Pituitary adenoma of the brain in adults
Содержимое
Learn about pituitary adenoma, a type of brain tumor that occurs in adults. Discover the symptoms, diagnosis methods, treatment options, and potential complications associated with this condition.
Pituitary adenoma, also known as pituitary tumor, is a noncancerous growth that develops in the pituitary gland, a small pea-sized gland located at the base of the brain. This gland plays a crucial role in regulating various hormones that control many bodily functions. When a pituitary adenoma occurs in adults, it can cause a range of symptoms and complications.
Common symptoms of pituitary adenoma in adults include headaches, vision problems, hormonal imbalances, and changes in the menstrual cycle. Other symptoms may include fatigue, weight gain, infertility, and reduced libido. The specific symptoms experienced can vary depending on the size and location of the tumor, as well as the hormones it produces.
Diagnosing a pituitary adenoma usually involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, hormone level testing, and imaging tests such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT). These tests help determine the size and location of the tumor, as well as its effect on hormone production and nearby structures.
Treatment for pituitary adenoma depends on various factors, including the size and location of the tumor, as well as the symptoms and complications it causes. Options may include medication to regulate hormone levels, surgery to remove the tumor, radiation therapy to shrink or destroy the tumor cells, and hormone replacement therapy to manage hormone deficiencies caused by the tumor.
Pituitary Adenoma of the Brain: An Overview
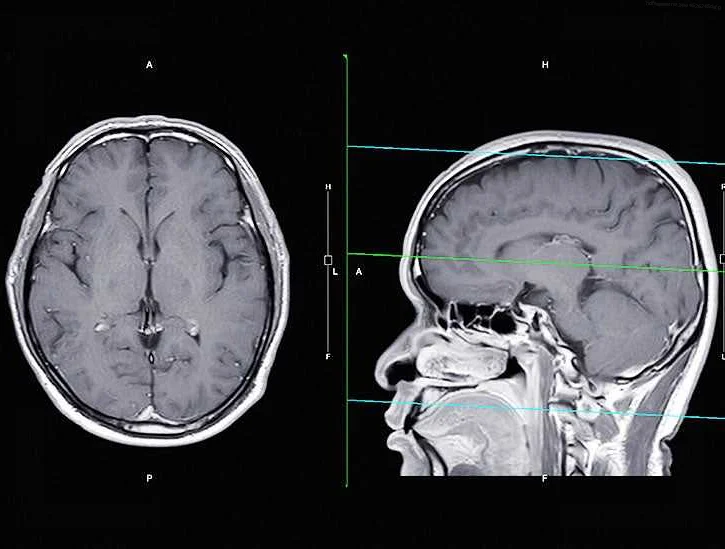
Pituitary adenoma is a common type of brain tumor that develops in the pituitary gland, a small gland located at the base of the brain. The pituitary gland plays a crucial role in regulating hormone production and is often referred to as the “master gland” of the body.
Although pituitary adenomas are generally benign, meaning they do not spread to other parts of the body, they can still cause significant health problems due to their size or hormone production. These tumors can result in excessive hormone production, leading to hormonal imbalances and various symptoms.
The exact cause of pituitary adenomas is still unknown, but certain risk factors have been identified, such as family history, certain genetic conditions, and certain endocrine disorders. In some cases, the use of hormone replacement therapy or exposure to radiation may also increase the risk of developing a pituitary adenoma.
Common symptoms of pituitary adenoma include headaches, vision problems, hormonal imbalances, and physical changes such as weight gain or loss. However, not all individuals with pituitary adenomas experience symptoms, and the size and location of the tumor can also influence the symptoms that occur.
Diagnosis of pituitary adenoma is typically made through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans. Blood tests may also be conducted to assess hormone levels and identify any hormonal imbalances.
Treatment options for pituitary adenoma depend on factors such as tumor size, symptoms, and hormone levels. In some cases, no immediate treatment is necessary, and the tumor is monitored through regular imaging tests and hormone level checks. If treatment is required, options may include medication, radiation therapy, or surgery to remove the tumor.
In conclusion, pituitary adenoma of the brain is a common type of brain tumor that can cause significant health problems due to its size or hormone production. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals with this condition.
Understanding Pituitary Adenoma
Pituitary adenoma is a common type of brain tumor that originates in the pituitary gland, a small pea-sized gland located at the base of the brain. This type of tumor is typically noncancerous, but it can still cause significant health problems due to its effects on hormone production and the pressure it puts on surrounding structures in the brain.
There are different types of pituitary adenomas, classified based on the hormones they produce. Some common types include:
- Prolactin-secreting adenomas: These tumors produce excessive amounts of prolactin, a hormone responsible for lactation in women.
- Growth hormone-secreting adenomas: These tumors produce too much growth hormone, leading to abnormal growth and development, known as acromegaly in adults.
- ACTH-secreting adenomas: These tumors produce adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which stimulates the adrenal glands to produce cortisol. Overproduction of cortisol leads to Cushing’s disease.
- Non-functioning adenomas: These tumors do not produce any hormones and are often discovered incidentally when imaging the brain for other reasons.
The signs and symptoms of pituitary adenoma can vary depending on the size and location of the tumor, as well as the hormones it produces. Common symptoms include:
- Headaches
- Vision problems
- Hormonal imbalances
- Infertility
- Loss of libido
- Fatigue
- Unexplained weight gain or loss
- Weakness
- Depression
Diagnosis of pituitary adenoma typically involves a combination of imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans, and hormone level measurements. Treatment options for pituitary adenoma include medication, radiation therapy, and surgery, depending on the size and type of the tumor, as well as the patient’s symptoms and overall health.
In conclusion, understanding pituitary adenoma is crucial for early detection and appropriate management of this common type of brain tumor. Recognizing the signs and symptoms, as well as the available treatment options, can help improve the outcomes for individuals affected by this condition.
Common Symptoms of Pituitary Adenoma in Adults
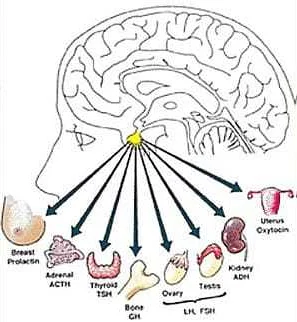
Pituitary adenoma is a type of tumor that develops in the pituitary gland, a small gland located at the base of the brain. This type of tumor is usually benign, but it can cause a variety of symptoms in adults. Here are some of the common symptoms associated with pituitary adenoma:
- Hormonal imbalances: Pituitary adenoma can disrupt the normal production and release of hormones by the pituitary gland. This can lead to symptoms such as excessive thirst and urination, fatigue, weight gain or loss, changes in menstrual cycle, infertility, and decreased libido.
- Headaches: Many adults with pituitary adenoma experience frequent headaches, which can range from mild to severe. These headaches are often persistent and can be accompanied by other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light and sound.
- Visual disturbances: As the pituitary tumor grows, it can compress the optic nerves or other structures in the brain, leading to visual problems. Some common visual disturbances associated with pituitary adenoma include double vision, blurry vision, loss of peripheral vision, and difficulty focusing.
- Fatigue and weakness: The hormonal imbalances caused by pituitary adenoma can also result in fatigue and weakness. Individuals may feel tired even after getting enough sleep and may have difficulty performing everyday tasks.
- Changes in body composition: Pituitary adenoma can affect the body’s metabolism, leading to changes in body composition. Some individuals may experience unexplained weight gain or loss, increased body fat, decreased muscle mass, and a decrease in bone density.
- Mood swings and emotional changes: Hormonal imbalances caused by pituitary adenoma can also affect a person’s mood and emotions. Some individuals may experience mood swings, irritability, depression, anxiety, and difficulty concentrating.
- Sexual dysfunction: Pituitary adenoma can disrupt normal reproductive function, leading to sexual dysfunction. This may include decreased libido, erectile dysfunction in men, and irregular menstrual periods or infertility in women.
- Other symptoms: Depending on the size and location of the tumor, pituitary adenoma may cause additional symptoms such as dizziness, memory problems, sleep disturbances, and changes in appetite.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and to discuss treatment options. Early detection and treatment of pituitary adenoma can help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Diagnosing Pituitary Adenoma in Adults
Diagnosing pituitary adenoma in adults involves a series of medical tests and evaluations to accurately identify and assess the presence of a tumor in the pituitary gland. The diagnostic process aims to determine the size, location, and functionality of the adenoma, as well as its potential effects on hormone production and overall health.
One of the primary diagnostic tools used is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which allows for detailed imaging of the brain and pituitary gland. An MRI scan can help visualize the size and location of the adenoma, as well as any potential compression of surrounding structures.
In addition to MRI, blood tests are typically conducted to measure hormone levels in the body. Pituitary adenomas can disrupt normal hormone production, leading to hormonal imbalances. Blood tests may include the measurement of hormones such as prolactin, growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, and follicle-stimulating hormone.
Visual field testing is another important diagnostic tool for pituitary adenoma. This test evaluates the peripheral vision and helps detect any vision loss or abnormalities caused by the tumor’s compression of the optic nerves.
If a pituitary adenoma is suspected, further evaluations may be performed, such as a neurological examination to assess signs of hormonal imbalance or neurological deficits. A thorough medical history review and physical examination are also crucial in the diagnostic process.
Once a pituitary adenoma has been diagnosed, additional tests may be conducted to determine the type of adenoma and its specific characteristics. These tests may include hormone stimulation tests, genetic testing, or biopsy.
Overall, diagnosing pituitary adenoma in adults requires comprehensive evaluation and a multidisciplinary approach involving neurologists, endocrinologists, and other specialists. The accurate diagnosis of pituitary adenoma plays a vital role in determining the most appropriate treatment options and ensuring optimal management of the condition.