Syncope: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Содержимое
Syncope is a temporary loss of consciousness usually caused by a lack of blood flow to the brain. This article provides an overview of syncope, its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options. Learn how to recognize and manage syncope episodes to ensure the safety and well-being of affected individuals.
Syncope, also known as fainting or passing out, is a temporary loss of consciousness typically caused by a temporary decrease in blood flow to the brain. It is a common condition that affects people of all ages and can be caused by various factors.
There are several potential causes of syncope, including cardiovascular conditions such as heart rhythm abnormalities, heart valve problems, or low blood pressure. Other factors that can lead to syncope include dehydration, medications, excessive heat, emotional stress, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes or seizures.
Symptoms of syncope can vary but often include a sudden loss of consciousness, pale skin, lightheadedness, confusion, and feeling weak or dizzy. It is important to note that syncope can be a sign of an underlying health issue and should not be ignored.
Treatment for syncope depends on the underlying cause and may include lifestyle changes, medication adjustments, or surgical interventions. It is crucial to seek medical attention if you experience syncope episodes, as proper diagnosis and treatment can help prevent future fainting episodes and manage any underlying health conditions.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for syncope. We will also provide tips on how to prevent syncope and when to seek medical attention. Understanding this condition can empower you to take control of your health and ensure your well-being.
Syncope: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Syncope, also known as fainting, is a temporary loss of consciousness caused by a lack of blood flow to the brain. It can be a symptom of an underlying medical condition or a result of certain triggers. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment of syncope is crucial for proper management and prevention of future episodes.
Causes:
Syncope can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Neurocardiogenic syncope: This is the most common form of syncope and is often triggered by emotional stress, pain, or sudden changes in body position.
- Cardiac syncope: This type of syncope is caused by an abnormal heart rhythm or other heart-related problems, such as heart valve disorders or heart attacks.
- Orthostatic hypotension: A sudden drop in blood pressure upon standing can lead to syncope. This can occur due to dehydration, medications, or as a result of certain medical conditions.
- Vasovagal syncope: This type of syncope is triggered by a reflex that causes the blood vessels to widen, leading to a sudden drop in blood pressure.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of syncope can vary but often include:
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Blurred vision or tunnel vision
- Paleness or sweating
- Nausea or vomiting
- Feeling weak or unsteady
Treatment:
The treatment of syncope depends on the underlying cause. In some cases, simple lifestyle changes can help prevent future episodes. These may include:
- Staying hydrated
- Avoiding triggers, such as extreme heat or stressful situations
- Wearing compression stockings to improve blood flow
- Medications to regulate blood pressure or heart rhythm
- Surgery or other interventions for specific heart conditions
If you experience syncope, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and discuss appropriate treatment options. Syncope can be a sign of a more serious underlying condition, so prompt evaluation is crucial for your health and well-being.
Understanding Syncope: A Brief Overview
Syncope, also known as fainting or passing out, is a temporary loss of consciousness caused by a decrease in blood flow to the brain. It is a common medical condition that can occur in people of all ages and can have various underlying causes. Understanding the basics of syncope can help individuals recognize its symptoms and seek appropriate medical attention.
There are several types of syncope, including vasovagal syncope, reflex syncope, and orthostatic hypotension. Vasovagal syncope is the most common type and is typically triggered by emotional stress, pain, or standing for long periods. Reflex syncope is caused by certain triggers, such as coughing, swallowing, or urinating. Orthostatic hypotension occurs when a drop in blood pressure happens upon standing or changing positions.
The symptoms of syncope may vary, but the most common ones include feeling lightheaded, dizzy, or nauseous before losing consciousness. Some individuals may experience blurred vision, sweating, and a slow pulse. After regaining consciousness, people often feel confused, weak, and tired.
It is crucial to determine the underlying cause of syncope as it can be a sign of an underlying medical condition. Common causes include dehydration, low blood sugar, heart problems, medication side effects, and neurological disorders. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional to receive a proper diagnosis and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment for syncope depends on its underlying cause. In some cases, lifestyle modifications such as staying hydrated, avoiding triggers, and standing up slowly can help prevent episodes of syncope. Medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms or address underlying conditions. In more severe cases, medical procedures or surgery may be necessary.
In conclusion, syncope is a temporary loss of consciousness caused by a decrease in blood flow to the brain. It is important to recognize the symptoms and seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment. By understanding syncope, individuals can take steps to manage and prevent future episodes.
Common Causes of Syncope
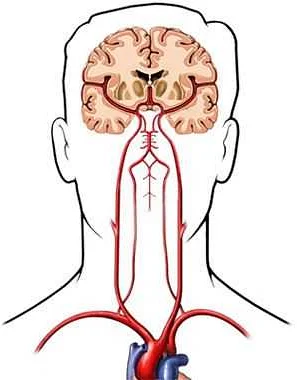
Syncope, also known as fainting or passing out, can occur for various reasons. While syncope itself is not usually harmful, it can be a sign of an underlying medical condition. Here are some common causes of syncope:
1. Vasovagal Syncope: This is the most common type of syncope and is often triggered by emotional stress, pain, or standing for long periods. It occurs when the body overreacts to certain triggers, leading to a sudden drop in blood pressure and heart rate.
2. Cardiac Syncope: In some cases, syncope may be caused by a problem with the heart, such as an arrhythmia or a structural issue. When the heart does not pump an adequate amount of blood to the brain, fainting can occur.
3. Neurological Syncope: Conditions that affect the nervous system, such as epilepsy or Parkinson’s disease, can also lead to syncope. These conditions can disrupt the normal functioning of the autonomic nervous system, which controls blood pressure and heart rate.
4. Medications: Certain medications, such as blood pressure medications, can cause syncope as a side effect. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider if you experience fainting while taking any medication.
5. Hypoglycemia: Low blood sugar levels can cause syncope, especially in individuals with diabetes. When blood sugar levels drop too low, the brain may not receive enough glucose to function properly, leading to fainting.
6. Dehydration: Severe dehydration can cause syncope due to a drop in blood volume and low blood pressure. It is important to stay hydrated, especially in hot weather or during strenuous physical activity.
7. Anemia: Anemia, a condition characterized by low red blood cell count, can lead to syncope. When there are not enough red blood cells to carry oxygen to the brain, fainting can occur.
8. Other Causes: Other potential causes of syncope include hyperventilation, heart valve disorders, and certain genetic conditions.
If you experience syncope, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment. While syncope can be unexpected and alarming, understanding the common causes can help you take steps to prevent future episodes.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Syncope
Syncope, also known as fainting, is a temporary loss of consciousness that is caused by a lack of blood flow to the brain. It is a common condition that can occur in people of all ages and can be caused by various factors.
Recognizing the symptoms of syncope is crucial in order to provide the necessary medical attention and prevent any further complications. Here are some common symptoms to look out for:
Dizziness: Feeling lightheaded or dizzy is often one of the first signs of an impending syncope episode. It may be accompanied by a spinning sensation or feeling unsteady on your feet.
Blurred Vision: Many people experience blurred or tunnel vision, where their sight becomes hazy or they lose their peripheral vision. This can be a warning sign that syncope is about to occur.
Pale Skin: A sudden pallor or paleness of the skin can occur due to the decreased blood flow to the brain. This is often noticeable in the face, but it can affect other parts of the body as well.
Rapid Heartbeat: An increased heart rate, also known as tachycardia, is a common symptom of syncope. It can be felt as palpitations or a pounding sensation in the chest.
Feeling Nauseous: Nausea or an upset stomach is another symptom that may precede a syncope episode. Some people may also experience sweating or clamminess.
Loss of Consciousness: The ultimate symptom of syncope is fainting or losing consciousness. This can happen suddenly and without warning. It is important to note that not all cases of fainting are due to syncope, but it should be considered as a possibility.
If you or someone around you experiences any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. A healthcare professional can evaluate the symptoms and determine the underlying cause of the syncope episode. Remember, early recognition and treatment can help prevent further complications and ensure the well-being of the individual affected by syncope.