variety of symptoms. It is important to be aware of these symptoms in order to seek prompt medical attention if necessary.
Some common symptoms of breast infection include:
- Pain and tenderness: The affected breast may be painful and tender to the touch. This pain may be continuous or may come and go.
- Swelling and redness: The breast may appear swollen and red. The skin may also feel warm to the touch.
- Flu-like symptoms: In some cases, a breast infection may cause flu-like symptoms such as fever, chills, body aches, and fatigue.
- Nipple discharge: There may be a discharge from the nipple that is pus-like or contains blood.
- Lump or thickening: A breast infection may cause a lump or thickening in the breast tissue.
- Tender lymph nodes: The lymph nodes under the arm on the affected side may become swollen and tender.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see your healthcare provider for an evaluation. They can determine if you have a breast infection and recommend appropriate treatment.
It is worth noting that breastfeeding women are more prone to developing breast infections. This is because bacteria can enter the breast tissue through a cracked or sore nipple. However, breast infections can also occur in women who are not breastfeeding.
If you suspect you have a breast infection, do not hesitate to contact your healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis of Breast Infection
To diagnose a breast infection, a healthcare professional will typically start by conducting a physical examination of the breast and asking about any symptoms the individual may be experiencing. The healthcare professional will look for signs of redness, swelling, warmth, tenderness, and pus or discharge from the nipple.
In some cases, the healthcare professional may also order additional tests to confirm the diagnosis. These tests may include:
- Breast ultrasound: This imaging test uses sound waves to create pictures of the breast. It can help determine if there are any abscesses or other abnormalities present.
- Mammogram: A mammogram is an X-ray of the breast. It may be used to evaluate any suspicious areas or to look for signs of an infection.
- Breast culture: A sample of breast milk or fluid may be collected and sent to a laboratory for analysis. This can help identify the specific bacteria causing the infection and determine the most effective treatment.
In some cases, a healthcare professional may also recommend a biopsy, which involves removing a small sample of breast tissue for further examination. This is typically done if there is a concern that the infection may be related to a more serious condition, such as breast cancer.
It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect you have a breast infection. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and promote a faster recovery.
Treatment of Breast Infection
The treatment for breast infections, also known as mastitis, typically involves a combination of antibiotics and self-care measures to relieve symptoms and promote healing. It is important to start treatment as soon as possible to prevent complications and avoid the spread of infection.
Antibiotics: Your healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics to fight the infection. It is important to take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if you start feeling better. This will ensure that the infection is completely eradicated and prevent it from recurring.
Pain relief: Pain and inflammation can be alleviated by taking over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Applying warm compresses to the affected breast can also help relieve discomfort and promote healing.
Breastfeeding or pumping: Continue breastfeeding or pumping milk to help drain the affected breast and promote healing. Emptying the breast regularly can prevent milk from building up and worsening the infection. If breastfeeding is too painful, you can try different feeding positions or consult a lactation specialist for assistance.
Rest and self-care: Get plenty of rest and take care of yourself during treatment. Make sure to stay hydrated and eat a healthy diet to support your immune system. Avoid tight bras or clothing that can put pressure on the affected breast and worsen symptoms.
Seeking medical advice: If symptoms do not improve within a few days of starting antibiotics or if they worsen, it is important to seek medical advice. Your healthcare provider may need to adjust your treatment or recommend further tests to rule out any complications.
Remember, early detection and prompt treatment are key to successfully managing breast infections. If you suspect you have a breast infection, contact your healthcare provider for proper evaluation and treatment.
Prevention of Breast Infection
While breast infections can occur unexpectedly, there are certain preventive measures that you can take to reduce your risk:
| 1. Maintain Proper Breast Hygiene | Make sure to keep your breasts clean and dry. Cleanse them gently with mild soap and warm water. Avoid using harsh chemicals or perfumed products on your breasts as they can irritate the skin and potentially lead to an infection. |
| 2. Ensure Proper Latching During Breastfeeding | If you are breastfeeding, ensure that your baby is properly latched onto your breast during feeding. A poor latch can lead to milk stasis and increase the risk of infection. If you experience difficulties with latching, seek assistance from a lactation consultant or healthcare provider. |
| 3. Practice Regular Breastfeeding or Expression | If you are breastfeeding, establish a regular feeding schedule to prevent engorgement and milk stasis. If you are not breastfeeding, but are still producing milk, express the milk regularly to prevent milk build-up. This can be done manually or with the help of a breast pump. |
| 4. Treat Cracked Nipples Promptly | If you develop cracked or sore nipples while breastfeeding, address the issue promptly. Use lanolin or a nipple cream to soothe and heal the skin. Cracked nipples can provide an entry point for bacteria, increasing the risk of infection. |
| 5. Wear Comfortable and Supportive Bras | Choose bras that fit well and provide adequate support. Ill-fitting or tight bras can put pressure on the breasts and potentially lead to blocked milk ducts and infections. Opt for breathable materials, such as cotton, to promote air circulation. |
| 6. Avoid Unnecessary Breast Manipulation | Avoid unnecessary touching, squeezing, or massaging of your breasts. Excessive manipulation can disrupt the natural balance of the breast tissue and increase the risk of infection. |
| 7. Practice Good Overall Health | Maintain a healthy lifestyle by eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress. A strong immune system can help prevent infections, including breast infections. |
By following these preventive measures, you can reduce your risk of developing a breast infection. However, if you notice any symptoms or have concerns, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.